Comprehensive Guide to Building a CI/CD Pipeline in AWS with GitHub
Introduction CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) pipelines are foundational to modern software development, enabling teams to automate building, testing, and deploying code. Benefits include: Faster Delivery: Automate repetitive tasks to release updates rapidly. Improved Quality: Catch bugs early with automated testing. Reduced Errors: Minimize manual intervention in deployments. Scalability: Easily adapt pipelines to handle growing workloads. Step 1: Prepare Sample Code Create a Simple Web Application Step 2 Push Code to GitHub Create a new repository on GitHub. Commit and push your code: git init git add README.md git commit -m "first commit" git branch -M main git remote add origin https://github.com/lufadeju/MyDemoRepo.git git push -u origin main Step 3: Create an Amazon EC2 Linux instance and install the CodeDeploy agent In this step, you create the Amazon EC2 instance where you deploy a sample application. As part of this process, create an instance role that allows install and management of the CodeDeploy agent on the instance. The CodeDeploy agent is a software package that enables an instance to be used in CodeDeploy deployments. You also attach policies that allow the instance to fetch files that the CodeDeploy agent uses to deploy your application and to allow the instance to be managed by SSM. To create an instance role Open the IAM console at site. From the console dashboard, choose Roles. Choose Create role. Under Select type of trusted entity, select AWS service.>> Under Choose a use case, select EC2.>> Under Select your use case, choose EC2. Choose Next: Permissions. Search for and select the policy named AmazonEC2RoleforAWSCodeDeploy. Search for and select the policy named AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore. Choose Next: Tags. Choose Next: Review. Enter a name for the role (for example, EC2InstanceRole). Note Make a note of your role name for the next step. You choose this role when you are creating your instance. Choose Create role. To launch an instance Open the Amazon EC2 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/. From the side navigation, choose Instances, and select Launch instances from the top of the page. In Name, enter MyCodePipelineDemo. This assigns the instance a tag Key of Name and a tag Value of MyCodePipelineDemo. Later, you create a CodeDeploy application that deploys the sample application to this instance. CodeDeploy selects instances to deploy based on the tags. Under Application and OS Images (Amazon Machine Image), locate the Amazon Linux AMI option with the AWS logo, and make sure it is selected. (This AMI is described as the Amazon Linux 2 AMI (HVM) and is labeled "Free tier eligible".) Under Instance type, choose the free tier eligible t2.micro type as the hardware configuration for your instance. Under Key pair (login), choose a key pair or create one. You can also choose Proceed without a key pair. For the purposes of this tutorial, you can proceed without a key pair. To use SSH to connect to your instances, create or use a key pair. Under Network settings, do the following. In Auto-assign Public IP, make sure the status is Enable. For the created security group, choose HTTP, and then under Source type, choose My IP. Expand Advanced details. In IAM instance profile, choose the IAM role you created in the previous procedure (for example, EC2InstanceRole). Under Summary, under Number of instances, enter 1.. Choose Launch instance. Step 4: Create an application in CodeDeploy In CodeDeploy, an application is a resource that contains the software application you want to deploy. Later, you use this application with CodePipeline to automate deployments of the sample application to your Amazon EC2 instance. First, you create a role that allows CodeDeploy to perform deployments. Then, you create a CodeDeploy application. To create a CodeDeploy service role Open the IAM console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/). From the console dashboard, choose Roles. Choose Create role. Under Select trusted entity, choose AWS service. >> Under Use case, choose CodeDeploy. >> Choose CodeDeploy from the options listed. Choose Next. The AWSCodeDeployRole managed policy is already attached to the role. Choose Next. Enter a name for the role (for example, CodeDeployRole), and then choose Create role. To create an application in CodeDeploy Open the CodeDeploy console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/codedeploy. If the Applications page does not appear, on the menu, choose Applications. Choose Create application. In Application name, enter MyDemoApplication. In Compute Platform, choose EC2/On-premises. Choose Create application. To create a deployment group in CodeDeploy A deployment group is a resource that defines deployment-related settings like which instances to deploy to and how fast to deplo
Introduction
CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) pipelines are foundational to modern software development, enabling teams to automate building, testing, and deploying code. Benefits include:
Faster Delivery: Automate repetitive tasks to release updates rapidly.
Improved Quality: Catch bugs early with automated testing.
Reduced Errors: Minimize manual intervention in deployments.
Scalability: Easily adapt pipelines to handle growing workloads.
