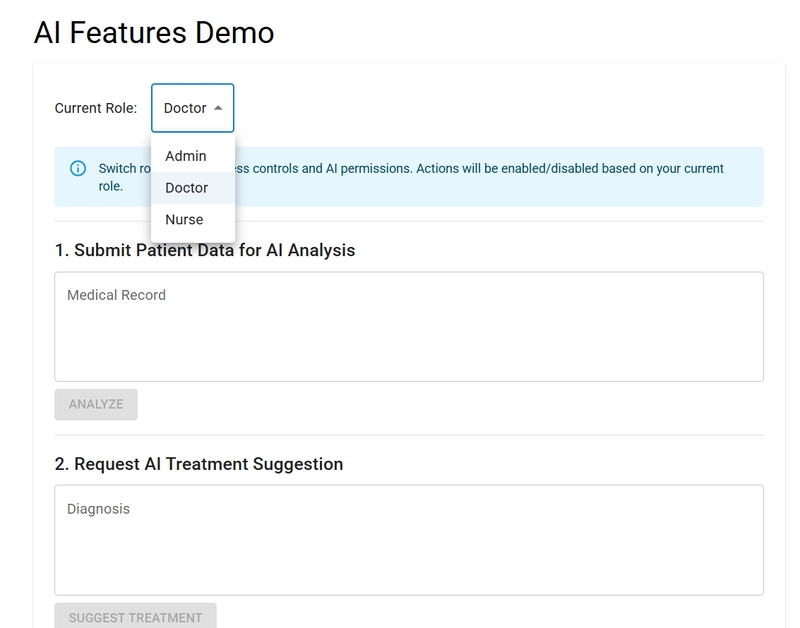
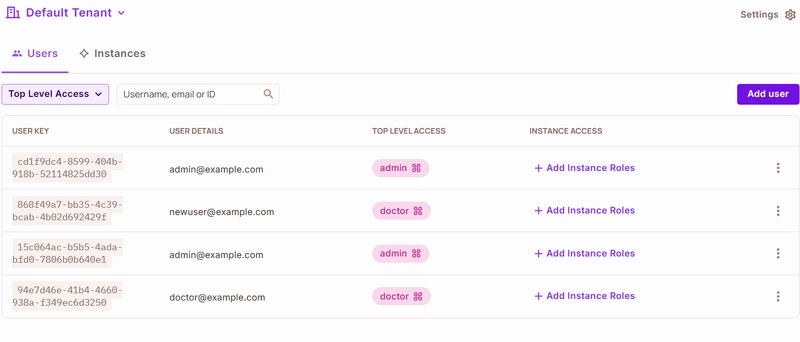
AICHA: AI-Powered Healthcare Assistant with Permit.io Authorization
This is a submission for the Permit.io Authorization Challenge: AI Access Control What is AICHA? AICHA (AI-powered Healthcare Assistant) is a modern healthcare management platform that uses artificial intelligence to help doctors, nurses, and administrators deliver better care. With features like AI-driven medical analysis, treatment suggestions, and secure patient data management, AICHA is designed to make healthcare smarter and safer. But with great power comes great responsibility—especially when it comes to sensitive medical data and AI features. That's why AICHA uses Permit.io for fine-grained, externalized authorization, ensuring that only the right people can access the right features at the right time. How AICHA Leverages Permit.io, Gemini AI, and Supabase. Permit.io Integration: Permit.io is the backbone of AICHA's access control and security. Every time a user logs in or tries to use a feature (like running Gemini AI analysis or viewing patient data), AICHA checks with Permit.io to see if they're allowed. All access policies (who can do what, when, and where) are managed centrally in Permit.io, not scattered in the code. User roles and permissions are synced from Supabase to Permit.io, so changes are reflected instantly. Permit.io logs every permission check and action for auditing and compliance. This means: Only doctors in the right department can run Gemini AI analysis on their patients Nurses can view results but not run or approve AI features Admins can manage everything, but all actions are tracked Permit.io makes it easy to update policies (like restricting AI use to working hours) without changing any code—just update the policy in the dashboard. Gemini AI Integration: AICHA uses Google Gemini AI to power its medical analysis and treatment suggestion features. Doctors can submit patient data for analysis, and Gemini provides: Disease risk predictions AI-generated treatment recommendations Natural language explanations for results Gemini's advanced language and reasoning capabilities help make AI suggestions more accurate and explainable for medical staff. All AI-powered actions are protected by Permit.io policies, so only authorized users can access Gemini features. Supabase Integration: Supabase is used as the backend database for AICHA. It stores: User accounts and