5G’s Role in Accelerating IoT Development
The Internet of Things (IoT) has long promised a future where devices seamlessly connect, communicate, and automate everyday life. From smart homes and wearable health monitors to industrial automation and connected vehicles, IoT is rapidly becoming a part of our daily routine. However, for this vast web of devices to truly reach its potential, it needs a network capable of handling massive data, low latency, and real-time responsiveness. Enter 5G. What Makes 5G Different? 5G, the fifth generation of wireless technology, is not just a speed upgrade—it’s a complete redesign of mobile networks. It offers three key features that are crucial for IoT: Ultra-low latency (as low as 1 millisecond) High data throughput (up to 10 Gbps) Massive device connectivity (up to 1 million devices per square kilometer) These capabilities open the door to a new wave of IoT innovation. Accelerating IoT Across Industries 1. Smart Cities Smart cities rely on thousands of sensors and interconnected devices—traffic cameras, environmental monitors, waste management systems, and more. With 5G, these devices can transmit real-time data without delay, enabling cities to make dynamic, data-driven decisions. Traffic flow can be optimized in real-time, emergency services can respond faster, and public safety can be enhanced with predictive analytics. Organizations like Bridge Group Solutions are helping to create smarter infrastructure 2. Healthcare and Wearables Remote healthcare devices, such as heart monitors, glucose sensors, and telemedicine platforms, demand uninterrupted, real-time communication. 5G’s reliability ensures these devices work with hospital-grade precision, even outside traditional care settings. This paves the way for more effective home care, real-time diagnostics, and even robotic surgeries powered remotely. 3. Industrial IoT (IIoT) Factories and supply chains are becoming smarter and more autonomous. With 5G, machines can communicate with each other with almost zero delay, improving precision, reducing downtime, and optimizing resource usage. Predictive maintenance, driven by real-time sensor data, can prevent costly breakdowns and improve efficiency. Companies like eInfraTech Systems are at the forefront of deploying industrial IoT 4. Connected Vehicles Self-driving cars and intelligent transport systems depend heavily on ultra-fast communication. 5G allows vehicles to interact not just with each other (V2V) but with infrastructure (V2I) and pedestrians (V2P). This real-time data exchange is critical for navigation, accident avoidance, and traffic efficiency. 5. Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring From soil sensors to drone surveillance, smart agriculture is on the rise. 5G enables wide-area deployment of sensors that can monitor weather, irrigation, and crop health in real time. This leads to increased yields, reduced waste, and more sustainable farming practices. Challenges and Considerations While 5G holds massive promise, challenges remain. Infrastructure rollout is still uneven, particularly in rural or underdeveloped regions. Security concerns also rise with the increased number of connected devices. Developers and engineers must build robust, secure solutions to protect user data and ensure reliable operation. Final Thoughts 5G is more than just a faster network—it’s a critical enabler for the next generation of IoT applications. As coverage expands and technology matures, we’re poised to witness an explosion of intelligent, connected systems that transform how we live, work, and interact with the world. For developers, engineers, and innovators, now is the time to build.
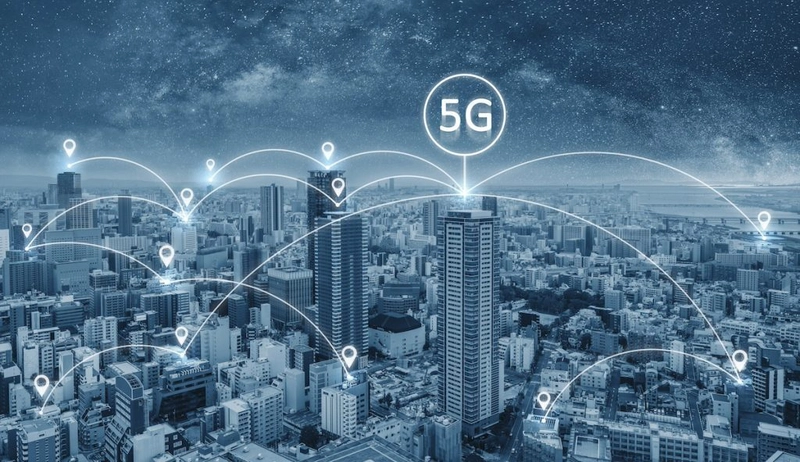

