What's in Cloud Computing..?
The cloud means storing and accessing data and programs over the internet instead of your computer’s hard drive. Instead of saving files only on your laptop, you save them online, where you can get them anytime. Example: Saving your vacation photos on Google Drive so you can open them from your phone, tablet, or computer. How Does Cloud Computing Work? Big companies like Microsoft, Amazon, and Google own huge buildings filled with powerful computers called data centers. When you use the cloud, your data is stored and processed on these computers. Why Use the Cloud? Access Anywhere: Get your files or apps from any device with internet. Example: Checking work emails from your phone while traveling. Cost Savings: No need to buy expensive servers or storage. Example: A startup hosts its website on Azure instead of buying its own servers. Scalability: Add or reduce resources easily. Example: An online shop uses more cloud servers during Black Friday sales. Security: Cloud providers have strong protection methods. Example: Your bank stores your account information securely in the cloud. What are Cloud Computing Services? Storage: Keeping files online. Example: Backing up photos using Dropbox. Databases: Managing large sets of information. Example: Uber stores driver and rider info in cloud databases. Computing: Running applications and websites. Example: A business runs its website on Microsoft Azure. Networking: Securely connecting services and people. Example: Hosting meetings on Microsoft Teams or Zoom. What are Cloud Deployment Models? Public Cloud: Services available to anyone over the internet. Example: Storing files on Google Drive. Private Cloud: Services for only one organization. Example: A hospital uses a private cloud to store patient data. Hybrid Cloud: A mix of public and private clouds. Example: A company keeps sensitive info on a private cloud but uses a public cloud for customer service apps. What are Cloud Service Models? 1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) You rent IT infrastructure like servers and storage from a cloud provider. Example: A company rents virtual servers from Azure to host its website. 2. PaaS (Platform as a Service) You rent both the hardware and the tools needed to build applications. Example: A developer uses Azure App Service to build an app without worrying about servers. 3. SaaS (Software as a Service) You use ready-made software applications online. Example: Using Microsoft 365 Word online without installing anything on your computer. Examples of Cloud Computing You use the cloud daily, often without realizing: Email Services: Example: Gmail or Outlook — emails stored and accessed through the cloud. Media Streaming: Example: Watching Netflix shows or listening to music on Spotify. Social Media: Example: Posting on Instagram or Facebook. Online Storage: Example: Saving documents on Google Drive. Collaboration Tools: Example: Video calls on Zoom or chatting on Microsoft Teams. Advantages of Cloud Computing Why people love the cloud: Cost Efficiency: Pay only for what you use. Speed: Quick setup and access. Scalability and Flexibility: Easily grow or shrink your resources. Performance: Big companies keep their servers fast and up-to-date. Security: Strong protection measures. Automatic Updates: No need to manually update software. Example: Instead of buying a supercomputer, a company uses AWS or Azure’s cloud computing for large projects when needed. Disadvantages of Cloud Computing The cloud has a few downsides: Internet Dependency: You need a good internet connection. Security Risks: While rare, no system is 100% safe. Limited Control: The cloud provider manages many aspects. Possible Downtime: Rare, but cloud services can sometimes go offline. Example: If your internet is down, you can't open your files on Google Drive. Is the Cloud Safe? Top cloud providers like Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, and Google Cloud use: Encryption: Data is scrambled so hackers can't read it. Firewalls: Block bad traffic. Regular Security Checks: Constant improvements. You should also help by using strong passwords and turning on two-factor authentication. Example: Even if someone steals your password, two-factor authentication protects your OneDrive files. The Future of the Cloud Cloud computing is growing fast with new technologies like: Artificial Intelligence (AI) Machine Learning (ML) Internet of Things (IoT) Soon, cloud services will run more parts of our daily lives — smart homes, self-driving cars, and even more. Example: In the future, your fridge could automatically order milk when you're running low — all powered by the cloud!
The cloud means storing and accessing data and programs over the internet instead of your computer’s hard drive. Instead of saving files only on your laptop, you save them online, where you can get them anytime.
Example: Saving your vacation photos on Google Drive so you can open them from your phone, tablet, or computer.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Big companies like Microsoft, Amazon, and Google own huge buildings filled with powerful computers called data centers.
When you use the cloud, your data is stored and processed on these computers.
Why Use the Cloud?
- Access Anywhere: Get your files or apps from any device with internet. Example: Checking work emails from your phone while traveling.
