Props in React: Passing Data Between Components
What Are Props? Props (short for "properties") are used to pass data from a parent component to a child component in React. Props make components reusable and dynamic. Props are: Immutable (Cannot be changed inside the component) Passed from parent to child Read-only Using Props in Functional Components Example: Passing Props to a Child Component function Greeting(props) { return Hello, {props.name}!; } function App() { return ; } export default App; The Greeting component receives the name prop and displays "Hello, Alice!". Using Props in Class Components (Older Method) import React, { Component } from "react"; class Greeting extends Component { render() { return Hello, {this.props.name}!; } } function App() { return ; } export default App; Functional components are preferred for props handling. Default Props You can set default values for props using defaultProps. Example: Default Props in Functional Components function Greeting({ name = "Guest" }) { return Hello, {name}!; } export default Greeting; or using defaultProps: Greeting.defaultProps = { name: "Guest", }; Props as Objects (props vs. Destructuring) Props are passed as an object. You can access them directly using props or destructure them. Using props object: function User(props) { return {props.name} is {props.age} years old; } Using destructuring: function User({ name, age }) { return {name} is {age} years old; } Destructuring is preferred for cleaner code. Passing Functions as Props Example: Child Component Calls Parent Function function Button({ onClick }) { return Click Me; } function App() { const handleClick = () => { alert("Button clicked!"); }; return ; } export default App; The onClick function is passed from App to Button. Passing Components as Props (children Prop) Props can also include React elements or components. Example: Using children Prop function Card({ children }) { return {children}; } function App() { return ( Title This is content inside the card. ); } export default App; The children prop lets you wrap elements inside a component. Props vs. State (Key Differences) Feature Props ( Passed from Parent) State ( Internal to Component) Mutability Immutable Mutable Where Defined? Parent Component Inside the Component How to Update? Cannot be changed Use useState() Summary Props allow data flow from parent to child. Props are immutable (read-only). Props can be objects, functions, or even React elements. Use children prop to pass JSX inside components.

What Are Props?
Props (short for "properties") are used to pass data from a parent component to a child component in React. Props make components reusable and dynamic.
Props are:
- Immutable (Cannot be changed inside the component)
- Passed from parent to child
- Read-only
Using Props in Functional Components
Example: Passing Props to a Child Component
function Greeting(props) {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}!h1>;
}
function App() {
return <Greeting name="Alice" />;
}
export default App;
The Greeting component receives the name prop and displays "Hello, Alice!".
Using Props in Class Components (Older Method)
import React, { Component } from "react";
class Greeting extends Component {
render() {
return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}!h1>;
}
}
function App() {
return <Greeting name="Alice" />;
}
export default App;
Functional components are preferred for props handling.
Default Props
You can set default values for props using defaultProps.
Example: Default Props in Functional Components
function Greeting({ name = "Guest" }) {
return <h1>Hello, {name}!h1>;
}
export default Greeting;
or using defaultProps:
Greeting.defaultProps = {
name: "Guest",
};
Props as Objects (props vs. Destructuring)
Props are passed as an object. You can access them directly using props or destructure them.
Using props object:
function User(props) {
return <h1>{props.name} is {props.age} years oldh1>;
}
Using destructuring:
function User({ name, age }) {
return <h1>{name} is {age} years oldh1>;
}
Destructuring is preferred for cleaner code.
Passing Functions as Props
Example: Child Component Calls Parent Function
function Button({ onClick }) {
return <button onClick={onClick}>Click Mebutton>;
}
function App() {
const handleClick = () => {
alert("Button clicked!");
};
return <Button onClick={handleClick} />;
}
export default App;
The onClick function is passed from App to Button.
Passing Components as Props (children Prop)
Props can also include React elements or components.
Example: Using children Prop
function Card({ children }) {
return <div className="card">{children}div>;
}
function App() {
return (
<Card>
<h2>Titleh2>
<p>This is content inside the card.p>
Card>
);
}
export default App;
The children prop lets you wrap elements inside a component.
Props vs. State (Key Differences)
| Feature | Props ( Passed from Parent) | State ( Internal to Component) |
|---|---|---|
| Mutability | Immutable | Mutable |
| Where Defined? | Parent Component | Inside the Component |
| How to Update? | Cannot be changed | Use useState()
|
Summary
- Props allow data flow from parent to child.
- Props are immutable (read-only).
- Props can be objects, functions, or even React elements.
-
Use
childrenprop to pass JSX inside components.






































