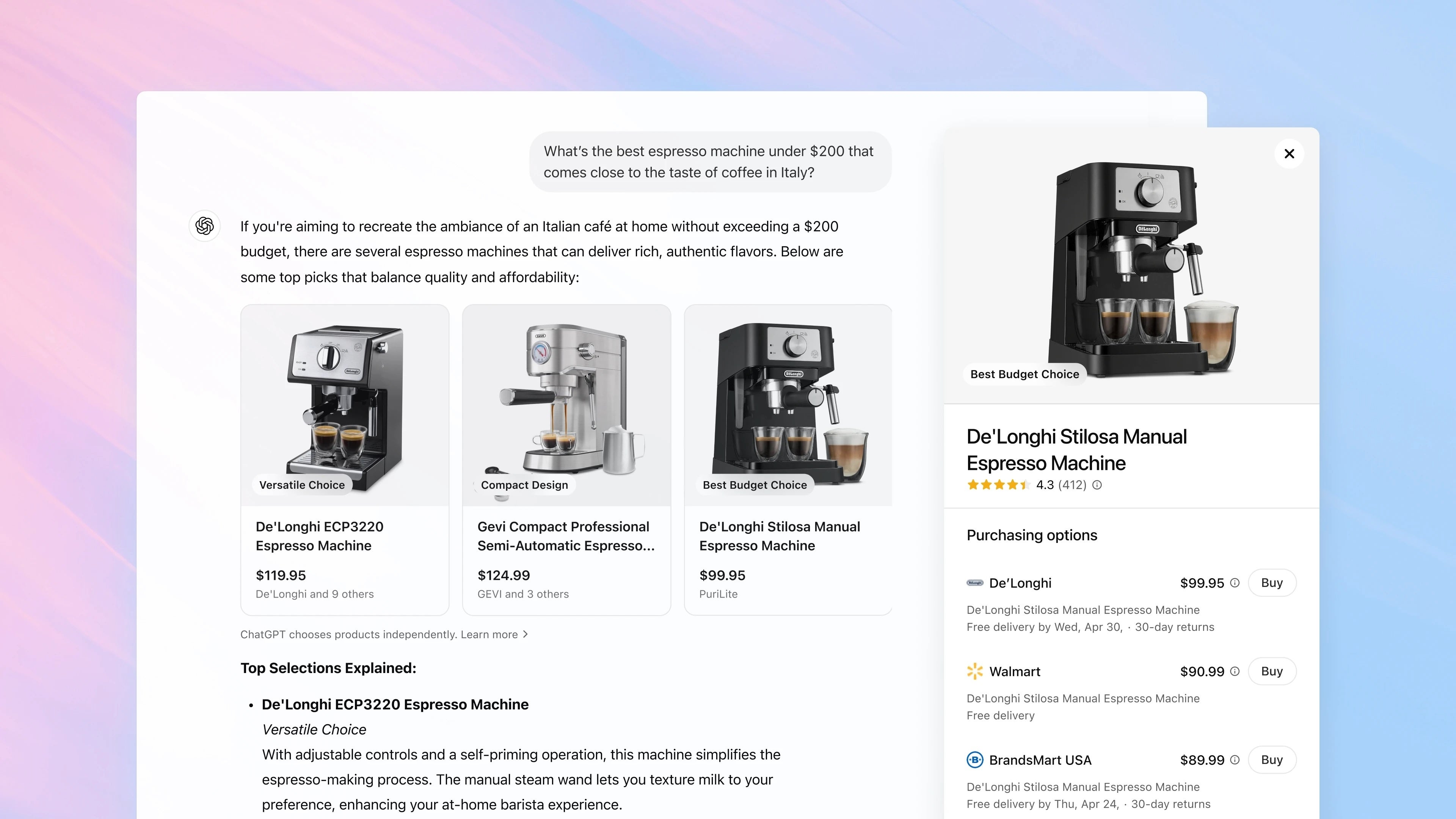
How to get a free AWS SSL certificate for your service
You've set up your web service on AWS, placed it behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB), and successfully pointed your custom domain (like www.your-app.com) to the ALB using your DNS provider. Great! The next crucial step is enabling HTTPS to secure the traffic between your users and your service. Fortunately, AWS provides free public SSL/TLS certificates through AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) that integrate seamlessly with ALBs. This guide shows you exactly how to request one and configure your existing ALB to use it. Scenario: You have a web server (e.g., on EC2) running your application. An AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) routes traffic to your web server. Your custom domain (e.g., yourdomain.com) already has a DNS record (like CNAME or ALIAS) pointing to the ALB's DNS name. You want to enable https://yourdomain.com. Prerequisites Existing AWS ALB. Access to manage your domain’s DNS settings (e.g., Route 53, Cloudflare, GoDaddy). Steps 1. Request SSL/TLS Certificate (ACM) Open AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) in the same region as your ALB. Request a public certificate for your domain (wildcards like *.yourdomain.com are supported). Validate ownership: DNS Validation (Recommended): Add ACM-provided CNAME to your DNS. Email Validation: (Alternative) Approve via domain contact email. Once you have added the values to prove your ownership. Wait for the certificate status to show Issued. 2. Configure ALB HTTPS Listener Go to EC2 → Load Balancers. Select your ALB → Listeners tab. Add or edit HTTPS listener: Protocol: HTTPS Port: 443 Default Action: Forward to target group. Select your target group. SSL Certificate: Select the ACM certificate Security Policy: Choose a modern policy (e.g., ELBSecurityPolicy-TLS13-1-2-2021-06) Default SSL/TLS server certificate: Choose from ACM and select the certificate that was requested. 3. Get ALB DNS Name Find the ALB’s DNS name (e.g., your-alb-name-1234567890.region.elb.amazonaws.com) under ALB details. 4. Update DNS Records Depending on where you want SSL: Subdomain (e.g., app.yourdomain.com): Create a CNAME pointing to the ALB DNS name. Root domain (e.g., yourdomain.com): Route 53: Create an Alias A record pointing to the ALB. Other DNS providers: Use ANAME or CNAME Flattening if supported. Note: CNAMEs are not allowed directly at root domains without ALIAS/ANAME/Flattening. 5. Verify Setup Wait for DNS propagation. Use tools like dig or nslookup: dig www.yourdomain.com dig yourdomain.com Visit your domain via HTTPS and check for a valid SSL certificate. By following these steps, your domain is now securely accessible over HTTPS through AWS ALB.