- Cost Savings: No need to buy expensive servers or storage. Example: A startup hosts its website on Azure instead of buying its own servers.
- Scalability: Add or reduce resources easily. Example: An online shop uses more cloud servers during Black Friday sales.
- Security: Cloud providers have strong protection methods. Example: Your bank stores your account information securely in the cloud.
What are Cloud Computing Services?
- Storage: Keeping files online. Example: Backing up photos using Dropbox.
- Databases: Managing large sets of information. Example: Uber stores driver and rider info in cloud databases.
- Computing: Running applications and websites. Example: A business runs its website on Microsoft Azure.
- Networking: Securely connecting services and people. Example: Hosting meetings on Microsoft Teams or Zoom.
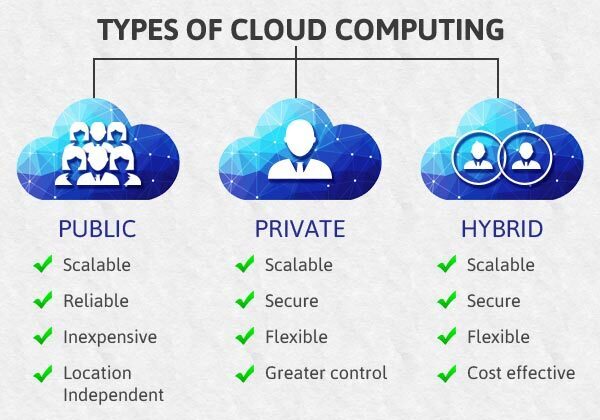
What are Cloud Deployment Models?
- Public Cloud: Services available to anyone over the internet. Example: Storing files on Google Drive.
- Private Cloud: Services for only one organization. Example: A hospital uses a private cloud to store patient data.
- Hybrid Cloud: A mix of public and private clouds. Example: A company keeps sensitive info on a private cloud but uses a public cloud for customer service apps.
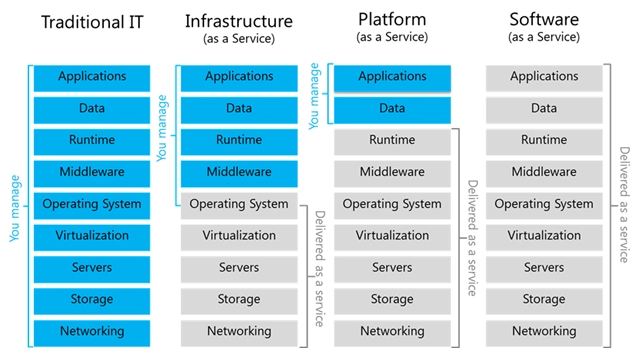
What are Cloud Service Models?
1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- You rent IT infrastructure like servers and storage from a cloud provider.
- Example: A company rents virtual servers from Azure to host its website.
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- You rent both the hardware and the tools needed to build applications.
- Example: A developer uses Azure App Service to build an app without worrying about servers.
3. SaaS (Software as a Service)
- You use ready-made software applications online.
- Example: Using Microsoft 365 Word online without installing anything on your computer.
Examples of Cloud Computing
You use the cloud daily, often without realizing:
- Email Services: Example: Gmail or Outlook — emails stored and accessed through the cloud.
- Media Streaming: Example: Watching Netflix shows or listening to music on Spotify.
- Social Media: Example: Posting on Instagram or Facebook.
- Online Storage: Example: Saving documents on Google Drive.
- Collaboration Tools: Example: Video calls on Zoom or chatting on Microsoft Teams.
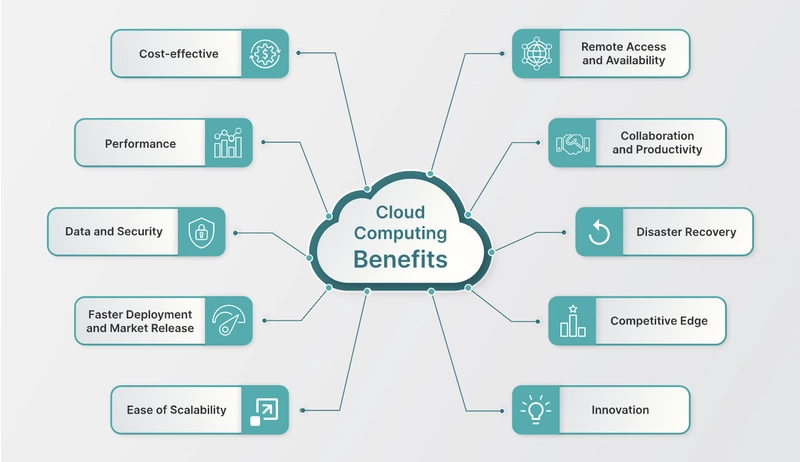
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Why people love the cloud:
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for what you use.
- Speed: Quick setup and access.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Easily grow or shrink your resources.
- Performance: Big companies keep their servers fast and up-to-date.
- Security: Strong protection measures.
- Automatic Updates: No need to manually update software.
Example: Instead of buying a supercomputer, a company uses AWS or Azure’s cloud computing for large projects when needed.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
The cloud has a few downsides:
- Internet Dependency: You need a good internet connection.
- Security Risks: While rare, no system is 100% safe.
- Limited Control: The cloud provider manages many aspects.
- Possible Downtime: Rare, but cloud services can sometimes go offline.
Example: If your internet is down, you can't open your files on Google Drive.
Is the Cloud Safe?
Top cloud providers like Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, and Google Cloud use:
- Encryption: Data is scrambled so hackers can't read it.
- Firewalls: Block bad traffic.
- Regular Security Checks: Constant improvements.
You should also help by using strong passwords and turning on two-factor authentication.
Example: Even if someone steals your password, two-factor authentication protects your OneDrive files.
The Future of the Cloud
Cloud computing is growing fast with new technologies like:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
Soon, cloud services will run more parts of our daily lives — smart homes, self-driving cars, and even more.
Example: In the future, your fridge could automatically order milk when you're running low — all powered by the cloud!






























































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)

























































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] AI and Business Rule Engines for Excel Power Users, Machine Learning Hero & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)








































































































































































































































![Hostinger Horizons lets you effortlessly turn ideas into web apps without coding [10% off]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/04/IMG_1551.png?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)



![This new Google TV streaming dongle looks just like a Chromecast [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/04/thomson-cast-150-google-tv-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)












![Apple Drops New Immersive Adventure Episode for Vision Pro: 'Hill Climb' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97133/97133/97133-640.jpg)

![Most iPhones Sold in the U.S. Will Be Made in India by 2026 [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97130/97130/97130-640.jpg)