The Internet of Things (IoT) has long promised a future where devices seamlessly connect,
communicate, and automate everyday life. From smart homes and wearable health monitors
to industrial automation and connected vehicles, IoT is rapidly becoming a part of our daily
routine. However, for this vast web of devices to truly reach its potential, it needs a network
capable of handling massive data, low latency, and real-time responsiveness. Enter 5G.
What Makes 5G Different?
5G, the fifth generation of wireless technology, is not just a speed upgrade—it’s a complete
redesign of mobile networks. It offers three key features that are crucial for IoT:
- Ultra-low latency (as low as 1 millisecond)
- High data throughput (up to 10 Gbps)
- Massive device connectivity (up to 1 million devices per square kilometer) These capabilities open the door to a new wave of IoT innovation.
Accelerating IoT Across Industries
1. Smart Cities
Smart cities rely on thousands of sensors and interconnected devices—traffic cameras,
environmental monitors, waste management systems, and more. With 5G, these devices can
transmit real-time data without delay, enabling cities to make dynamic, data-driven decisions.
Traffic flow can be optimized in real-time, emergency services can respond faster, and public
safety can be enhanced with predictive analytics.
 Organizations like Bridge Group Solutions are helping to create smarter infrastructure
Organizations like Bridge Group Solutions are helping to create smarter infrastructure
2. Healthcare and Wearables
Remote healthcare devices, such as heart monitors, glucose sensors, and telemedicine
platforms, demand uninterrupted, real-time communication. 5G’s reliability ensures these
devices work with hospital-grade precision, even outside traditional care settings. This paves
the way for more effective home care, real-time diagnostics, and even robotic surgeries
powered remotely.
3. Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Factories and supply chains are becoming smarter and more autonomous. With 5G, machines
can communicate with each other with almost zero delay, improving precision, reducing
downtime, and optimizing resource usage. Predictive maintenance, driven by real-time sensor
data, can prevent costly breakdowns and improve efficiency.
 Companies like eInfraTech Systems are at the forefront of deploying industrial IoT
Companies like eInfraTech Systems are at the forefront of deploying industrial IoT
4. Connected Vehicles
Self-driving cars and intelligent transport systems depend heavily on ultra-fast
communication. 5G allows vehicles to interact not just with each other (V2V) but with
infrastructure (V2I) and pedestrians (V2P). This real-time data exchange is critical for
navigation, accident avoidance, and traffic efficiency.
5. Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring
From soil sensors to drone surveillance, smart agriculture is on the rise. 5G enables wide-area
deployment of sensors that can monitor weather, irrigation, and crop health in real time. This
leads to increased yields, reduced waste, and more sustainable farming practices.
Challenges and Considerations
While 5G holds massive promise, challenges remain. Infrastructure rollout is still uneven,
particularly in rural or underdeveloped regions. Security concerns also rise with the increased
number of connected devices. Developers and engineers must build robust, secure solutions
to protect user data and ensure reliable operation.
Final Thoughts
5G is more than just a faster network—it’s a critical enabler for the next generation of IoT
applications. As coverage expands and technology matures, we’re poised to witness an
explosion of intelligent, connected systems that transform how we live, work, and interact
with the world. For developers, engineers, and innovators, now is the time to build.

































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)









































































































































































































































































_Muhammad_R._Fakhrurrozi_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_NicoElNino_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)












































































































![Apple Releases iOS 18.5 Beta 4 and iPadOS 18.5 Beta 4 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97145/97145/97145-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds watchOS 11.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97147/97147/97147-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds visionOS 2.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97150/97150/97150-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds tvOS 18.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97153/97153/97153-640.jpg)