Step 1: Prepare Sample Code
Create a Simple Web Application
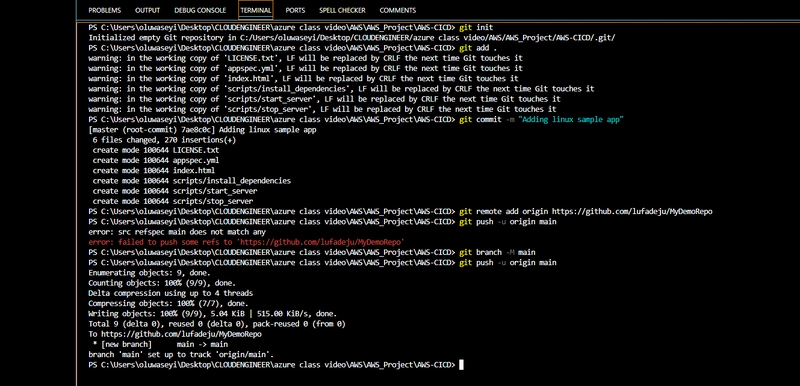
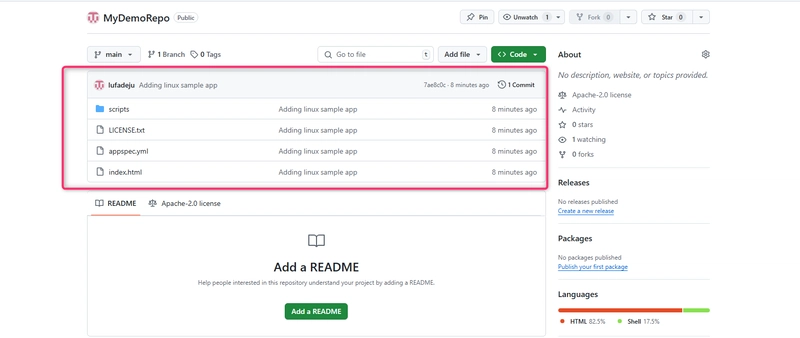
Step 2 Push Code to GitHub
- Create a new repository on GitHub.
- Commit and push your code:
git init
git add README.md
git commit -m "first commit"
git branch -M main
git remote add origin https://github.com/lufadeju/MyDemoRepo.git
git push -u origin main
Step 3: Create an Amazon EC2 Linux instance and install the CodeDeploy agent
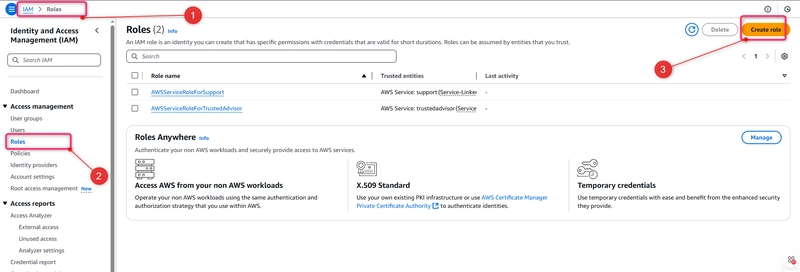
In this step, you create the Amazon EC2 instance where you deploy a sample application. As part of this process, create an instance role that allows install and management of the CodeDeploy agent on the instance. The CodeDeploy agent is a software package that enables an instance to be used in CodeDeploy deployments. You also attach policies that allow the instance to fetch files that the CodeDeploy agent uses to deploy your application and to allow the instance to be managed by SSM.
To create an instance role
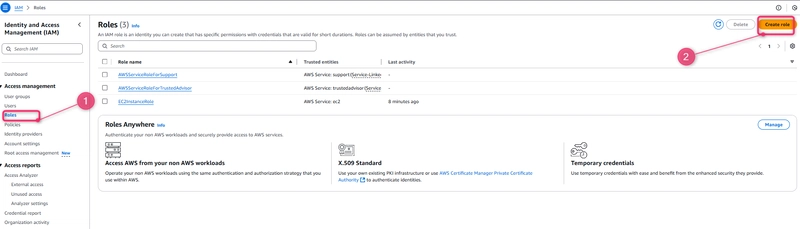
- Open the IAM console at site.
- From the console dashboard, choose Roles.
- Choose Create role.
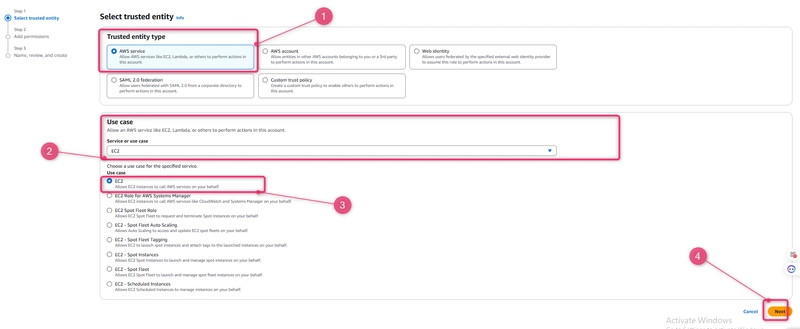
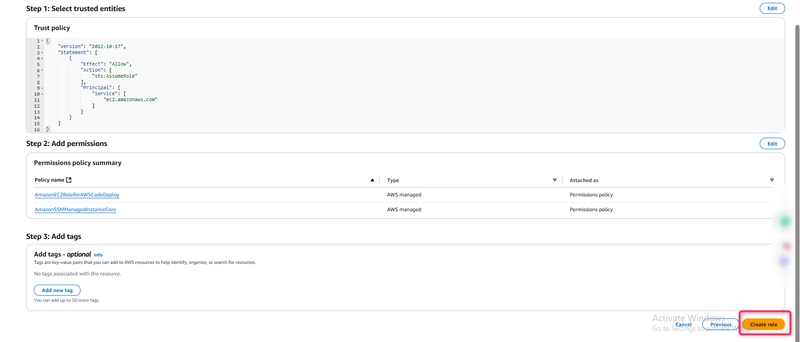
Under Select type of trusted entity, select AWS service.>> Under Choose a use case, select EC2.>> Under Select your use case, choose EC2. Choose Next: Permissions.