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)

























































































































































![Is This Programming Paradigm New? [closed]](https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:1200/format:webp/1*nKR2930riHA4VC7dLwIuxA.gif)























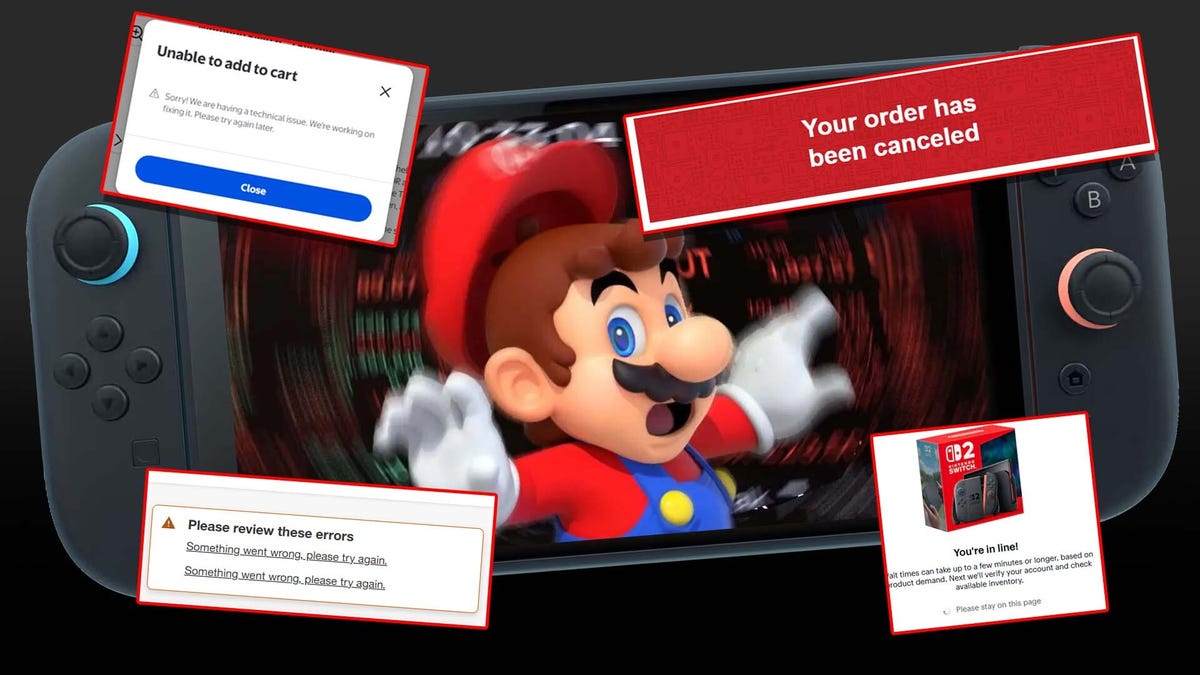

























































(1).jpg?#)
.jpg?#)





-Classic-Nintendo-GameCube-games-are-coming-to-Nintendo-Switch-2!-00-00-13.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
