roles Patient records Audit logs of all actions (including Permit.io permission checks) Supabase's real-time features help keep user data and permissions in sync with Permit.io. When users are created or updated in Supabase, they are automatically synced to Permit.io for up-to-date access control. Key Features of AICHA (and Who Gets to Use Them) AICHA is built for different types of users, each with their own set of features: Administrators Full access to all patient records and system settings Manage users and roles Approve or audit AI analysis and treatments Doctors Run AI-powered medical analysis on patient data Suggest and approve treatments View and update patient records Nurses View patient records and AI analysis results Monitor patient vitals Patients (optional/future) View their own health records and AI-generated reports How does AICHA make sure only the right people can do these things? That's where Permit.io comes in! Every action—like running an AI analysis or viewing a patient record—is checked against Permit.io's policies before it happens. This means: Doctors can't approve treatments for patients outside their department Nurses can't run AI analysis, but can view results Admins can do everything, but every action is logged for compliance Why Permit.io? (vs. Traditional Authorization) Traditionally, access control is hard-coded into the app. This means: Authorization logic is scattered everywhere Changing permissions means changing code (and redeploying) It's easy to miss a check, leading to security holes Auditing who did what is a pain With Permit.io (externalized authorization): All policies are managed in one place (the Permit.io dashboard or config) You can update permissions instantly—no code changes needed Every access check is logged automatically It's easy to create complex, context-aware rules (like department-based or time-based access) Example: Want to let doctors run AI analysis only during working hours? Just update the policy in Permit.io—no code changes required! How AICHA Leverages Permit.io (In Simple Terms) Role-Based Access: Each user is assigned a role (admin, doctor, nurse) and only sees features they're allowed to use. Context-Aware Policies: Access can depend on department, time of day, or even the type of AI analysis. User Management: Users are synced from our database to Permit.io, so roles and permissions are always up to date. Real-Time Checks: Every time a user tries to do something importan

