Introduction to Forms-Building Interactive Web Pages
In this session, we explore HTML forms—the essential tool for collecting user input. Whether it's a simple contact page or a dynamic game settings menu, forms are the backbone of user interaction on the web. Today, we'll cover: The structure of forms Common form elements Basic validation techniques. Understanding Forms Forms allow us to gather user data through elements such as text fields, check-boxes, radio buttons, and submit buttons. Mastering forms is key to building interactive interfaces that can later serve as menus or control panels in a more complex projects, like a game. Step-by-Step Explanation 1. The Element Purpose: The form tag wraps all the form controls and sets the context for user data submission. Attributes: action: Specifies the URL where the form data will be sent upon submission. method: Defines how the data is sent, typically using GET or POST. 2. Common Form Elements Labels () Associates a text description with form controls, improving accessibility. Use the for attribute to link a label to its corresponding input field. Inputs(inputs) Used for various types of data entry. Common input types includes: + text for single-line text input, + email for email addresses + password for passwords Textarea() Provides a multi-line text input area-perfect for messages for longer inputs. Select(): Creates a drop down list for selecting one or more options. Button(): Submits the form or triggers other actions. 3. Basic Form Validation required Attribute: Ensures that a field is filled out before the form can be submitted. pattern Attribute: Uses a regular expression to validate the format of the input (e.g., allowing only alphabetic characters). Interactive Coding Example Let's create a simple contract form that could also serve as a game menu or setting panel. Open your favorite code editor or online tool like CodePen or JSFiddle and try the code below: Contact Form /* Basic styling for clarity */ form { max-width: 400px; margin: auto; } label, input, textarea { display: block; width: 100%; margin-bottom: 10px; } Contact Us Name: Email: Message: Send Message Hands-On Exercises Extend the form Add an input field for "Subject" right below the Email field: Subject: Enhance Validation Experiment with the "Name"z input by adding a pattern attribute so that it allows alphabetic characters: Test the Form Click the "Send Message" button and observe how modern browsers enforce these validations automatically. Additional Resources MDN Web Docs – Your First Form MDN Web Docs – Form Validation By understanding the structure and functionality of forms, we've taken a significant step towards creating interactive web application. The concepts covered today lay the foundation for dynamic interfaces and user-friendly applications, include game menus and settings panels. Stay tuned for more insights as we continue building our project!

In this session, we explore HTML forms—the essential tool for collecting user input. Whether it's a simple contact page or a dynamic game settings menu, forms are the backbone of user interaction on the web. Today, we'll cover:
- The structure of forms
- Common form elements
- Basic validation techniques.
Understanding Forms
Forms allow us to gather user data through elements such as text fields, check-boxes, radio buttons, and submit buttons.
Mastering forms is key to building interactive interfaces that can later serve as menus or control panels in a more complex projects, like a game.
Step-by-Step Explanation
1. The
Purpose:
The form tag wraps all the form controls and sets the context for user data submission.
Attributes:
-
action: Specifies the URL where the form data will be sent upon submission. -
method: Defines how the data is sent, typically usingGETorPOST.
2. Common Form Elements
Labels ()
Associates a text description with form controls, improving accessibility. Use the for attribute to link a label to its corresponding input field.
Inputs(inputs)
Used for various types of data entry. Common input types includes:
+ text for single-line text input,
+ email for email addresses
+ password for passwords
Textarea(










































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)












































































































































































































































.jpg?#)









































































































































![YouTube Announces New Creation Tools for Shorts [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96923/96923/96923-640.jpg)

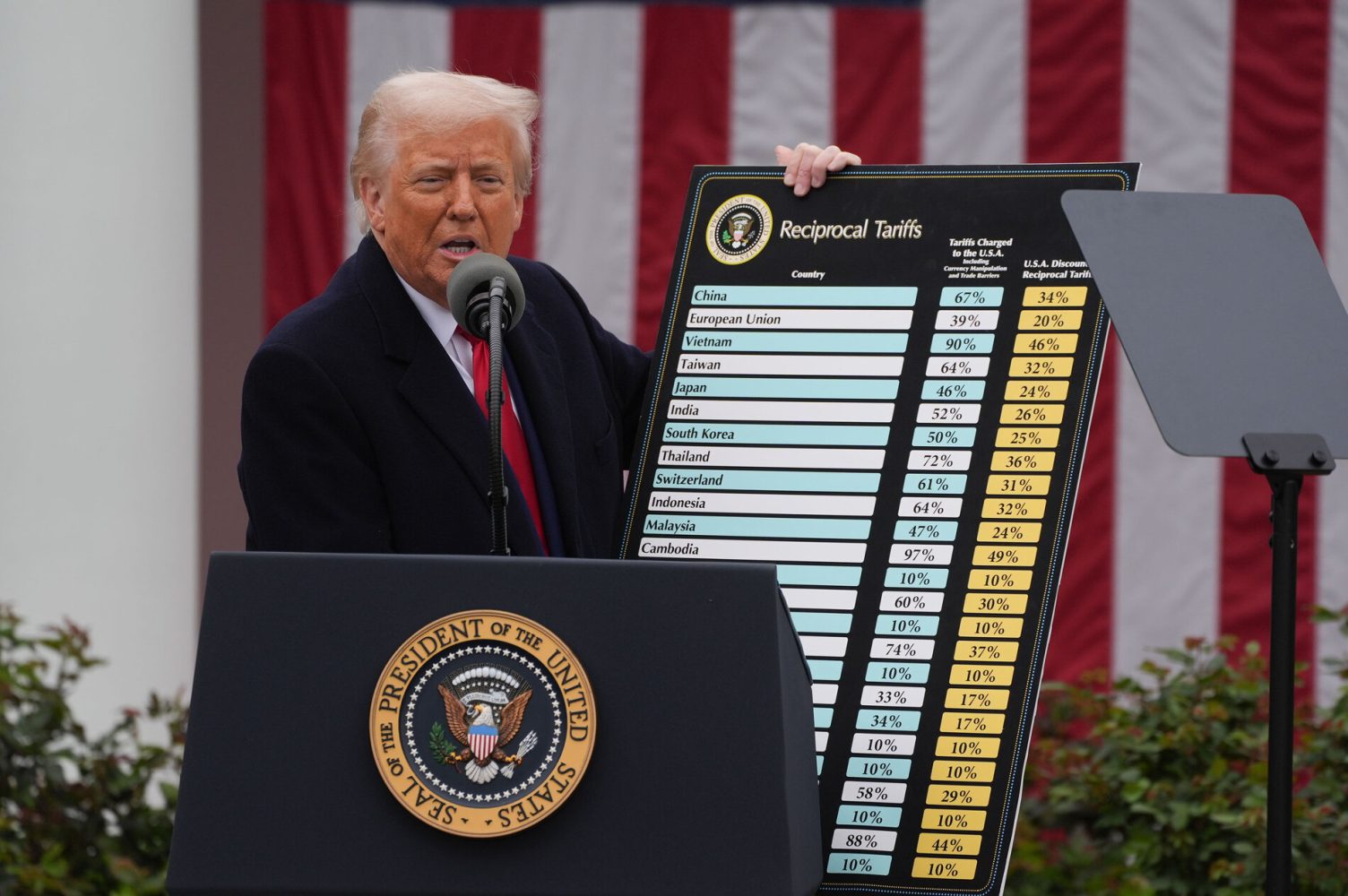
![Apple Faces New Tariffs but Has Options to Soften the Blow [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96921/96921/96921-640.jpg)