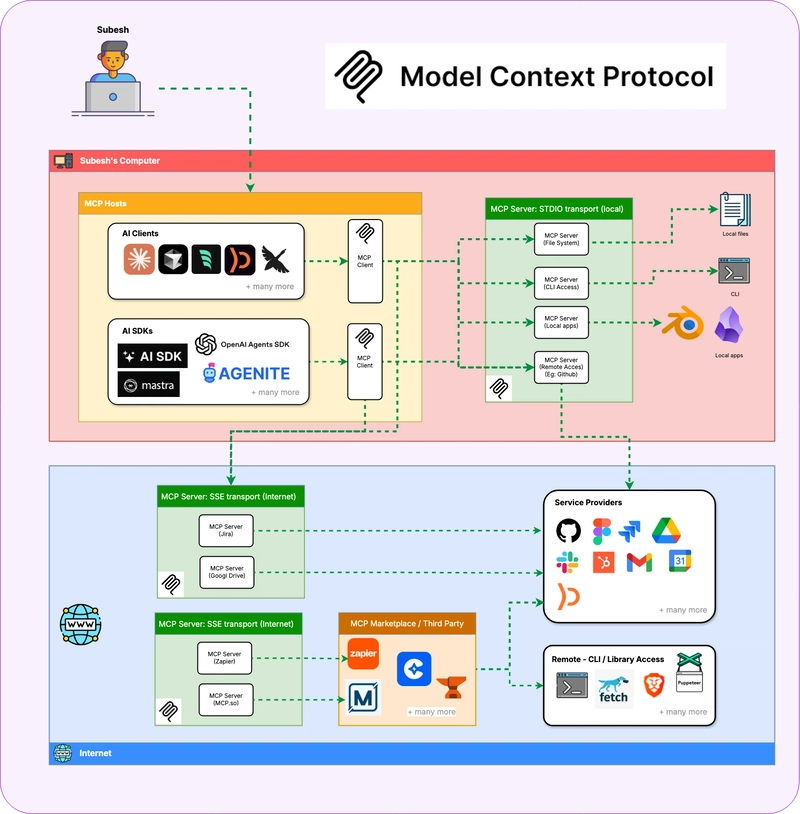
Building a REST API with Django REST Framework: A Beginners Guide
Introduction Imagine you're building a book management system where users can browse available books and add new ones. To make this possible, we need a REST API to handle book data efficiently. REST APIs are the backbone of modern web applications, enabling seamless communication between frontend and backend systems. Django REST Framework (DRF) simplifies API development by providing a powerful toolkit built on top of Django. In this guide, we'll build a simple REST API to manage books. Prerequisites Before starting this tutorial, you should have: ✅ Basic understanding of Python programming ✅ Familiarity with web development concepts ✅ Python 3.8+ installed on your system ✅ Basic knowledge of the Django framework ✅ Understanding of HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) ✅ Experience using the command-line interface Learning Objectives By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to: ✅ Set up a Django REST Framework project from scratch ✅ Create API endpoints using function-based views (FBVs) and class-based views (CBVs) ✅ Implement model serialization for JSON responses ✅ Perform CRUD operations via a REST API ✅ Test API endpoints using browsable API and cURL commands Why Django REST Framework? Django REST Framework has become the go-to choice for building APIs with Django because it offers: ✔️ Powerful serialization capabilities ✔️ Built-in authentication and permissions ✔️ Browsable API interface for easy testing ✔️ Extensive documentation and strong community support ✔️ Flexible request/response handling ✔️ Support for pagination, filtering, and throttling Project Setup Let’s start building our REST API step by step. Step 1: Environment Setup First, create a clean development environment: # Create a project folder mkdir book-api && cd book-api # Create a virtual environment python -m venv venv # Activate the virtual environment (Windows) venv\Scripts\activate # Activate the virtual environment (Mac/Linux) source venv/bin/activate # Install Django and Django REST Framework pip install django djangorestframework Step 2: Project Creation Now, create a Django project and an app for managing books. # Create a Django project django-admin startproject bookapi cd bookapi # Create a Django app python manage.py startapp books Step 3: Configuration Register Django REST Framework and the books app in settings.py: INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', # Third-party apps 'rest_framework', # Local apps 'books', ] Building the API Step 4: Model Definition Define a Book model in books/models.py: from django.db import models class Book(models.Model): title = models.CharField(max_length=255) author = models.CharField(max_length=255) published_date = models.DateField() isbn = models.CharField(max_length=13, unique=True) def __str__(self): return self.title Apply the migrations: python manage.py makemigrations books python manage.py migrate Step 5: Serializer Creation Create books/serializers.py to handle data conversion: from rest_framework import serializers from .models import Book class BookSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): class Meta: model = Book fields = '__all__' Step 6: API Views We'll implement both function-based views (FBVs) and class-based views (CBVs). Function-Based Views (FBVs) Edit books/views.py: from rest_framework.response import Response from rest_framework.decorators import api_view from .models import Book from .serializers import BookSerializer @api_view(['GET']) def book_list(request): books = Book.objects.all() serializer = BookSerializer(books, many=True) return Response(serializer.data) @api_view(['POST']) def book_create(request): serializer = BookSerializer(data=request.data) if serializer.is_valid(): serializer.save() return Response(serializer.data, status=201) return Response(serializer.errors, status=400) Class-Based Views (CBVs) For a more scalable approach, use Django REST Framework’s generic views: from rest_framework import generics from .models import Book from .serializers import BookSerializer class BookListCreateView(generics.ListCreateAPIView): queryset = Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer Step 7: URL Configuration Set up books/urls.py: from django.urls import path from .views import book_list, book_create, BookListCreateView urlpatterns = [ # Function-based views path('books/', book_list, name='book-list'), path('books/create/', book_create, name='book-create'), # Class-based views path('books/cbv/', BookListCreateView.as_view(), name='book-list-cbv'), ] **Update bookapi/urls.py:

Introduction
Imagine you're building a book management system where users can browse available books and add new ones. To make this possible, we need a REST API to handle book data efficiently.
REST APIs are the backbone of modern web applications, enabling seamless communication between frontend and backend systems. Django REST Framework (DRF) simplifies API development by providing a powerful toolkit built on top of Django. In this guide, we'll build a simple REST API to manage books.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, you should have:
✅ Basic understanding of Python programming
✅ Familiarity with web development concepts
✅ Python 3.8+ installed on your system
✅ Basic knowledge of the Django framework
✅ Understanding of HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
✅ Experience using the command-line interface
Learning Objectives
By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to:
✅ Set up a Django REST Framework project from scratch
✅ Create API endpoints using function-based views (FBVs) and class-based views (CBVs)
✅ Implement model serialization for JSON responses
✅ Perform CRUD operations via a REST API
✅ Test API endpoints using browsable API and cURL commands
Why Django REST Framework?
Django REST Framework has become the go-to choice for building APIs with Django because it offers:
✔️ Powerful serialization capabilities
✔️ Built-in authentication and permissions
✔️ Browsable API interface for easy testing
✔️ Extensive documentation and strong community support
✔️ Flexible request/response handling
✔️ Support for pagination, filtering, and throttling
Project Setup
Let’s start building our REST API step by step.
Step 1: Environment Setup
First, create a clean development environment:
# Create a project folder
mkdir book-api && cd book-api
# Create a virtual environment
python -m venv venv
# Activate the virtual environment (Windows)
venv\Scripts\activate
# Activate the virtual environment (Mac/Linux)
source venv/bin/activate
# Install Django and Django REST Framework
pip install django djangorestframework
Step 2: Project Creation
Now, create a Django project and an app for managing books.
# Create a Django project
django-admin startproject bookapi
cd bookapi
# Create a Django app
python manage.py startapp books
Step 3: Configuration
Register Django REST Framework and the books app in settings.py:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
# Third-party apps
'rest_framework',
# Local apps
'books',
]
Building the API
Step 4: Model Definition
Define a Book model in books/models.py:
from django.db import models
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=255)
author = models.CharField(max_length=255)
published_date = models.DateField()
isbn = models.CharField(max_length=13, unique=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.title
Apply the migrations:
python manage.py makemigrations books
python manage.py migrate
Step 5: Serializer Creation
Create books/serializers.py to handle data conversion:
from rest_framework import serializers
from .models import Book
class BookSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Book
fields = '__all__'
Step 6: API Views
We'll implement both function-based views (FBVs) and class-based views (CBVs).
Function-Based Views (FBVs)
Edit books/views.py:
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.decorators import api_view
from .models import Book
from .serializers import BookSerializer
@api_view(['GET'])
def book_list(request):
books = Book.objects.all()
serializer = BookSerializer(books, many=True)
return Response(serializer.data)
@api_view(['POST'])
def book_create(request):
serializer = BookSerializer(data=request.data)
if serializer.is_valid():
serializer.save()
return Response(serializer.data, status=201)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=400)
Class-Based Views (CBVs)
For a more scalable approach, use Django REST Framework’s generic views:
from rest_framework import generics
from .models import Book
from .serializers import BookSerializer
class BookListCreateView(generics.ListCreateAPIView):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookSerializer
Step 7: URL Configuration
Set up books/urls.py:
from django.urls import path
from .views import book_list, book_create, BookListCreateView
urlpatterns = [
# Function-based views
path('books/', book_list, name='book-list'),
path('books/create/', book_create, name='book-create'),
# Class-based views
path('books/cbv/', BookListCreateView.as_view(), name='book-list-cbv'),
]
**Update bookapi/urls.py:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('api/', include('books.urls')),
]
Testing the API
Using Browsable API
Run the server and visit:











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)























.webp?#)










_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)




































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)