This is a submission for the Permit.io Authorization Challenge: AI Access Control
What is AICHA?
AICHA (AI-powered Healthcare Assistant) is a modern healthcare management platform that uses artificial intelligence to help doctors, nurses, and administrators deliver better care. With features like AI-driven medical analysis, treatment suggestions, and secure patient data management, AICHA is designed to make healthcare smarter and safer.
But with great power comes great responsibility—especially when it comes to sensitive medical data and AI features. That's why AICHA uses Permit.io for fine-grained, externalized authorization, ensuring that only the right people can access the right features at the right time.
How AICHA Leverages Permit.io, Gemini AI, and Supabase.
Permit.io Integration:
- Permit.io is the backbone of AICHA's access control and security.
- Every time a user logs in or tries to use a feature (like running Gemini AI analysis or viewing patient data), AICHA checks with Permit.io to see if they're allowed.
- All access policies (who can do what, when, and where) are managed centrally in Permit.io, not scattered in the code.
- User roles and permissions are synced from Supabase to Permit.io, so changes are reflected instantly.
- Permit.io logs every permission check and action for auditing and compliance.
- This means:
- Only doctors in the right department can run Gemini AI analysis on their patients
- Nurses can view results but not run or approve AI features
- Admins can manage everything, but all actions are tracked
- Permit.io makes it easy to update policies (like restricting AI use to working hours) without changing any code—just update the policy in the dashboard.
Gemini AI Integration:
- AICHA uses Google Gemini AI to power its medical analysis and treatment suggestion features.
- Doctors can submit patient data for analysis, and Gemini provides:
- Disease risk predictions
- AI-generated treatment recommendations
- Natural language explanations for results
- Gemini's advanced language and reasoning capabilities help make AI suggestions more accurate and explainable for medical staff.
- All AI-powered actions are protected by Permit.io policies, so only authorized users can access Gemini features.
Supabase Integration:
- Supabase is used as the backend database for AICHA.
- It stores:
- User accounts and roles
- Patient records
- Audit logs of all actions (including Permit.io permission checks)
- Supabase's real-time features help keep user data and permissions in sync with Permit.io.
- When users are created or updated in Supabase, they are automatically synced to Permit.io for up-to-date access control.
Key Features of AICHA (and Who Gets to Use Them)
AICHA is built for different types of users, each with their own set of features:
-
Administrators
- Full access to all patient records and system settings
- Manage users and roles
- Approve or audit AI analysis and treatments
-
Doctors
- Run AI-powered medical analysis on patient data
- Suggest and approve treatments
- View and update patient records
-
Nurses
- View patient records and AI analysis results
- Monitor patient vitals
-
Patients (optional/future)
- View their own health records and AI-generated reports
How does AICHA make sure only the right people can do these things?
That's where Permit.io comes in! Every action—like running an AI analysis or viewing a patient record—is checked against Permit.io's policies before it happens. This means:
- Doctors can't approve treatments for patients outside their department
- Nurses can't run AI analysis, but can view results
- Admins can do everything, but every action is logged for compliance
Why Permit.io? (vs. Traditional Authorization)
Traditionally, access control is hard-coded into the app. This means:
- Authorization logic is scattered everywhere
- Changing permissions means changing code (and redeploying)
- It's easy to miss a check, leading to security holes
- Auditing who did what is a pain
With Permit.io (externalized authorization):
- All policies are managed in one place (the Permit.io dashboard or config)
- You can update permissions instantly—no code changes needed
- Every access check is logged automatically
- It's easy to create complex, context-aware rules (like department-based or time-based access)
Example:
Want to let doctors run AI analysis only during working hours? Just update the policy in Permit.io—no code changes required!
How AICHA Leverages Permit.io (In Simple Terms)
- Role-Based Access: Each user is assigned a role (admin, doctor, nurse) and only sees features they're allowed to use.
- Context-Aware Policies: Access can depend on department, time of day, or even the type of AI analysis.
- User Management: Users are synced from our database to Permit.io, so roles and permissions are always up to date.
- Real-Time Checks: Every time a user tries to do something important, AICHA checks with Permit.io to see if it's allowed.
- Audit Logging: Every action is logged for compliance and security.
Setting Up Permit.io for AICHA (For First-Time Users)
Option 1: Manual Setup via Permit.io Dashboard
-
Create a Permit.io Account:
- Go to Permit.io and sign up
- Create a new project called "AICHA"
Configure Resources:
Navigate to the Resources tab and create three key resources:
