CISA Warns of Windows NTFS Vulnerability Actively Exploited to Access Sensitive Data
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) escalated its cybersecurity alert, by adding six critical Microsoft Windows vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, with four directly impacting the New Technology File System (NTFS). These flaws CVE-2025-24984, CVE-2025-24991, CVE-2025-24993, and CVE-2021-31956 enable attackers to access sensitive data, execute arbitrary code, or escalate privileges, posing […] The post CISA Warns of Windows NTFS Vulnerability Actively Exploited to Access Sensitive Data appeared first on Cyber Security News.

The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) escalated its cybersecurity alert, by adding six critical Microsoft Windows vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, with four directly impacting the New Technology File System (NTFS).
These flaws CVE-2025-24984, CVE-2025-24991, CVE-2025-24993, and CVE-2021-31956 enable attackers to access sensitive data, execute arbitrary code, or escalate privileges, posing systemic risks to federal and private networks alike.
All the vulnerabilities are fix at Microsoft Patch Tuesday March 2025 that has been released earlier today.
Overview of Windows NTFS Vulnerabilities
CVE-2025-24984: NTFS Information Disclosure Vulnerability
This vulnerability (CVSS 4.6) allows local attackers with physical access to insert sensitive data into log files, potentially exposing heap memory contents.
By leveraging removable media like malicious USB drives, adversaries could extract credentials or system configuration details stored in memory.
The weakness stems from improper logging practices within NTFS, classified under CWE-532: Insertion of Sensitive Information into Log File.
CVE-2025-24991: NTFS Out-of-Bounds Read Vulnerability
Rated 5.5 on the CVSS scale, this flaw enables unauthorized users to perform out-of-bounds reads (CWE-125) by mounting a specially crafted Virtual Hard Disk (VHD).
Successful exploitation bypasses access controls, leaking file structures or uninitialized memory fragments that could aid in lateral movement.
Microsoft confirmed anonymous reporting of this vulnerability, noting its exploitation in limited, targeted attacks.
CVE-2025-24993: NTFS Heap-Based Buffer Overflow
With a CVSS score of 7.8, this heap-based buffer overflow (CWE-122) permits local attackers to execute arbitrary code by tricking users into mounting a malicious VHD.
The overflow corrupts memory structures, enabling privilege escalation to SYSTEM-level access—a critical vector for ransomware deployment.
CISA emphasized its active exploitation in attacks leveraging multi-staged payloads.
CVE-2021-31956 : NTFS Privilege Escalation Vulnerability
CVE-2021-31956 stems from a heap-based buffer overflow in the NtfsQueryEaUserEaList function of ntfs.sys, the Windows NTFS driver.
The flaw arises during the processing of Extended Attributes (EAs), where improper validation of user-supplied buffer sizes enables integer underflows.
Successful exploitation allows attackers to escalate privileges via a specially crafted application.
Attack Methodology and Observed Exploitation Patterns
Adversaries chain these vulnerabilities to compromise networks. For example:
Initial Access: Social engineering campaigns distribute VHD files disguised as legitimate documents.
Data Exfiltration: CVE-2025-24984 extracts credentials from memory logs, while CVE-2025-24991 maps network file systems.
Privilege Escalation: CVE-2025-24993,CVE-2021-31956 grants administrative rights, enabling persistence mechanisms or ransomware deployment.
Trend Micro researchers observed over 600 organizations targeted via malicious Microsoft Management Console (MMC) files exploiting CVE-2025-26633, another KEV-listed flaw often paired with NTFS vulnerabilities.
Mitigation Strategies
CISA mandates federal agencies to remediate these vulnerabilities by April 1, 2025, under Binding Operational Directive (BOD) 22-01. Recommended actions include:
Patch Management: Deploy Microsoft’s March 2025 Patch Tuesday updates immediately, addressing 67 vulnerabilities, including seven zero-days.
Network Segmentation: Isolate legacy systems running Windows Server 2008 or unsupported FAT32 drivers.
User Education: Train employees to recognize phishing attempts distributing malicious VHD/MSC files
As CISA Director Jen Easterly noted, “These vulnerabilities are not theoretical—they are actively being weaponized.”
The convergence of NTFS flaws with privilege escalation vectors like CVE-2025-24983 (Win32k use-after-free) creates a perfect storm for enterprise breaches, demanding urgent action.
In an era where file system vulnerabilities comprise 23% of KEV entries, the March 2025 advisories serve as a stark reminder: patch, segment, and verify—before attackers exploit the gaps.
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams? – Analyse Malware Incidents & get live Access with ANY.RUN -> Start Now for Free.
The post CISA Warns of Windows NTFS Vulnerability Actively Exploited to Access Sensitive Data appeared first on Cyber Security News.










































































































































































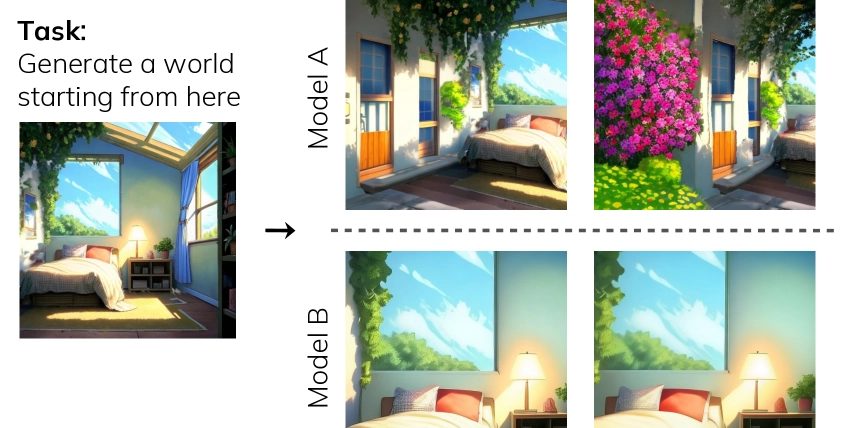
![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)










































































































































































































































.jpg?#)












































































































































![YouTube Announces New Creation Tools for Shorts [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96923/96923/96923-640.jpg)

![Apple Faces New Tariffs but Has Options to Soften the Blow [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96921/96921/96921-640.jpg)