Using JWT with Django REST Framework and Vue.js
Here’s how JWT (JSON Web Token) works in Django DRF: Step-by-Step JWT Flow 1️⃣ User Logs In Frontend sends username & password to /api/token/. Django returns access and refresh tokens. { "access": "eyJhbGciOi... (valid for 60 minutes)", "refresh": "eyJhbGciOi... (valid for 7 days)" } 2️⃣ Frontend Stores the Tokens The access token is stored in Vuex, Pinia, or LocalStorage. The refresh token is stored in HTTP-only cookies (for security). 3️⃣ Frontend Sends Access Token with Every API Request When making a request to Django, Vue.js adds the token to the Authorization header: fetch("/api/chats/", { method: "POST", headers: { "Authorization": `Bearer ${accessToken}`, "Content-Type": "application/json" }, body: JSON.stringify(data) }); 4️⃣ Backend Verifies the Token DRF checks if the access token is valid. If valid → The request is processed. If expired → The backend rejects it (401 Unauthorized). 5️⃣ Frontend Uses Refresh Token to Get a New Access Token If the access token expires, Vue.js sends the refresh token to /api/token/refresh/ to get a new one. Request to Refresh Token: { "refresh": "eyJhbGciOi... (old refresh token)" } Backend Response (New Access Token): { "access": "eyJhbGciOi... (new access token)" } 6️⃣ Frontend Stores the New Access Token and Continues The new access token replaces the old one and API requests continue normally. Vue.js Example: Sending JWT Token When the frontend sends a request to create a chat, it includes the JWT token: async function sendChat(question, personas) { const accessToken = localStorage.getItem("accessToken"); const response = await fetch("/api/chats/", { method: "POST", headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json", "Authorization": `Bearer ${accessToken}` }, body: JSON.stringify({ question: question, personas: personas.map(p => p.name), responses: personas.map(p => ({ persona: p.name, response_text: "Simulated AI response" })) }) }); if (response.status === 401) { console.log("Access token expired. Refreshing..."); await refreshToken(); return sendChat(question, personas); } }
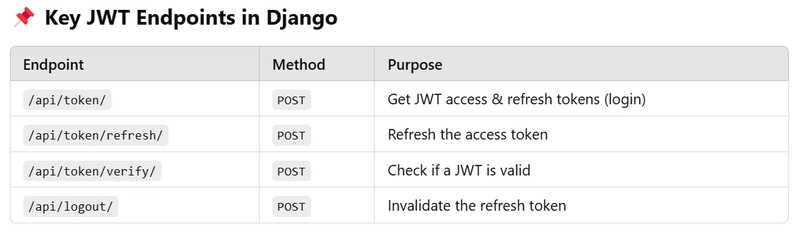
Here’s how JWT (JSON Web Token) works in Django DRF:
Step-by-Step JWT Flow
1️⃣ User Logs In
- Frontend sends
username&passwordto/api/token/. - Django returns
accessandrefreshtokens.
{
"access": "eyJhbGciOi... (valid for 60 minutes)",
"refresh": "eyJhbGciOi... (valid for 7 days)"
}
2️⃣ Frontend Stores the Tokens
- The access token is stored in Vuex, Pinia, or LocalStorage.
- The refresh token is stored in HTTP-only cookies (for security).
3️⃣ Frontend Sends Access Token with Every API Request
- When making a request to Django, Vue.js adds the token to the
Authorizationheader:
fetch("/api/chats/", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Authorization": `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
body: JSON.stringify(data)
});
4️⃣ Backend Verifies the Token
- DRF checks if the
accesstoken is valid. - If valid → The request is processed.
- If expired → The backend rejects it (401 Unauthorized).
5️⃣ Frontend Uses Refresh Token to Get a New Access Token
- If the access token expires, Vue.js sends the
refreshtoken to/api/token/refresh/to get a new one.
Request to Refresh Token:
{
"refresh": "eyJhbGciOi... (old refresh token)"
}
Backend Response (New Access Token):
{
"access": "eyJhbGciOi... (new access token)"
}
6️⃣ Frontend Stores the New Access Token and Continues
The new access token replaces the old one and API requests continue normally.
Vue.js Example: Sending JWT Token
When the frontend sends a request to create a chat, it includes the JWT token:
async function sendChat(question, personas) {
const accessToken = localStorage.getItem("accessToken");
const response = await fetch("/api/chats/", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": `Bearer ${accessToken}`
},
body: JSON.stringify({
question: question,
personas: personas.map(p => p.name),
responses: personas.map(p => ({
persona: p.name,
response_text: "Simulated AI response"
}))
})
});
if (response.status === 401) {
console.log("Access token expired. Refreshing...");
await refreshToken();
return sendChat(question, personas);
}
}










































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)



























































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] The Kubernetes Bible, The Ultimate Linux Shell Scripting Guide & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)



![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)






































































































.png?#)




.jpg?#)































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)








































































































![Rapidus in Talks With Apple as It Accelerates Toward 2nm Chip Production [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96937/96937/96937-640.jpg)