- Search for and select the policy named AmazonEC2RoleforAWSCodeDeploy.
- Search for and select the policy named AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore. Choose Next: Tags.
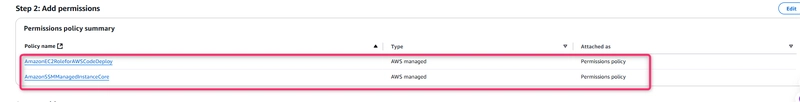
Choose Next: Review. Enter a name for the role (for example, EC2InstanceRole).
Note
Make a note of your role name for the next step. You choose this role when you are creating your instance.
Choose Create role.
To launch an instance
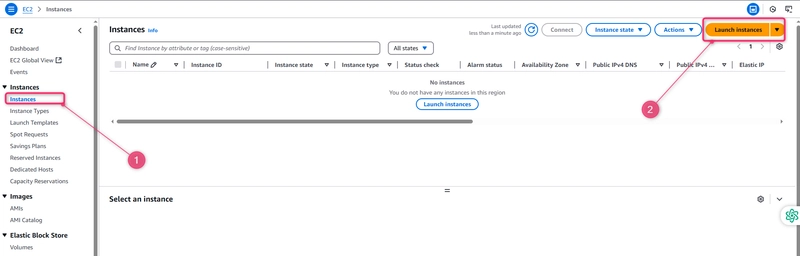
- Open the Amazon EC2 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/.
- From the side navigation, choose Instances, and select Launch instances from the top of the page.
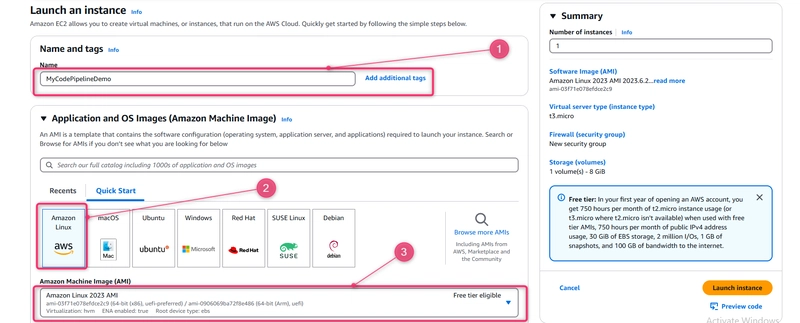
- In Name, enter MyCodePipelineDemo. This assigns the instance a tag Key of Name and a tag Value of MyCodePipelineDemo. Later, you create a CodeDeploy application that deploys the sample application to this instance. CodeDeploy selects instances to deploy based on the tags.
- Under Application and OS Images (Amazon Machine Image), locate the Amazon Linux AMI option with the AWS logo, and make sure it is selected. (This AMI is described as the Amazon Linux 2 AMI (HVM) and is labeled "Free tier eligible".)
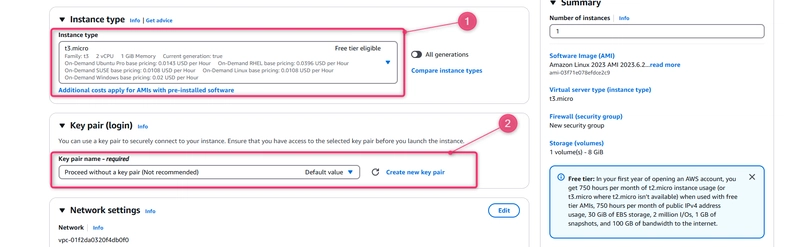
- Under Instance type, choose the free tier eligible t2.micro type as the hardware configuration for your instance.
- Under Key pair (login), choose a key pair or create one.
- You can also choose Proceed without a key pair.
For the purposes of this tutorial, you can proceed without a key pair. To use SSH to connect to your instances, create or use a key pair.
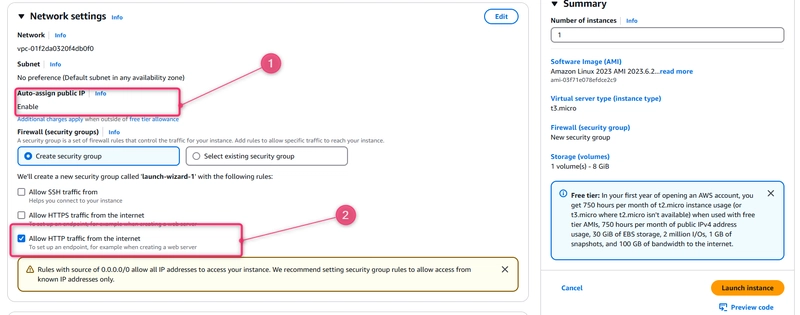
- Under Network settings, do the following.
