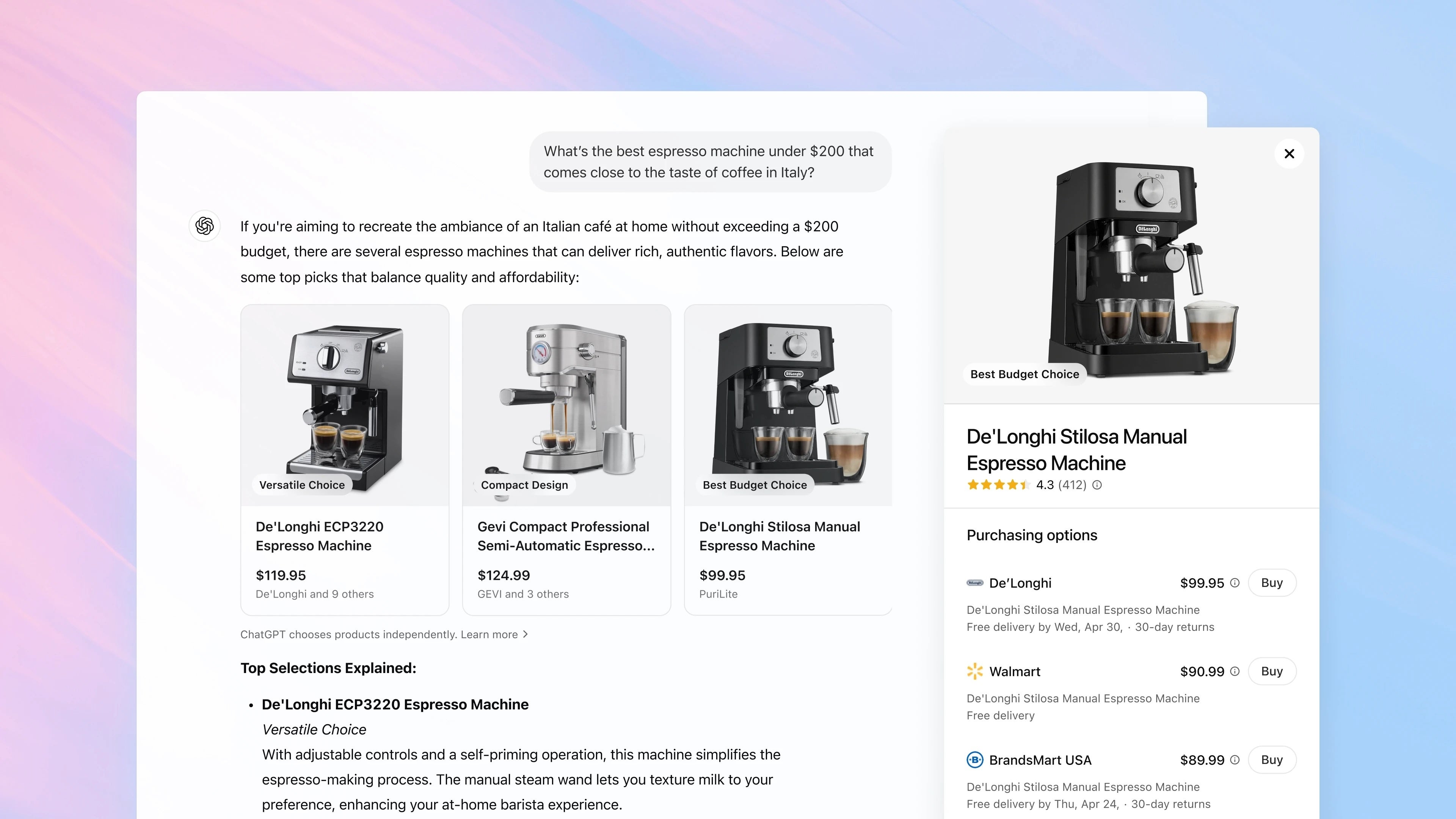
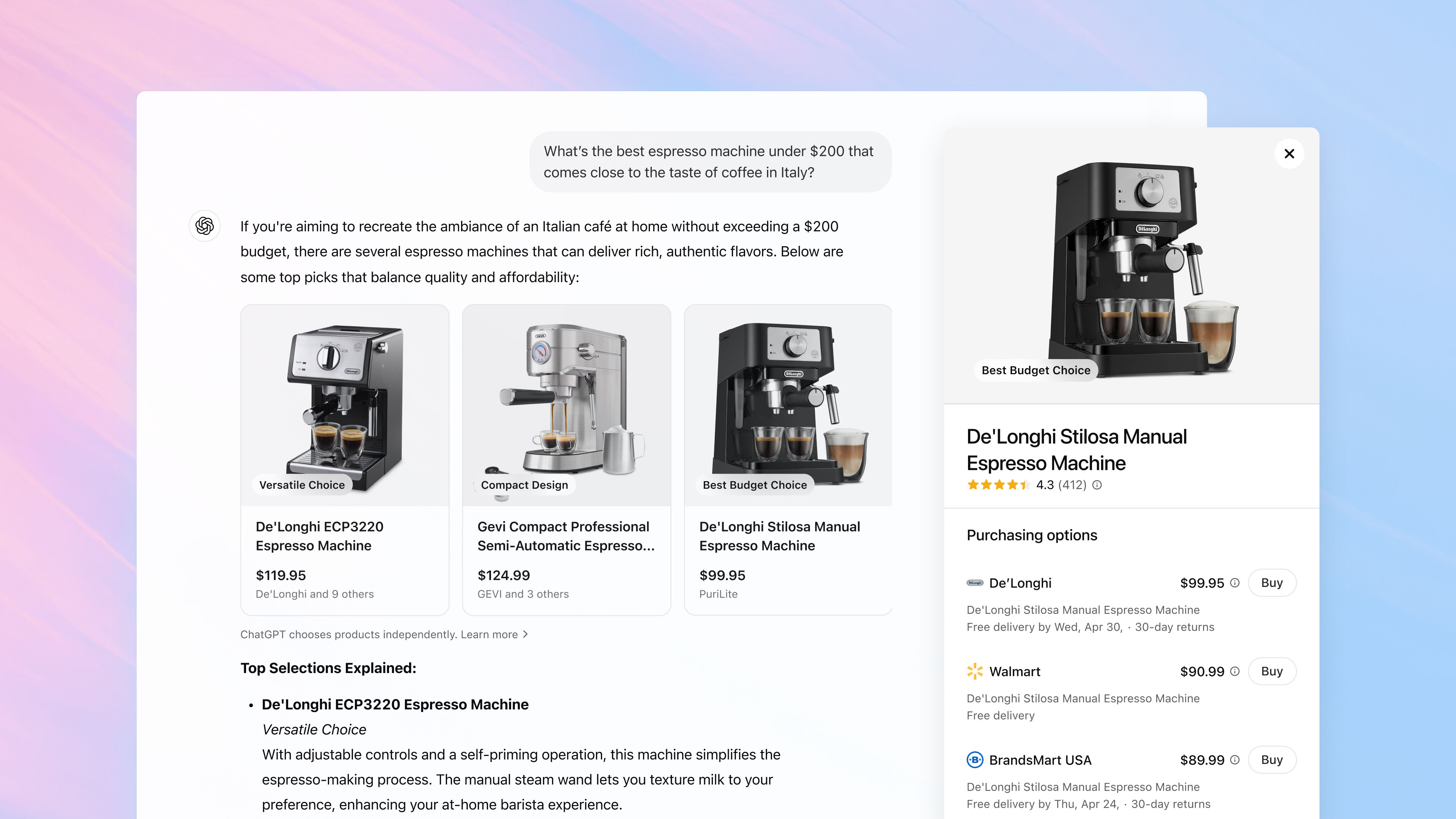
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Speeding Up the Web Introduction: Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are geographically distributed groups of servers that work together to deliver content to users based on their proximity. This significantly reduces latency and improves the speed of website loading, video streaming, and other online services. Prerequisites: Implementing a CDN typically requires a website or application with substantial amounts of static content (images, CSS, JavaScript, videos) and a significant user base geographically dispersed across various regions. You'll need to choose a CDN provider and integrate their service with your website or application, often involving DNS configuration changes. Advantages: Reduced Latency: Content is served from a server closer to the user, resulting in faster loading times. Improved Performance: Faster loading times lead to better user experience, higher conversion rates, and improved SEO rankings. Increased Scalability: CDNs can easily handle traffic spikes, ensuring website availability during peak times. Enhanced Security: Many CDNs offer features like DDoS protection and SSL encryption, safeguarding your content and users. Cost Savings: By reducing server load on your origin server, CDNs can reduce infrastructure costs. Disadvantages: Cost: CDN services are not free; costs vary depending on usage and features. Caching Issues: Outdated content can be served from a CDN cache if not properly invalidated, leading to inconsistencies. Complexity: Setting up and managing a CDN can be complex, requiring technical expertise. Vendor Lock-in: Migrating from one CDN provider to another can be challenging. Features: CDNs typically offer features like: Caching: Storing frequently accessed content on edge servers. Load Balancing: Distributing traffic across multiple servers. HTTPS Support: Ensuring secure connections. Real-time Monitoring and Analytics: Providing insights into CDN performance. Conclusion: CDNs are crucial for delivering high-performance online experiences. While there are some disadvantages to consider, the benefits of reduced latency, improved scalability, and enhanced security significantly outweigh them for websites and applications with substantial content and a broad user base. Choosing the right CDN provider and properly configuring its services is key to maximizing its benefits.

Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Speeding Up the Web
Introduction:
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are geographically distributed groups of servers that work together to deliver content to users based on their proximity. This significantly reduces latency and improves the speed of website loading, video streaming, and other online services.
Prerequisites:
Implementing a CDN typically requires a website or application with substantial amounts of static content (images, CSS, JavaScript, videos) and a significant user base geographically dispersed across various regions. You'll need to choose a CDN provider and integrate their service with your website or application, often involving DNS configuration changes.
Advantages:
- Reduced Latency: Content is served from a server closer to the user, resulting in faster loading times.
- Improved Performance: Faster loading times lead to better user experience, higher conversion rates, and improved SEO rankings.
- Increased Scalability: CDNs can easily handle traffic spikes, ensuring website availability during peak times.
- Enhanced Security: Many CDNs offer features like DDoS protection and SSL encryption, safeguarding your content and users.
- Cost Savings: By reducing server load on your origin server, CDNs can reduce infrastructure costs.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: CDN services are not free; costs vary depending on usage and features.
- Caching Issues: Outdated content can be served from a CDN cache if not properly invalidated, leading to inconsistencies.
- Complexity: Setting up and managing a CDN can be complex, requiring technical expertise.
- Vendor Lock-in: Migrating from one CDN provider to another can be challenging.
Features:
CDNs typically offer features like:
- Caching: Storing frequently accessed content on edge servers.
- Load Balancing: Distributing traffic across multiple servers.
- HTTPS Support: Ensuring secure connections.
- Real-time Monitoring and Analytics: Providing insights into CDN performance.
Conclusion:
CDNs are crucial for delivering high-performance online experiences. While there are some disadvantages to consider, the benefits of reduced latency, improved scalability, and enhanced security significantly outweigh them for websites and applications with substantial content and a broad user base. Choosing the right CDN provider and properly configuring its services is key to maximizing its benefits.















































.jpg)
















































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)













































































































































































.jpg?#)































































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)


























_Muhammad_R._Fakhrurrozi_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
























































































![macOS 15.5 beta 4 now available for download [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/04/macOS-Sequoia-15.5-b4.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)
















![AirPods Pro 2 With USB-C Back On Sale for Just $169! [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96315/96315/96315-640.jpg)
![Apple Releases iOS 18.5 Beta 4 and iPadOS 18.5 Beta 4 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97145/97145/97145-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds watchOS 11.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97147/97147/97147-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds visionOS 2.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97150/97150/97150-640.jpg)





































![Apple Seeds Fourth Beta of iOS 18.5 to Developers [Update: Public Beta Available]](https://images.macrumors.com/t/uSxxRefnKz3z3MK1y_CnFxSg8Ak=/2500x/article-new/2025/04/iOS-18.5-Feature-Real-Mock.jpg)
![Apple Seeds Fourth Beta of macOS Sequoia 15.5 [Update: Public Beta Available]](https://images.macrumors.com/t/ne62qbjm_V5f4GG9UND3WyOAxE8=/2500x/article-new/2024/08/macOS-Sequoia-Night-Feature.jpg)