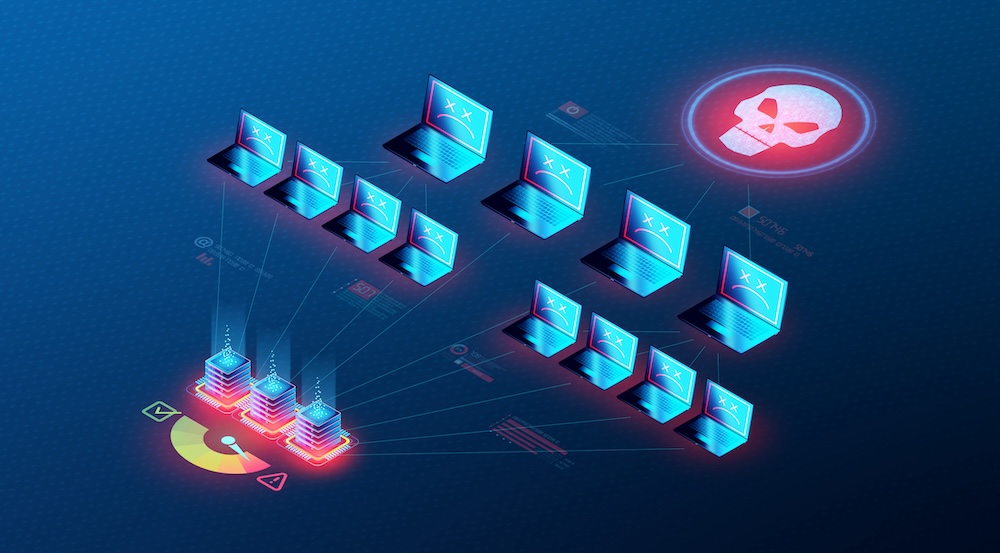
Chinese Hackers Actively Exploiting Ivanti VPN Vulnerability to Deploy Malware
Security researchers have identified a critical vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure (ICS) VPN appliances that is being actively exploited by suspected Chinese threat actors. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-22457, is a buffer overflow flaw affecting ICS version 22.7R2.5 and earlier that can lead to remote code execution. Evidence suggests exploitation began in mid-March 2025, with […] The post Chinese Hackers Actively Exploiting Ivanti VPN Vulnerability to Deploy Malware appeared first on Cyber Security News.

Security researchers have identified a critical vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure (ICS) VPN appliances that is being actively exploited by suspected Chinese threat actors.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-22457, is a buffer overflow flaw affecting ICS version 22.7R2.5 and earlier that can lead to remote code execution.
Evidence suggests exploitation began in mid-March 2025, with attackers leveraging the vulnerability to deploy sophisticated malware strains designed for espionage operations.
The attacks have been attributed to UNC5221, a suspected China-nexus espionage actor with a history of targeting edge devices through zero-day exploitations dating back to 2023.
This group has demonstrated sophisticated capabilities, including the ability to reverse-engineer security patches to develop working exploits.
In this campaign, they likely studied the February 2025 patch for ICS 22.7R2.6 to develop their attack methodology.
Google Threat Intelligence analysts identified that following successful exploitation, the threat actors deploy multiple malware families, including two newly discovered tools – TRAILBLAZE and BRUSHFIRE – alongside their previously documented SPAWN ecosystem of malware.
These tools work in concert to establish persistent access while evading detection mechanisms.
The vulnerability’s exploitation represents a concerning evolution in UNC5221’s tactics, as they transition from exclusively using zero-day vulnerabilities to also leveraging n-day flaws in their arsenal.
According to security researchers, the group targets a wide range of countries and vertical sectors, demonstrating an aggressive operational tempo and extensive toolset.
Post-Exploitation Tactics
After successfully exploiting the vulnerability, attackers deploy a sophisticated attack chain starting with a shell script dropper.
This initial script executes TRAILBLAZE, an in-memory dropper written in bare C using raw syscalls, designed to be minimal and stealthy.
TRAILBLAZE then injects the BRUSHFIRE passive backdoor into a running /home/bin/web process.
The infection process creates several temporary files that store information about the target process, including:-
/tmp/.p: contains the PID of the /home/bin/web process
/tmp/.m: contains a memory map of that process
/tmp/.w: contains the base address of the web binary
/tmp/.s: contains the base address of libssl.so
/tmp/.r: contains the BRUSHFIRE passive backdoor
/tmp/.i: contains the TRAILBLAZE dropperBRUSHFIRE operates by hooking the SSL_read function, allowing it to intercept encrypted communications.
When specific trigger strings are detected, it decrypts and executes shellcode contained in the intercepted data, sending results back through SSL_write.
This sophisticated technique enables attackers to maintain a persistent presence while minimizing detection risk, as they operate entirely in memory without writing malicious files to disk.
Security experts recommend organizations immediately upgrade affected Ivanti Connect Secure appliances to version 22.7R2.6 or later and utilize the Integrity Checker Tool to identify any suspicious activity.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links & Phishing Attacks With Threat Intelligence Lookup - Try 50 Request for Free
The post Chinese Hackers Actively Exploiting Ivanti VPN Vulnerability to Deploy Malware appeared first on Cyber Security News.





















































.jpg)
%20Abstract%20Background%20112024%20SOURCE%20Amazon.jpg)


















































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)































































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)
















































.png?#)


























































































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)










































































































![Rapidus in Talks With Apple as It Accelerates Toward 2nm Chip Production [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96937/96937/96937-640.jpg)





































































































