- In Auto-assign Public IP, make sure the status is Enable.
- For the created security group, choose HTTP, and then under Source type, choose My IP.
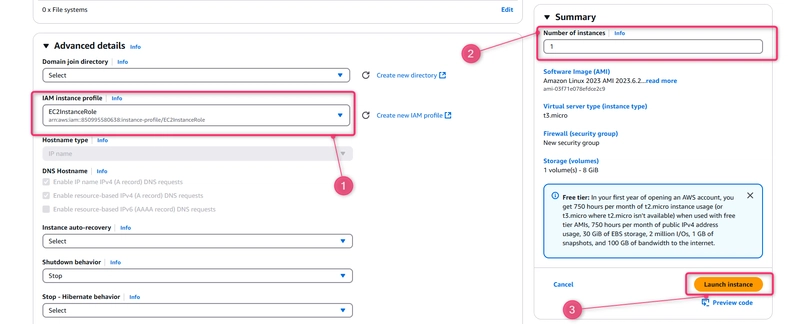
- Expand Advanced details. In IAM instance profile, choose the IAM role you created in the previous procedure (for example, EC2InstanceRole).
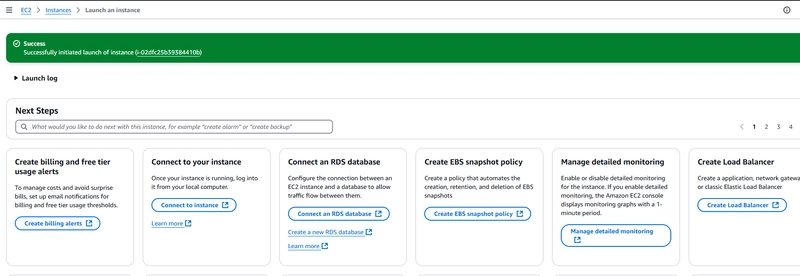
- Under Summary, under Number of instances, enter 1..
- Choose Launch instance.
Step 4: Create an application in CodeDeploy
In CodeDeploy, an application is a resource that contains the software application you want to deploy. Later, you use this application with CodePipeline to automate deployments of the sample application to your Amazon EC2 instance.
First, you create a role that allows CodeDeploy to perform deployments. Then, you create a CodeDeploy application.
To create a CodeDeploy service role
- Open the IAM console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/).
- From the console dashboard, choose Roles.
- Choose Create role.
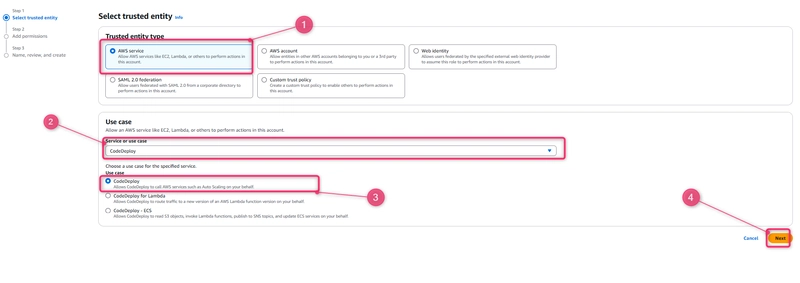
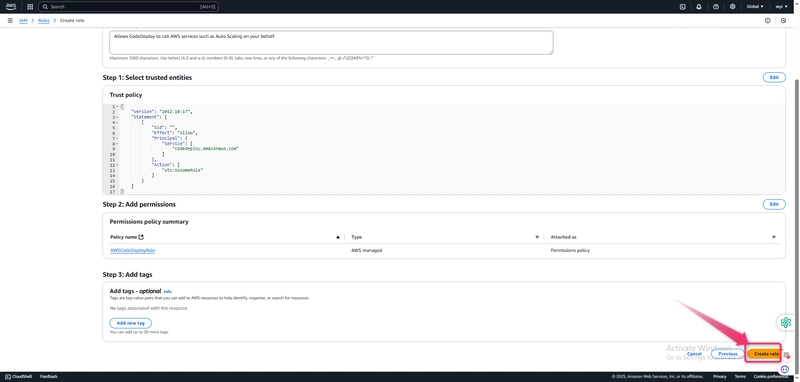
Under Select trusted entity, choose AWS service. >> Under Use case, choose CodeDeploy. >> Choose CodeDeploy from the options listed. Choose Next. The AWSCodeDeployRole managed policy is already attached to the role.
Choose Next.
Enter a name for the role (for example, CodeDeployRole), and then choose Create role.
