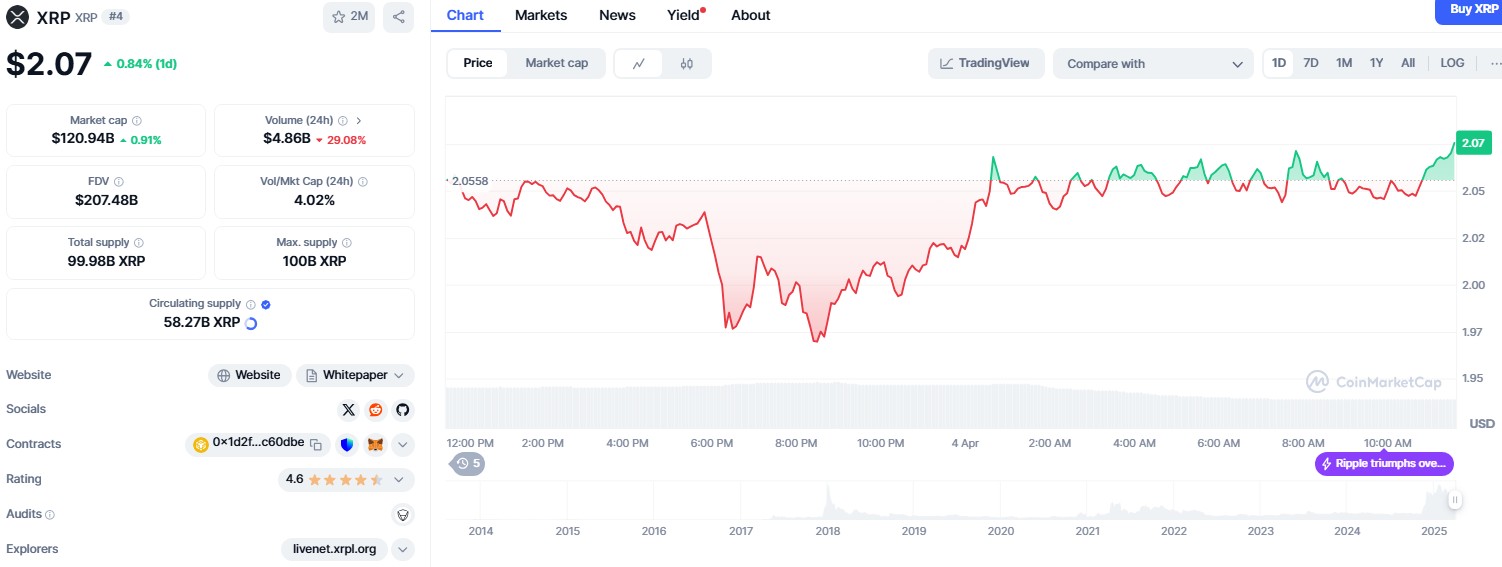
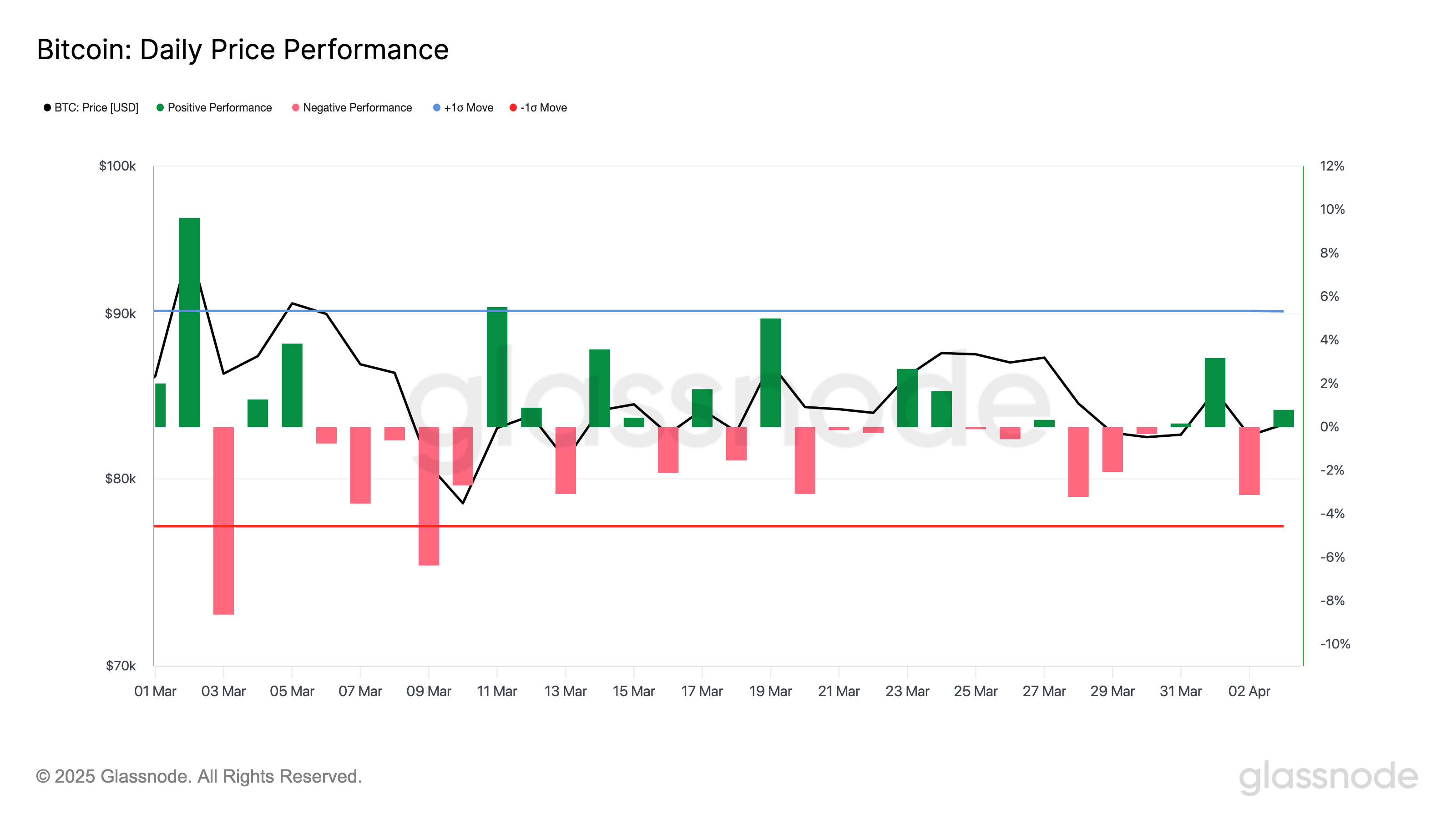
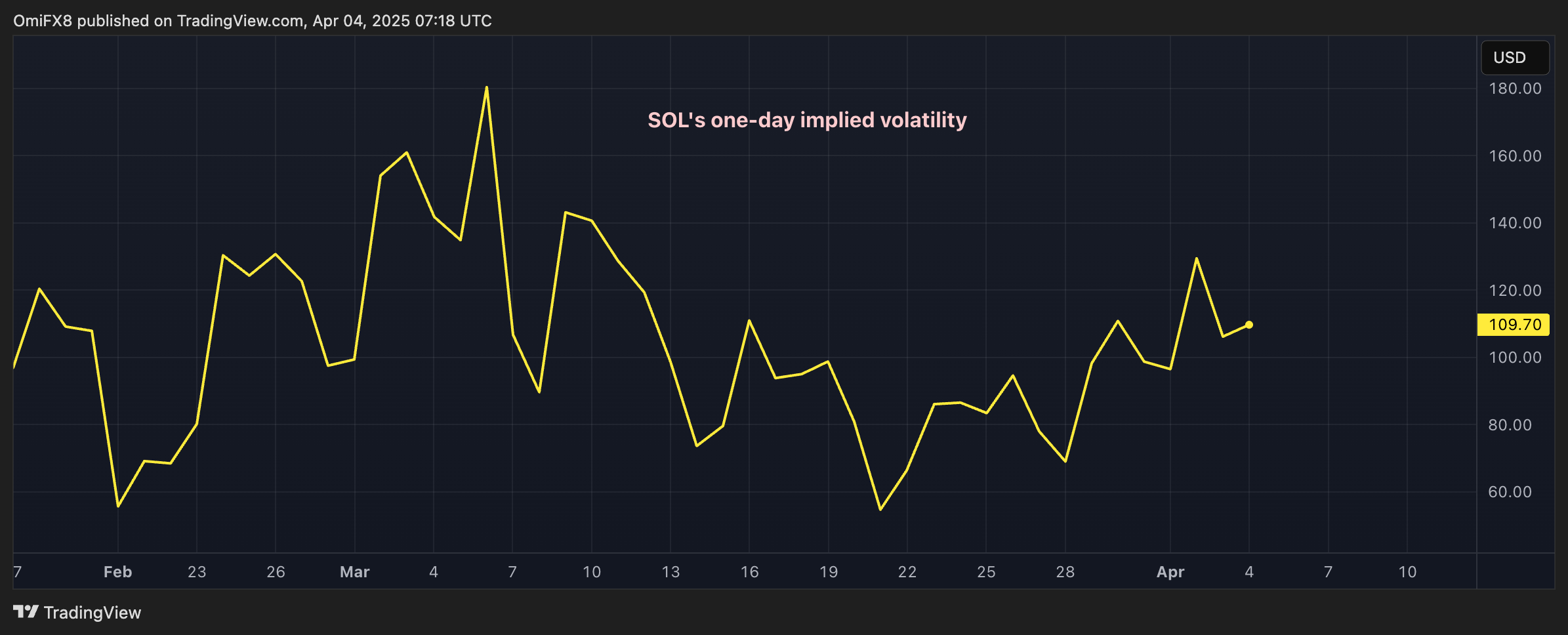
Lightweight Web visualization of forest data using GISBox
GISBox Official Teams: https://teams.live.com/l/invite/FEAr12sInvEVy4hFQE Official Teams Group: https://teams.live.com/l/invite/FBAFp0pbqhqlpe1BQI Geographic information systems (GIS) have become an indispensable tool in modern forestry management and environmental monitoring. By utilizing GIS technology, it is possible not only to accurately locate forest resources, but also to dynamically monitor forest cover changes. GISBox is a professional GIS data processing software, and its terrain tiling function plays an important role in forest cover monitoring. Drone photography and remote sensing image data are tiled into Cesium Terrain format and three-dimensional visualization is realized on the web, providing the forestry sector with a basis for scientific decision-making. Efficient visualization of forest data Forest cover change monitoring uses DSM (digital surface model) and GeoTIFF format terrain data acquired from drones and remote sensing satellites. These data have large file sizes and can be difficult to display directly on the web. However, by utilizing the tiling function of GISBox, these large-scale data can be converted into the lightweight Cesium Terrain format and smoothly visualized in three dimensions