You've set up your web service on AWS, placed it behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB), and successfully pointed your custom domain (like www.your-app.com) to the ALB using your DNS provider. Great! The next crucial step is enabling HTTPS to secure the traffic between your users and your service.
Fortunately, AWS provides free public SSL/TLS certificates through AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) that integrate seamlessly with ALBs. This guide shows you exactly how to request one and configure your existing ALB to use it.
Scenario:
- You have a web server (e.g., on EC2) running your application.
- An AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) routes traffic to your web server.
- Your custom domain (e.g.,
yourdomain.com) already has a DNS record (like CNAME or ALIAS) pointing to the ALB's DNS name. - You want to enable
https://yourdomain.com.
Prerequisites
- Existing AWS ALB.
- Access to manage your domain’s DNS settings (e.g., Route 53, Cloudflare, GoDaddy).
Steps
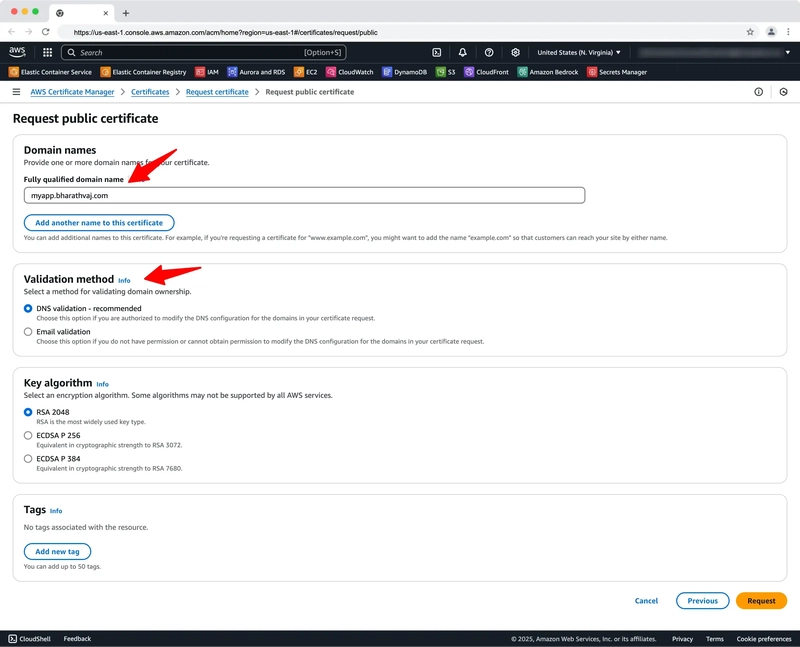
1. Request SSL/TLS Certificate (ACM)
- Open AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) in the same region as your ALB.
- Request a public certificate for your domain (wildcards like
*.yourdomain.comare supported).
-
Validate ownership:
- DNS Validation (Recommended): Add ACM-provided CNAME to your DNS.
- Email Validation: (Alternative) Approve via domain contact email.
Once you have added the values to prove your ownership. Wait for the certificate status to show Issued.
2. Configure ALB HTTPS Listener
- Go to EC2 → Load Balancers.
- Select your ALB → Listeners tab.
- Add or edit HTTPS listener:
- Protocol: HTTPS
- Port: 443
- Default Action: Forward to target group. Select your target group.
- SSL Certificate: Select the ACM certificate
-
Security Policy: Choose a modern policy (e.g.,
ELBSecurityPolicy-TLS13-1-2-2021-06) - Default SSL/TLS server certificate: Choose from ACM and select the certificate that was requested.
3. Get ALB DNS Name
- Find the ALB’s DNS name (e.g.,
your-alb-name-1234567890.region.elb.amazonaws.com) under ALB details.
4. Update DNS Records