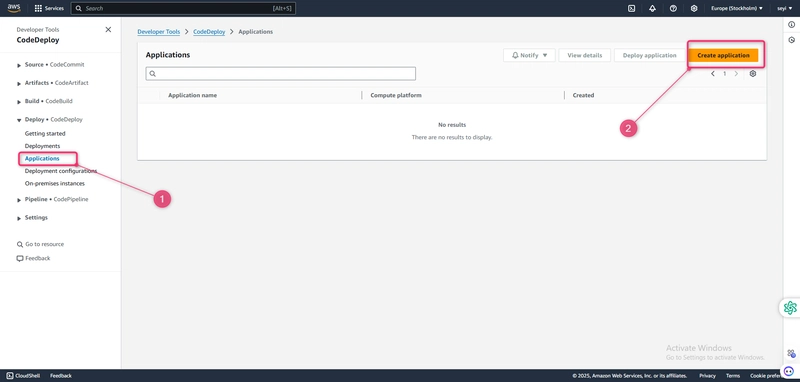
To create an application in CodeDeploy
Open the CodeDeploy console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/codedeploy.
If the Applications page does not appear, on the menu, choose Applications.
Choose Create application.
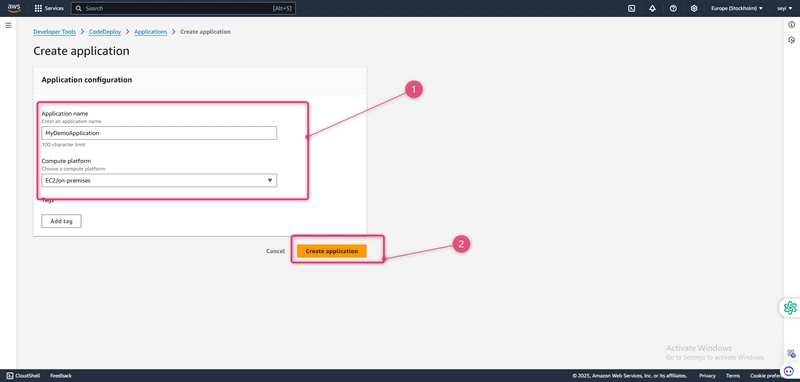
- In Application name, enter MyDemoApplication.
- In Compute Platform, choose EC2/On-premises.
- Choose Create application.
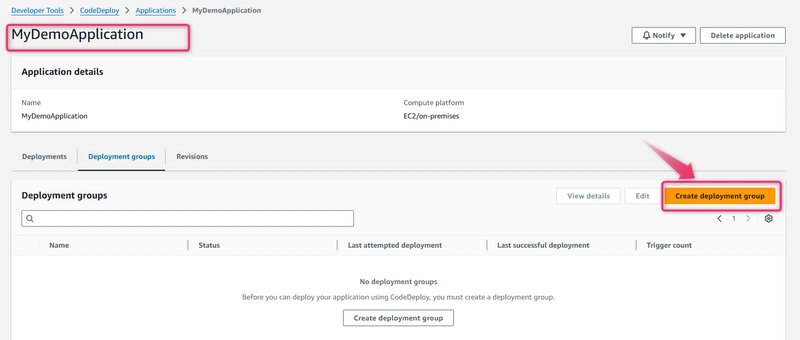
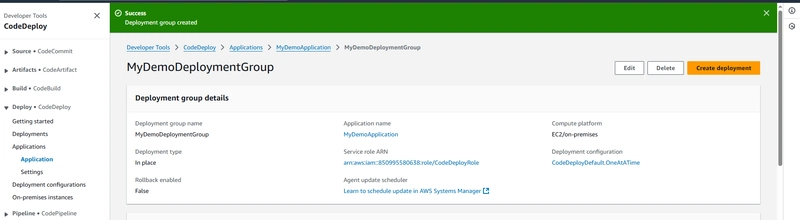
To create a deployment group in CodeDeploy
A deployment group is a resource that defines deployment-related settings like which instances to deploy to and how fast to deploy them.
- On the page that displays your application, choose Create deployment group.
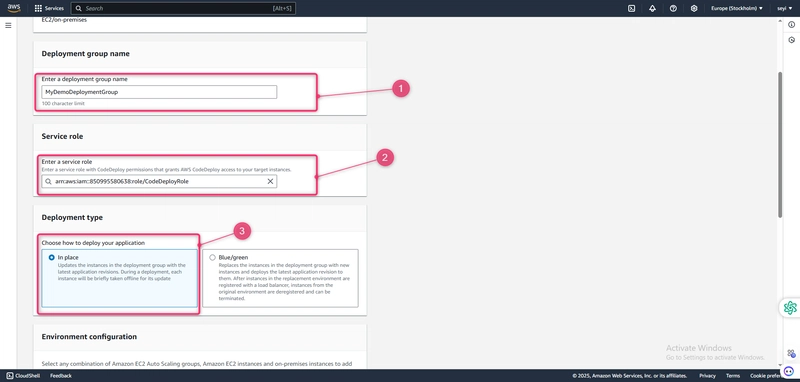
- In Deployment group name, enter MyDemoDeploymentGroup.
- In Service role, choose the ARN of the service role you created earlier (for example, arn:aws:iam::account_ID:role/CodeDeployRole).
- Under Deployment type, choose In-place.
