Elastic Beanstalk + VPC integration
What’s a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)? A VPC is your own private data center in the cloud: You control the IP range, subnets, routing, firewalls (Security Groups & NACLs). You can run Elastic Beanstalk inside your VPC, so your app isn’t publicly exposed (unless you want it to be). Useful for private APIs, secure database access (RDS), or hybrid cloud setups. How to Deploy Elastic Beanstalk into a Custom VPC Step 1: Create Your VPC Use VPC wizard or manual setup: 1 VPC (e.g., 10.0.0.0/16) 2 Public subnets (for load balancer) 2 Private subnets (for EC2 instances) Internet Gateway (for public access) NAT Gateway (for internet from private subnets) Route Tables for each Tip: Keep EC2 instances in private subnets for security, expose only the ALB in public subnet. Step 2: Tag Your Subnets Tag your subnets so Beanstalk can find them: Key: elasticbeanstalk:environment-type Value: LoadBalanced Step 3: Create Elastic Beanstalk App in the VPC eb init -p python-3.8 my-secure-app eb create my-secure-env \ --vpc \ --vpc.id vpc-xxxxxxxx \ --vpc.publicip \ --vpc.elbpublic \ --vpc.ec2subnets subnet-private-a,subnet-private-b \ --vpc.elbsubnets subnet-public-a,subnet-public-b --vpc.elbpublic: Makes load balancer public --vpc.publicip: Assigns public IP to EC2 (optional) --vpc.ec2subnets: List your private subnets --vpc.elbsubnets: List your public subnets Step 4: Confirm Security Group Access Your EC2 security group must allow: Inbound HTTP/HTTPS from ELB Outbound to internet (via NAT) If using RDS, allow inbound from the Beanstalk SG Sample eb config Output You can verify your settings: eb config Use Case Scenarios Use Case Why VPC Matters? RDS database Private subnet access only Internal APIs Block external exposure Custom routing/NAT Control egress traffic Hybrid architecture Connect on-prem to cloud
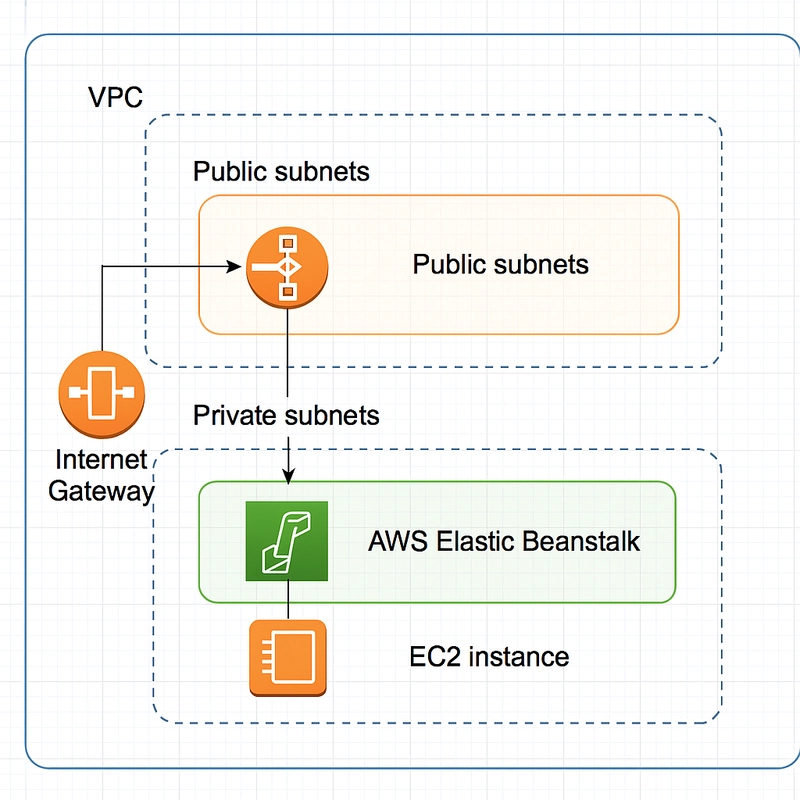
What’s a VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)?
A VPC is your own private data center in the cloud:
- You control the IP range, subnets, routing, firewalls (Security Groups & NACLs).
- You can run Elastic Beanstalk inside your VPC, so your app isn’t publicly exposed (unless you want it to be).
- Useful for private APIs, secure database access (RDS), or hybrid cloud setups.
How to Deploy Elastic Beanstalk into a Custom VPC
Step 1: Create Your VPC
Use VPC wizard or manual setup:
- 1 VPC (e.g.,
10.0.0.0/16) - 2 Public subnets (for load balancer)
- 2 Private subnets (for EC2 instances)
- Internet Gateway (for public access)
- NAT Gateway (for internet from private subnets)
- Route Tables for each
Tip: Keep EC2 instances in private subnets for security, expose only the ALB in public subnet.
Step 2: Tag Your Subnets
Tag your subnets so Beanstalk can find them:
Key: elasticbeanstalk:environment-type
Value: LoadBalanced
Step 3: Create Elastic Beanstalk App in the VPC
eb init -p python-3.8 my-secure-app
eb create my-secure-env \
--vpc \
--vpc.id vpc-xxxxxxxx \
--vpc.publicip \
--vpc.elbpublic \
--vpc.ec2subnets subnet-private-a,subnet-private-b \
--vpc.elbsubnets subnet-public-a,subnet-public-b
-
--vpc.elbpublic: Makes load balancer public -
--vpc.publicip: Assigns public IP to EC2 (optional) -
--vpc.ec2subnets: List your private subnets -
--vpc.elbsubnets: List your public subnets
Step 4: Confirm Security Group Access
- Your EC2 security group must allow:
- Inbound HTTP/HTTPS from ELB
- Outbound to internet (via NAT)
- If using RDS, allow inbound from the Beanstalk SG
Sample eb config Output
You can verify your settings:
eb config
Use Case Scenarios
| Use Case | Why VPC Matters? |
|---|---|
| RDS database | Private subnet access only |
| Internal APIs | Block external exposure |
| Custom routing/NAT | Control egress traffic |
| Hybrid architecture | Connect on-prem to cloud |








































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)































































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)






































































































.png?#)






(1).jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)






























_NicoElNino_Alamy.png?#)
.webp?#)
.webp?#)

































































































![Apple to Source More iPhones From India to Offset China Tariff Costs [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96954/96954/96954-640.jpg)
![Blackmagic Design Unveils DaVinci Resolve 20 With Over 100 New Features and AI Tools [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96951/96951/96951-640.jpg)