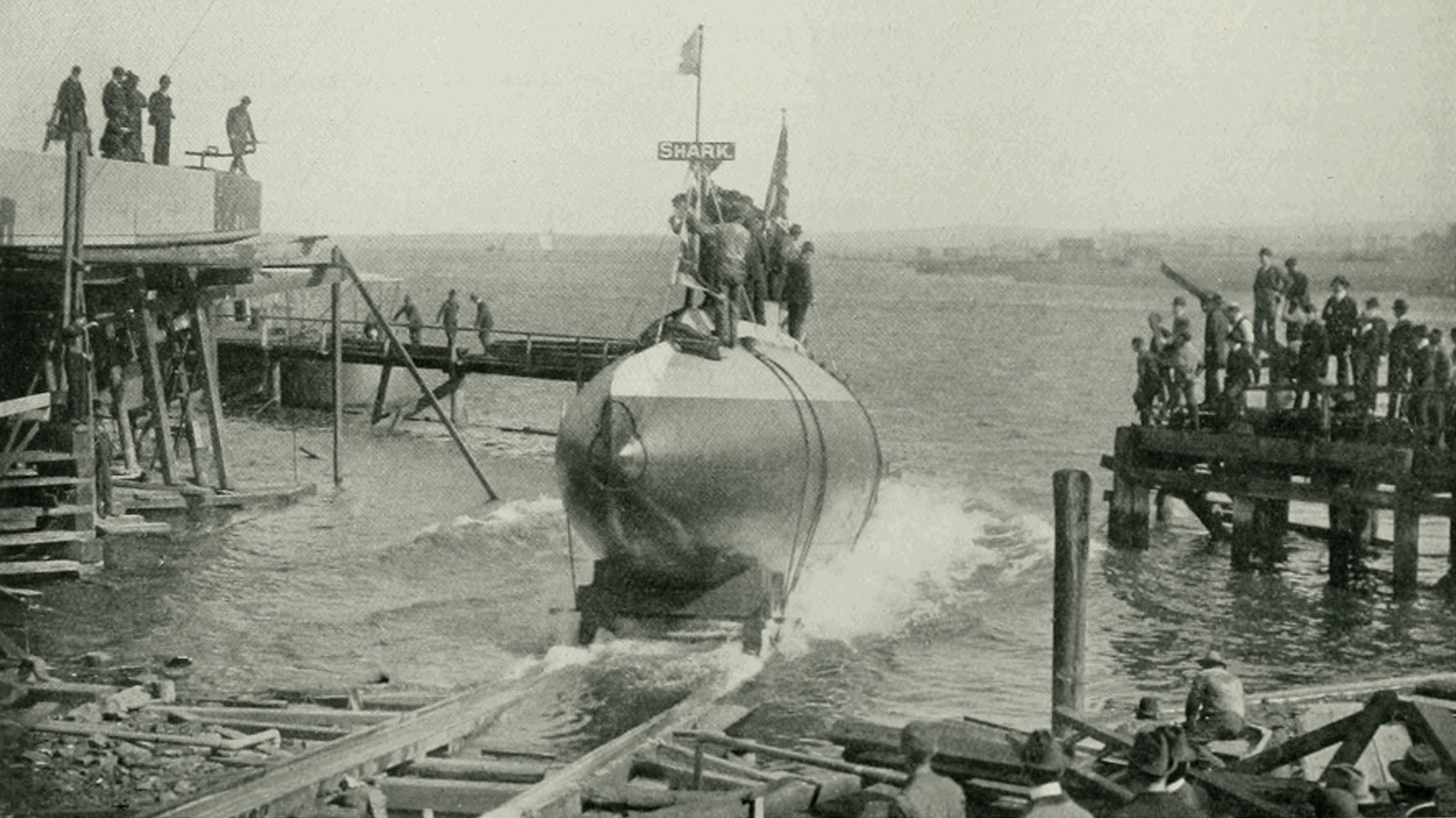
_Olekcii_Mach_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)










































































































![M4 MacBook Air Drops to New All-Time Low of $912 [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97108/97108/97108-640.jpg)
![New iPhone 17 Dummy Models Surface in Black and White [Images]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97106/97106/97106-640.jpg)