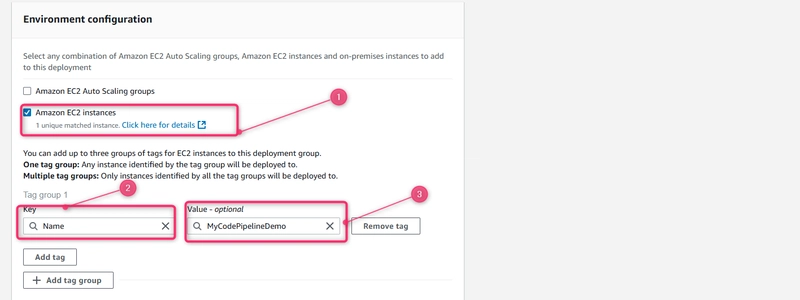
Under Environment configuration, choose Amazon EC2 Instances.>> In the Key field, enter Name.>> In the Value field, enter the name you used to tag the instance (for example, MyCodePipelineDemo).
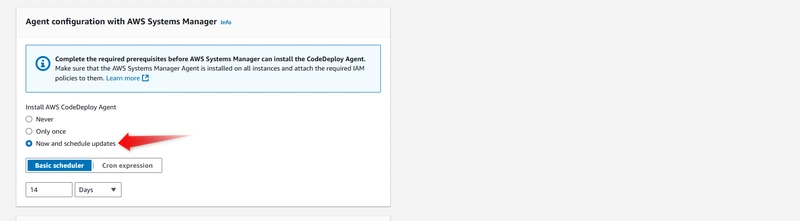
Under Agent configuration with AWS Systems Manager, choose Now and schedule updates. This installs the agent on the instance. The Linux instance is already configured with the SSM agent and will now be updated with the CodeDeploy agent.
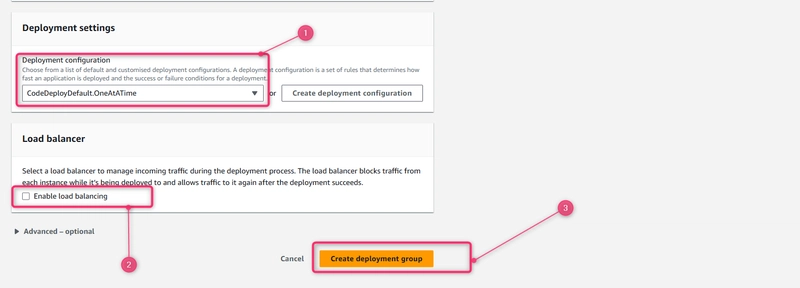
Under Deployment configuration, choose CodeDeployDefault.OneAtaTime.
Under Load Balancer, make sure Enable load balancing is not selected. You do not need to set up a load balancer or choose a target group for this example.
Choose Create deployment group.
Step 5: Create your first pipeline in CodePipeline
You're now ready to create and run your first pipeline. In this step, you create a pipeline that runs automatically when code is pushed to your CodeCommit repository.
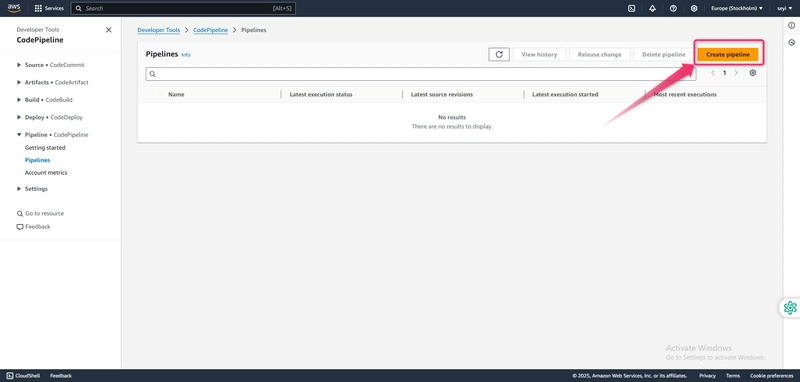
To create a CodePipeline pipeline
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the CodePipeline console at http://console.aws.amazon.com/codesuite/codepipeline/home.
- Open the CodePipeline console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/codepipeline/.
- On the Welcome page, Getting started page, or the Pipelines page, choose Create pipeline.
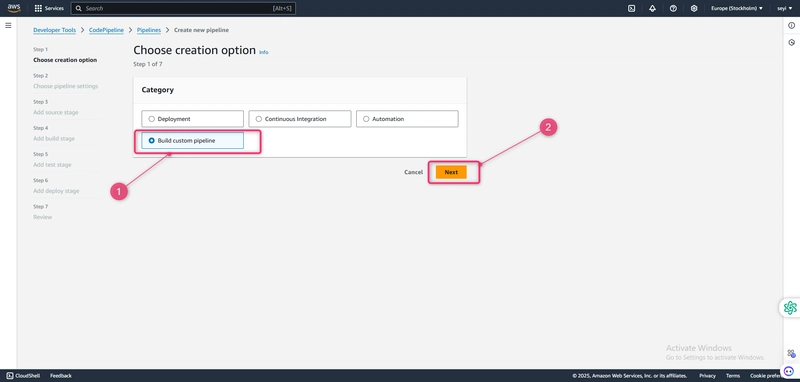
On the Step 1: Choose creation option page, under Creation options, choose the Build custom pipeline option. Choose Next.