a. Patient Records:
Key: patients
Name: Patient Records
Description: Medical patient information
Actions:
- create (Create new patient records)
- read (View patient information)
- update (Modify patient details)
- delete (Remove patient records)
Attributes:
- department_id: string
- record_type: string
b. AI Analysis:
Key: ai_analysis
Name: AI Analysis
Description: AI-powered medical analysis
Actions:
- run (Execute AI analysis)
- approve (Approve analysis results)
- view (View analysis reports)
Attributes:
- analysis_type: string
- department_id: string
c. Treatment Plans:
Key: treatment
Name: Treatment Plans
Description: Patient treatment recommendations
Actions:
- suggest (Create treatment suggestions)
- approve (Approve treatment plans)
- view (View treatment details)
Attributes:
- department_id: string
- treatment_type: string
- Set Up Roles and Permissions: Create the following roles with specific permissions:
a. Administrator:
Key: admin
Permissions:
- create:patients
- read:patients
- update:patients
- delete:patients
- run:ai_analysis
- approve:ai_analysis
- view:ai_analysis
- suggest:treatment
- approve:treatment
- view:treatment
b. Doctor:
Key: doctor
Permissions:
- read:patients
- update:patients
- run:ai_analysis
- view:ai_analysis
- suggest:treatment
- approve:treatment
- view:treatment
c. Nurse:
Key: nurse
Permissions:
- read:patients
- view:ai_analysis
- view:treatment
-
Get API Credentials:
- Go to Settings > API Keys
- Copy your API key, project ID, and environment
- Add them to your
.envfile:
PERMIT_API_KEY=your_api_key PERMIT_PROJECT_ID=your_project_id PERMIT_ENVIRONMENT=dev
Option 2: Automated Setup (Using Our Scripts)
If you want to set up everything automatically, just run our setup script!
-
Configure your
.envfile (see above) - Run the setup script:
cd backend
npm install
node scripts/permit-setup.js
This will:
- Create all resources and roles in Permit.io
- Set up permissions and policies
- Sync all users from your database
How Permissions Are Checked in AICHA
Whenever a user logs in or tries to use a feature, AICHA:
- Checks their role and department
- Asks Permit.io if they're allowed to do the action (like run AI analysis)
- If Permit.io says yes, the action happens; if not, it's blocked
- Every check and action is logged for auditing
Example:
// Check if a doctor can run AI analysis
const canRunAI = await permit.checkAIAccess(currentUser, 'diagnosis', patientDepartment);
if (!canRunAI) {
return res.status(403).json({ error: 'Not allowed to run AI analysis' });
}
Core Implementation Files (How We Use Permit.io)
1. permit.js (Core Permit.io Integration)
const { Permit } = require('@permit.io/permit-node');
const dotenv = require('dotenv');
dotenv.config();
class PermitService {
constructor() {
this.permit = new Permit({
token: process.env.PERMIT_API_KEY,
pdp: "https://cloudpdp.api.permit.io",
projectId: process.env.PERMIT_PROJECT_ID,
environment: process.env.PERMIT_ENVIRONMENT
});
this.initializeSyncService();
}
async initializeSyncService() {
const { syncUsers } = require('./permit-sync-users');
await syncUsers();
setInterval(syncUsers, 5 * 60 * 1000);
}
async checkPermission(user, action, resource) {
return await this.permit.check(user.id, action, resource);
}
async checkContextualPermission(user, action, resource, context) {
const baseContext = {
user: { role: user.role, department_id: user.department_id },
resource: { type: resource, department_id: context.department_id },
time: new Date().toLocaleTimeString('en-US', { hour12: false })
};
return await this.permit.check(user.id, action, resource, { ...baseContext, ...context });
}
async checkAIAccess(user, analysisType, patientDepartment) {
const context = { analysis_type: analysisType, department_id: patientDepartment, time: new Date().toLocaleTimeString('en-US', { hour12: false }) };
return await this.checkContextualPermission(user, 'run', 'ai_analysis', context);
}
async checkTreatmentAccess(user, treatmentType, patientDepartment) {
const context = { treatment_type: treatmentType, department_id: patientDepartment };
return await this.checkContextualPermission(user, 'suggest', 'treatment', context);
}
async logAudit(userId, action, resource, details) {
await this.permit.audit.log({ user: userId, action, resource, details });
}
}
module.exports = new PermitService();
What does this do?
- Connects to Permit.io
- Syncs users
- Checks permissions (including context-aware checks)
- Logs every important action
2. permit-utils.js (Permission Helpers)
async function checkAccess(permit, user, action, resource) {
const permitted = await permit.check(user.id, action, resource);
if (!permitted) return false;
const context = {
user: { role: user.role, department_id: user.department_id },
resource: { type: resource, department_id: user.department_id }
};
return await permit.checkWithContext(user.id, action, resource, context);
}
module.exports = { checkAccess };
What does this do?
- Checks if a user can do something, with extra context (like department)
3. permit-sync-users.js (User Sync)
const { Pool } = require('pg');
const permit = require('./permit');
const dotenv = require('dotenv');
dotenv.config();
const pool = new Pool({
user: process.env.DB_USER,
host: process.env.DB_HOST,
database: process.env.DB_NAME,
password: process.env.DB_PASSWORD,
port: process.env.DB_PORT