on the web platform. Application process Terrain data acquired by drones and satellites in GeoTIFF and DSM formats are imported into GISBox. Select the "Terrain Tile Split" function and set the parameters. After tiling is completed, GISBox will automatically generate a web service address and can be displayed online. Users can check the forest terrain relief and vegetation distribution in a three-dimensional perspective in a web browser. Support forest change monitoring and ecological evaluation In monitoring forest cover changes, terrain and image data from different periods are regularly compared to evaluate the growth, deterioration, and felling status of forests. By using the tile split function of GISBox, data from multiple periods can be converted into Cesium Terrain format, enabling time-series comparative analysis on the web. Application example Monitoring forest degradation: Images taken by a drone in 2020 and 2024 are split into tiles, respectively, to generate three-dimensional terrain models for the two periods. By overlaying them on the web, forest degradation areas can be intuitively visualized and the reduced tree area can be quantified. Evaluation of vegetation recovery: In ecological restoration projects, GISBox displays tiled topographical data from different periods to evaluate the vegetation recovery status. This allows the forestry department to formulate a more scientific ecosystem management strategy. Efficiency through data sharing on the web Traditional GIS data required display on local software, making it difficult to share with other departments. However, GISBox's tiled function converts large-volume topographical data into a lightweight Cesium Terrain format and generates a web service address, allowing it to be displayed and operated directly in a browser. Main benefits Lightweight and fast display: Tiled Cesium Terrain is lightweight and can be loaded quickly on the web, so even large-scale topographical data can be displayed smoothly. Easy inter-departmental collaboration: The forestry department can share the generated web address with other agencies, enabling remote collaboration. Multi-device support: Forest cover changes can be confirmed not only from PCs but also from tablets and smartphones, allowing work to be done anywhere. Summary GISBox's terrain tile division function is a powerful tool for forest cover change monitoring. It efficiently converts terrain data acquired by drones or remote sensing into Cesium Terrain format and enables 3D visualization on the web. It can be used in a variety of scenarios such as forest degradation monitoring, vegetation recovery evaluation, forest district planning, and disaster prevention measures, greatly improving the efficiency of data processing and the scientific nature of decision-making.