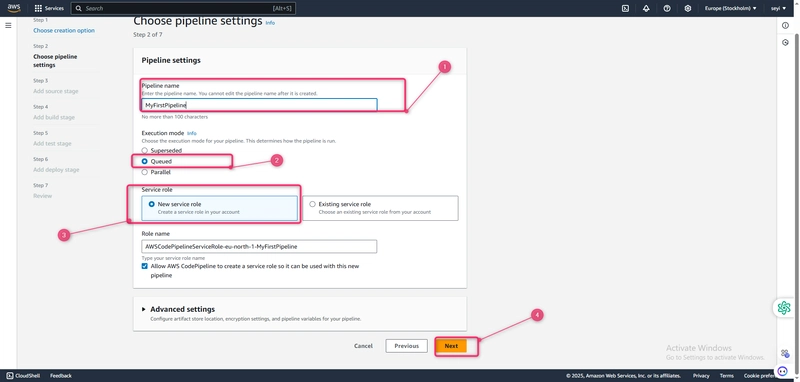
- In Step 2: Choose pipeline settings, in Pipeline name, enter MyFirstPipeline.
- CodePipeline provides V1 and V2 type pipelines, which differ in characteristics and price. The V2 type is the only type you can choose in the console. For more information, see pipeline types. For information about pricing for CodePipeline, see Pricing.
- In Service role, choose New service role to allow CodePipeline to create a service role in IAM.
- Leave the settings under Advanced settings at their defaults, and then choose Next.
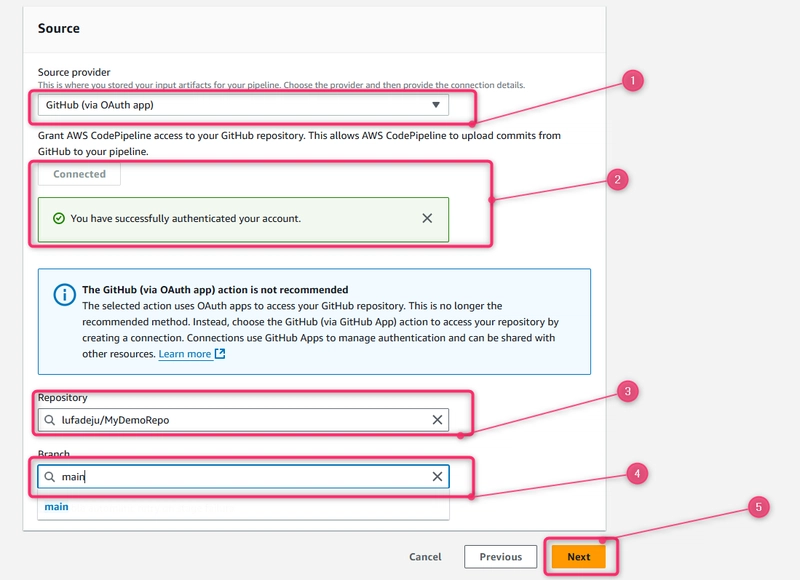
- In Step 3: Add source stage, in Source provider, choose GitHub Via OAuth App.
- Choose Next.
- In Step 4: Add build stage, choose Skip build stage, and then accept the warning message by choosing Skip again. Choose Next.
- In Step 5: Add test stage, choose Skip test stage, and then accept the warning message by choosing Skip again.
Choose Next.
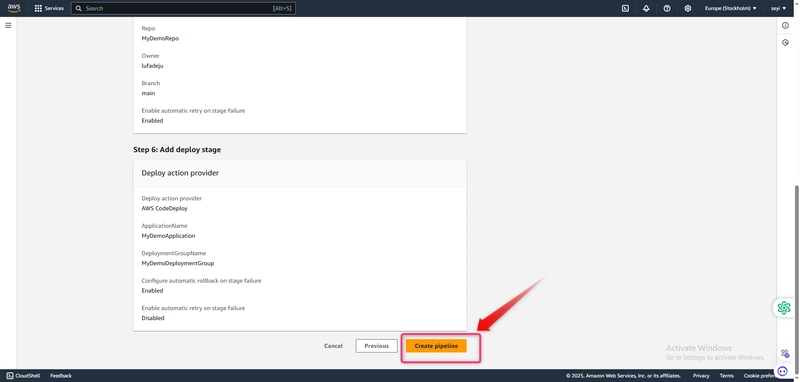
In Step 6: Add deploy stage, in Deploy provider, choose CodeDeploy. In Application name, choose MyDemoApplication. In Deployment group, choose MyDemoDeploymentGroup, and then choose Next step.