Depending on where you want SSL:
-
Subdomain (e.g.,
app.yourdomain.com):- Create a CNAME pointing to the ALB DNS name.
-
Root domain (e.g.,
yourdomain.com):- Route 53: Create an Alias A record pointing to the ALB.
- Other DNS providers: Use ANAME or CNAME Flattening if supported.
Note: CNAMEs are not allowed directly at root domains without ALIAS/ANAME/Flattening.
5. Verify Setup
- Wait for DNS propagation.
- Use tools like
digornslookup:
dig www.yourdomain.com
dig yourdomain.com
- Visit your domain via HTTPS and check for a valid SSL certificate.
By following these steps, your domain is now securely accessible over HTTPS through AWS ALB.















































.jpg)
















































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)













































































































































































.jpg?#)































































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)


























_Muhammad_R._Fakhrurrozi_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
























































































![macOS 15.5 beta 4 now available for download [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/04/macOS-Sequoia-15.5-b4.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)
















![AirPods Pro 2 With USB-C Back On Sale for Just $169! [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96315/96315/96315-640.jpg)
![Apple Releases iOS 18.5 Beta 4 and iPadOS 18.5 Beta 4 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97145/97145/97145-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds watchOS 11.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97147/97147/97147-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds visionOS 2.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97150/97150/97150-640.jpg)





































![Apple Seeds Fourth Beta of iOS 18.5 to Developers [Update: Public Beta Available]](https://images.macrumors.com/t/uSxxRefnKz3z3MK1y_CnFxSg8Ak=/2500x/article-new/2025/04/iOS-18.5-Feature-Real-Mock.jpg)
![Apple Seeds Fourth Beta of macOS Sequoia 15.5 [Update: Public Beta Available]](https://images.macrumors.com/t/ne62qbjm_V5f4GG9UND3WyOAxE8=/2500x/article-new/2024/08/macOS-Sequoia-Night-Feature.jpg)