GISBox Official Teams: https://teams.live.com/l/invite/FEAr12sInvEVy4hFQE
Official Teams Group: https://teams.live.com/l/invite/FBAFp0pbqhqlpe1BQI
Geographic information systems (GIS) have become an indispensable tool in modern forestry management and environmental monitoring. By utilizing GIS technology, it is possible not only to accurately locate forest resources, but also to dynamically monitor forest cover changes.
GISBox is a professional GIS data processing software, and its terrain tiling function plays an important role in forest cover monitoring. Drone photography and remote sensing image data are tiled into Cesium Terrain format and three-dimensional visualization is realized on the web, providing the forestry sector with a basis for scientific decision-making.
- Efficient visualization of forest data Forest cover change monitoring uses DSM (digital surface model) and GeoTIFF format terrain data acquired from drones and remote sensing satellites.
These data have large file sizes and can be difficult to display directly on the web. However, by utilizing the tiling function of GISBox, these large-scale data can be converted into the lightweight Cesium Terrain format and smoothly visualized in three dimensions on the web platform.
Application process
Terrain data acquired by drones and satellites in GeoTIFF and DSM formats are imported into GISBox.
Select the "Terrain Tile Split" function and set the parameters.
After tiling is completed, GISBox will automatically generate a web service address and can be displayed online.
Users can check the forest terrain relief and vegetation distribution in a three-dimensional perspective in a web browser.
- Support forest change monitoring and ecological evaluation In monitoring forest cover changes, terrain and image data from different periods are regularly compared to evaluate the growth, deterioration, and felling status of forests.
By using the tile split function of GISBox, data from multiple periods can be converted into Cesium Terrain format, enabling time-series comparative analysis on the web.
Application example
Monitoring forest degradation:
Images taken by a drone in 2020 and 2024 are split into tiles, respectively, to generate three-dimensional terrain models for the two periods. By overlaying them on the web, forest degradation areas can be intuitively visualized and the reduced tree area can be quantified.
Evaluation of vegetation recovery:
In ecological restoration projects, GISBox displays tiled topographical data from different periods to evaluate the vegetation recovery status. This allows the forestry department to formulate a more scientific ecosystem management strategy.
- Efficiency through data sharing on the web Traditional GIS data required display on local software, making it difficult to share with other departments. However, GISBox's tiled function converts large-volume topographical data into a lightweight Cesium Terrain format and generates a web service address, allowing it to be displayed and operated directly in a browser.
Main benefits
Lightweight and fast display: Tiled Cesium Terrain is lightweight and can be loaded quickly on the web, so even large-scale topographical data can be displayed smoothly.
Easy inter-departmental collaboration: The forestry department can share the generated web address with other agencies, enabling remote collaboration.
Multi-device support: Forest cover changes can be confirmed not only from PCs but also from tablets and smartphones, allowing work to be done anywhere.
Summary
GISBox's terrain tile division function is a powerful tool for forest cover change monitoring.
It efficiently converts terrain data acquired by drones or remote sensing into Cesium Terrain format and enables 3D visualization on the web.
It can be used in a variety of scenarios such as forest degradation monitoring, vegetation recovery evaluation, forest district planning, and disaster prevention measures, greatly improving the efficiency of data processing and the scientific nature of decision-making.










