});
async function syncUsers() {
try {
const result = await pool.query(`
SELECT u.id, u.email, u.role, u.department_id, u.first_name, u.last_name
FROM users u
WHERE u.active = true
`);
for (const user of result.rows) {
await permit.users.sync({
key: user.id,
email: user.email,
firstName: user.first_name,
lastName: user.last_name,
attributes: { role: user.role, department_id: user.department_id }
});
}
console.log(`✅ Successfully synced ${result.rows.length} users with Permit.io`);
} catch (error) {
console.error('❌ Error syncing users:', error);
} finally {
await pool.end();
}
}
module.exports = { syncUsers };
What does this do?
- Syncs all active users from our database to Permit.io, so permissions are always up to date
4. permit.json (Resource & Role Config)
{
"resources": {
"patients": {
"name": "Patient Records",
"actions": ["create", "read", "update", "delete"]
},
"ai_analysis": {
"name": "AI Analysis",
"actions": ["run", "approve", "view"]
},
"treatment": {
"name": "Treatment Plans",
"actions": ["suggest", "approve", "view"]
}
},
"roles": {
"admin": {
"permissions": ["create:patients", "read:patients", "update:patients", "delete:patients", "run:ai_analysis", "approve:ai_analysis", "view:ai_analysis", "suggest:treatment", "approve:treatment", "view:treatment"]
},
"doctor": {
"permissions": ["read:patients", "update:patients", "run:ai_analysis", "view:ai_analysis", "suggest:treatment", "approve:treatment", "view:treatment"]
},
"nurse": {
"permissions": ["read:patients", "view:ai_analysis", "view:treatment"]
}
}
}
What does this do?
- Defines all resources, actions, and roles for Permit.io
5. permit-setup.js (Automated Setup Script)
const { Permit } = require('@permit.io/permit-node');
const dotenv = require('dotenv');
const { syncUsers } = require('../utils/permit-sync-users');
dotenv.config();
const permit = new Permit({
token: process.env.PERMIT_API_KEY,
pdp: "https://cloudpdp.api.permit.io",
projectId: process.env.PERMIT_PROJECT_ID,
environment: process.env.PERMIT_ENVIRONMENT
});
const resources = {
patients: {
name: "Patient Records",
description: "Medical patient information",
actions: ["create", "read", "update", "delete"],
attributes: { department_id: "string", record_type: "string" }
},
ai_analysis: {
name: "AI Analysis",
description: "AI-powered medical analysis",
actions: ["run", "approve", "view"],
attributes: { analysis_type: "string", department_id: "string" }
},
treatment: {
name: "Treatment Plans",
description: "Patient treatment recommendations",
actions: ["suggest", "approve", "view"],
attributes: { department_id: "string", treatment_type: "string" }
}
};
const roles = {
admin: {
name: "Administrator",
description: "Full system access",
permissions: ["create:patients", "read:patients", "update:patients", "delete:patients", "run:ai_analysis", "approve:ai_analysis", "view:ai_analysis", "suggest:treatment", "approve:treatment", "view:treatment"]
},
doctor: {
name: "Doctor",
description: "Medical staff with AI access",
permissions: ["read:patients", "update:patients", "run:ai_analysis", "view:ai_analysis", "suggest:treatment", "approve:treatment", "view:treatment"]
},
nurse: {
name: "Nurse",
description: "Basic medical staff access",
permissions: ["read:patients", "view:ai_analysis", "view:treatment"]
}
};
async function setupPermit() {
try {
console.log(' 

































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)





























































































































![[DEALS] Microsoft 365: 1-Year Subscription (Family/Up to 6 Users) (23% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)



![From Art School Drop-out to Microsoft Engineer with Shashi Lo [Podcast #170]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1746203291209/439bf16b-c820-4fe8-b69e-94d80533b2df.png?#)




















![Re-designing a Git/development workflow with best practices [closed]](https://i.postimg.cc/tRvBYcrt/branching-example.jpg)



















































































(1).jpg?#)































_Inge_Johnsson-Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)






























































































![The Material 3 Expressive redesign of Google Clock leaks out [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/03/Google-Clock-v2.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)
![What Google Messages features are rolling out [May 2025]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2023/12/google-messages-name-cover.png?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)













![New Apple iPad mini 7 On Sale for $399! [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96096/96096/96096-640.jpg)
![Apple to Split iPhone Launches Across Fall and Spring in Major Shakeup [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97211/97211/97211-640.jpg)
![Apple to Move Camera to Top Left, Hide Face ID Under Display in iPhone 18 Pro Redesign [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97212/97212/97212-640.jpg)
![Apple Developing Battery Case for iPhone 17 Air Amid Battery Life Concerns [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97208/97208/97208-640.jpg)