Data Acquisition Methods
The IDC reports show that the data will cross 174 zettabytes by 2025 worldwide. Over the last two years, 90% of the world's data has been created (Forbes). We are drowning in data, but millions of organizations can't extract insights from it. The ability of data depends on how the data is collected, processed, and analyzed. Data Acquisition (DAQ) does that. What Is Data Acquisition? Data acquisition is the process of collecting and digitizing real-world information for analysis. It involves hardware and software that capture signals, process inputs, and convert data into a usable format. Whether it’s monitoring cybersecurity threats, collecting forensic evidence, or analyzing business metrics, an efficient data acquisition methodology ensures accuracy, integrity, and usability. Key Components of Data Acquisition To have a strong data acquisition system, you need to understand various core components. 1.Sensors and Transducers: Convert physical phenomena (temperature, voltage, motion) into measurable signals for further processing. 2. Signal Conditioning: Signal conditioning refers to modifying the signal so that it can be used for accurate measurement. 3. Data Converters: Convert analog signals into digital form for processing. 4. Processing Units: Analyze and store data, often using software-driven systems. 5. Storage and Transmission: Securely store data for real-time or later use, ensuring compliance with standards. Types of Data Acquisition Methods Different industries need different methods of data acquisition. Here are some of the most widely used methodologies. 1. Manual Data Acquisition ● Old-school but sometimes necessary. In systematic investigations, human reasoning is required to process logs and draw conclusions. ● May fail, but very useful for situations that need expert help. 2. Automated Data Acquisition ● Employs computer-controlled systems to gather and analyze large data sets in real-time. ● Perfect for fields such as cyber security, finance, and scientific research where accuracy and speed are paramount. 3. Network-Based Acquisition ● Network traffic capture, log analysis, and anomaly detection are common in incident response. ● Used in cybersecurity monitoring tools like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems. 4. Cloud-Based Data Acquisition ● More organizations are adopting cloud storage and services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to improve scalability. ● It provides flexibility, but there are issues with privacy and compliance. 5. Forensic Data Acquisition ● Used in digital investigations to gather evidence from computers, phones, and networks. ● Must ensure the integrity of data with the help of Forensic tools like EnCase and Autopsy. Best Practices for Effective Data Acquisition A flawed data acquisition process leads to bad data, bad decisions, and costly mistakes. Here’s how to do it right: ● Ensure Data Integrity: Use cryptographic hashing and forensic tools to maintain authenticity. ● Automate Where Possible: Reduces human errors and speeds up data processing. ● Secure Data from the Start: Implement encryption and access controls to protect sensitive information. ● Follow Compliance Standards: GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations demand proper data handling. ● Use Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous data acquisition allows for proactive decision-making rather than reactive firefighting. DFIR with InfosecTrain The way you acquire and handle data directly impacts the quality of insights and the security of information. Whether you’re in forensics, business intelligence, or cybersecurity, a well-structured data acquisition methodology helps streamline operations, reduce risks, and make data-driven decisions with confidence. Get it right, and you’ll gain a competitive edge. Get it wrong, and you’ll be chasing bad data forever. If you're serious about mastering Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR), InfosecTrain's DFIR training equips you with hands-on expertise in data acquisition, forensic investigation, and cybersecurity threat response. Learn from industry veterans, gain practical skills, and stay ahead in the ever-evolving field of cybersecurity. Take the next step in your career—enroll today!