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)












































































































































































































































.jpg?#)





















































































































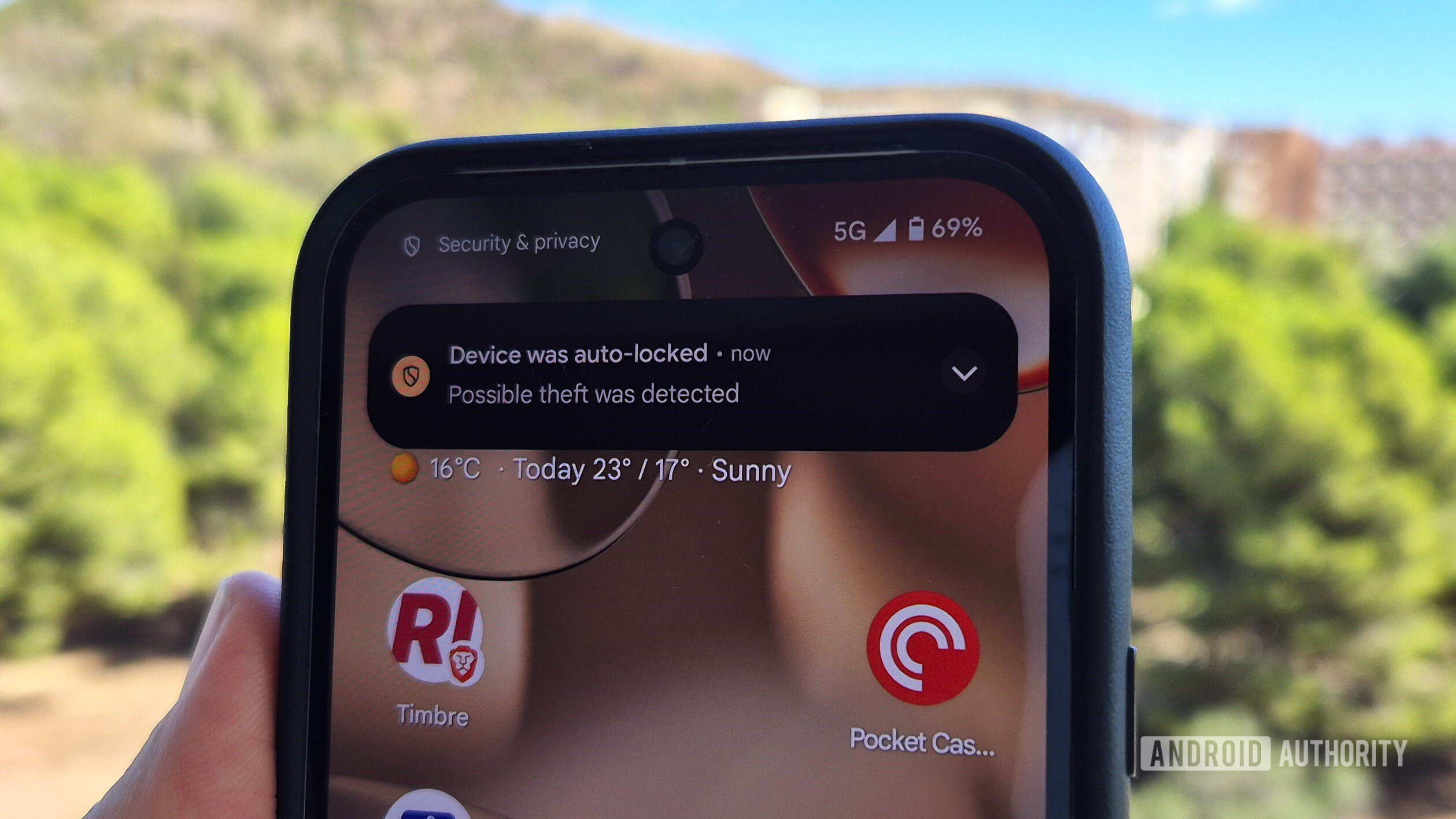




















![YouTube Announces New Creation Tools for Shorts [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96923/96923/96923-640.jpg)

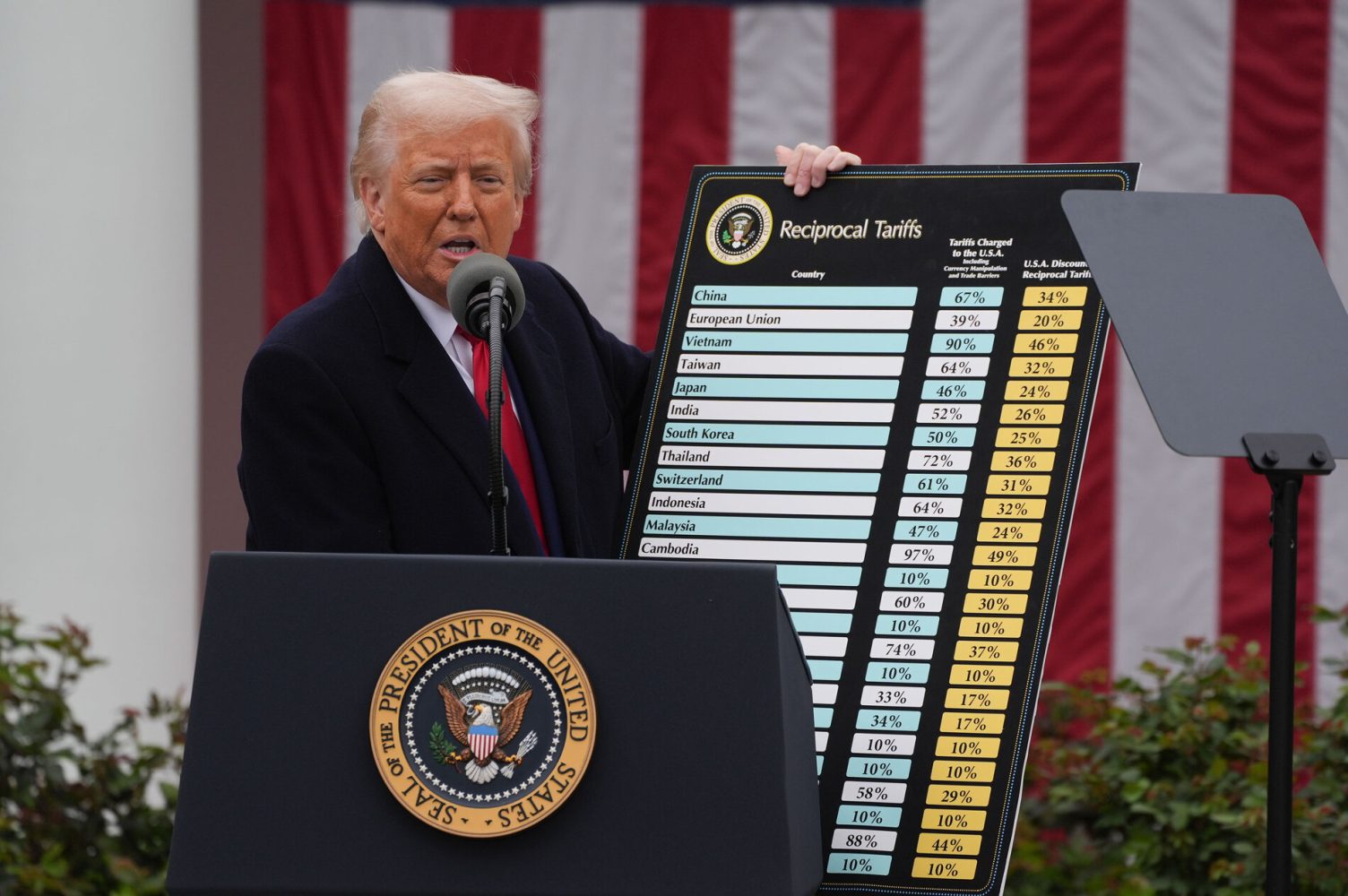
![Apple Faces New Tariffs but Has Options to Soften the Blow [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96921/96921/96921-640.jpg)