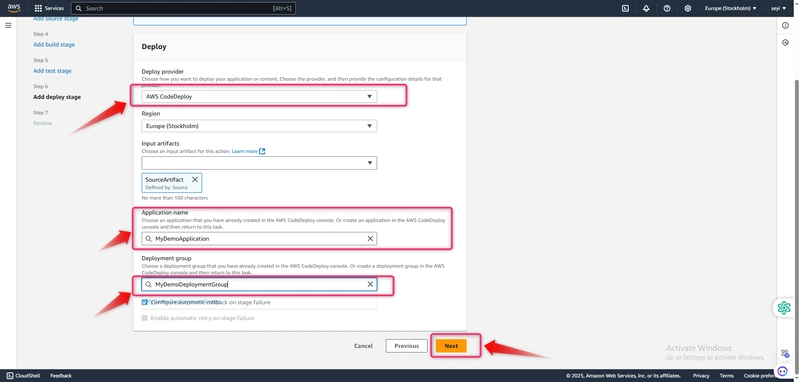
In Step 7: Review, review the information, and then choose Create pipeline.
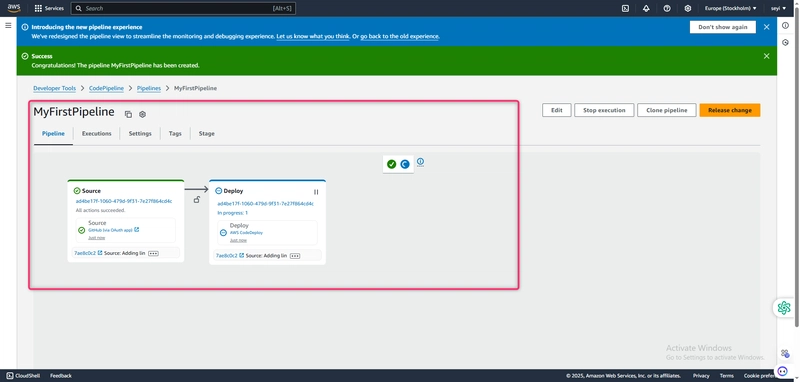
The pipeline starts running after it is created. It downloads the code from your CodeCommit repository and creates a CodeDeploy deployment to your EC2 instance. You can view progress and success and failure messages as the CodePipeline sample deploys the webpage to the Amazon EC2 instance in the CodeDeploy deployment.
Congratulations! You just created a simple pipeline in CodePipeline.
Next, you verify the results.
To verify your pipeline ran successfully
View the initial progress of the pipeline. The status of each stage changes from No executions yet to In Progress, and then to either Succeeded or Failed. The running of the pipeline should be complete within a few minutes.
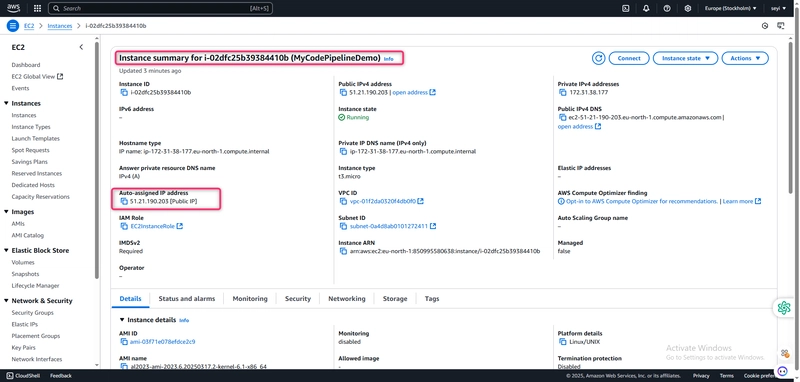
After Succeeded is displayed for the action status, refresh the demo page you accessed earlier in your browser.
To Get the link go to the EC 2 instance and copy the ip address
The updated webpage is displayed.
Conclusion
This guide outlines how to automate software delivery using AWS CI/CD services (CodePipeline, CodeDeploy) and GitHub. By integrating these tools, teams can streamline building, testing, and deploying code with minimal manual intervention.










































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)



























































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] The Kubernetes Bible, The Ultimate Linux Shell Scripting Guide & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)



![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)






































































































.png?#)




.jpg?#)































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)








































































































![Rapidus in Talks With Apple as It Accelerates Toward 2nm Chip Production [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96937/96937/96937-640.jpg)