The IDC reports show that the data will cross 174 zettabytes by 2025 worldwide. Over the last two years, 90% of the world's data has been created (Forbes). We are drowning in data, but millions of organizations can't extract insights from it. The ability of data depends on how the data is collected, processed, and analyzed. Data Acquisition (DAQ) does that.
What Is Data Acquisition?
Data acquisition is the process of collecting and digitizing real-world information for analysis. It involves hardware and software that capture signals, process inputs, and convert data into a usable format. Whether it’s monitoring cybersecurity threats, collecting forensic evidence, or analyzing business metrics, an efficient data acquisition methodology ensures accuracy, integrity, and usability.
Key Components of Data Acquisition
To have a strong data acquisition system, you need to understand various core components.
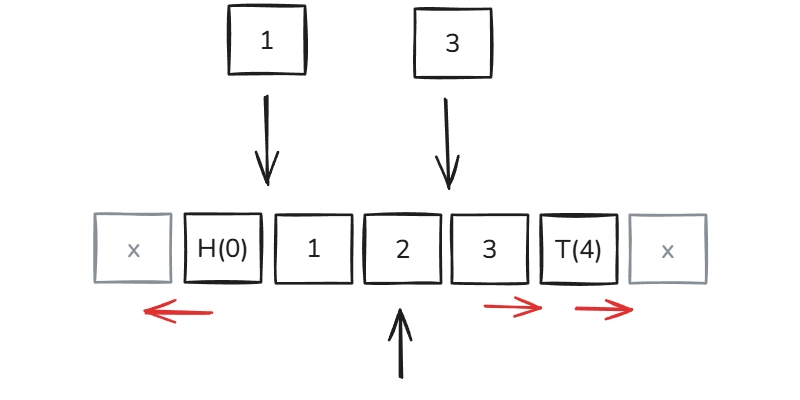
1.Sensors and Transducers: Convert physical phenomena (temperature, voltage, motion) into measurable signals for further processing.
2. Signal Conditioning: Signal conditioning refers to modifying the signal so that it can be used for accurate measurement.
3. Data Converters: Convert analog signals into digital form for processing.
4. Processing Units: Analyze and store data, often using software-driven systems.
5. Storage and Transmission: Securely store data for real-time or later use, ensuring compliance with standards.
Types of Data Acquisition Methods
Different industries need different methods of data acquisition. Here are some of the most widely used methodologies.
1. Manual Data Acquisition
● Old-school but sometimes necessary. In systematic investigations, human reasoning is required to process logs and draw conclusions.
● May fail, but very useful for situations that need expert help.
2. Automated Data Acquisition
● Employs computer-controlled systems to gather and analyze large data sets in real-time.
● Perfect for fields such as cyber security, finance, and scientific research where accuracy and speed are paramount.
3. Network-Based Acquisition
● Network traffic capture, log analysis, and anomaly detection are common in incident response.
● Used in cybersecurity monitoring tools like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems.
4. Cloud-Based Data Acquisition
● More organizations are adopting cloud storage and services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to improve scalability.
● It provides flexibility, but there are issues with privacy and compliance.
5. Forensic Data Acquisition
● Used in digital investigations to gather evidence from computers, phones, and networks.
● Must ensure the integrity of data with the help of Forensic tools like EnCase and Autopsy.
Best Practices for Effective Data Acquisition
A flawed data acquisition process leads to bad data, bad decisions, and costly mistakes. Here’s how to do it right:
● Ensure Data Integrity: Use cryptographic hashing and forensic tools to maintain authenticity.
● Automate Where Possible: Reduces human errors and speeds up data processing.
● Secure Data from the Start: Implement encryption and access controls to protect sensitive information.
● Follow Compliance Standards: GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations demand proper data handling.
● Use Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous data acquisition allows for proactive decision-making rather than reactive firefighting.
DFIR with InfosecTrain
The way you acquire and handle data directly impacts the quality of insights and the security of information. Whether you’re in forensics, business intelligence, or cybersecurity, a well-structured data acquisition methodology helps streamline operations, reduce risks, and make data-driven decisions with confidence. Get it right, and you’ll gain a competitive edge. Get it wrong, and you’ll be chasing bad data forever.
If you're serious about mastering Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR), InfosecTrain's DFIR training equips you with hands-on expertise in data acquisition, forensic investigation, and cybersecurity threat response. Learn from industry veterans, gain practical skills, and stay ahead in the ever-evolving field of cybersecurity.
Take the next step in your career—enroll today!


.jpg)




































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)












































































































































































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)





















![Blue Archive tier list [April 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33404-1636469504/blue-archive-screenshot-2.jpg?#)


































.png?#)





































.webp?#)








































































































![Apple to Split Enterprise and Western Europe Roles as VP Exits [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97032/97032/97032-640.jpg)
![Nanoleaf Announces New Pegboard Desk Dock With Dual-Sided Lighting [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97030/97030/97030-640.jpg)

![Apple's Foldable iPhone May Cost Between $2100 and $2300 [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97028/97028/97028-640.jpg)