3375. Minimum Operations to Make Array Values Equal to K
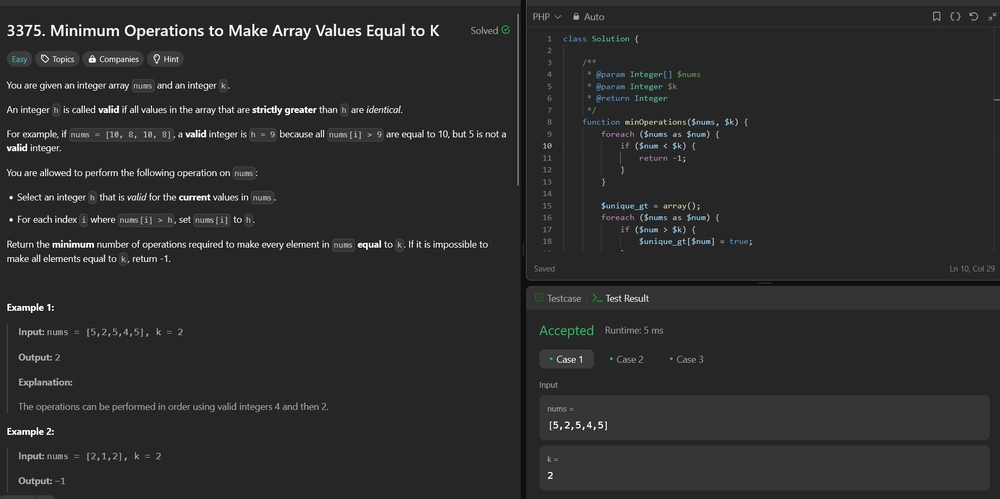
3375. Minimum Operations to Make Array Values Equal to K Difficulty: Easy Topics: Array, Hash Table You are given an integer array nums and an integer k. An integer h is called valid if all values in the array that are strictly greater than h are identical. For example, if nums = [10, 8, 10, 8], a valid integer is h = 9 because all nums[i] > 9 are equal to 10, but 5 is not a valid integer. You are allowed to perform the following operation on nums: Select an integer h that is valid for the current values in nums. For each index i where nums[i] > h, set nums[i] to h. Return the minimum number of operations required to make every element in nums equal to k. If it is impossible to make all elements equal to k, return -1. Example 1: Input: nums = [5,2,5,4,5], k = 2 Output: 2 Explanation: The operations can be performed in order using valid integers 4 and then 2. Example 2: Input: nums = [2,1,2], k = 2 Output: -1 Explanation: It is impossible to make all the values equal to 2. Example 3: Input: nums = [9,7,5,3], k = 1 Output: 4 Explanation: The operations can be performed using valid integers in the order 7, 5, 3, and 1. Constraints: 1
3375. Minimum Operations to Make Array Values Equal to K
Difficulty: Easy
Topics: Array, Hash Table
You are given an integer array nums and an integer k.
An integer h is called valid if all values in the array that are strictly greater than h are identical.
For example, if nums = [10, 8, 10, 8], a valid integer is h = 9 because all nums[i] > 9 are equal to 10, but 5 is not a valid integer.
You are allowed to perform the following operation on nums:
- Select an integer
hthat is valid for the current values innums. - For each index
iwherenums[i] > h, setnums[i]toh.
Return the minimum number of operations required to make every element in nums equal to k. If it is impossible to make all elements equal to k, return -1.
Example 1:
- Input: nums = [5,2,5,4,5], k = 2
- Output: 2
- Explanation: The operations can be performed in order using valid integers 4 and then 2.
Example 2:
- Input: nums = [2,1,2], k = 2
- Output: -1
- Explanation: It is impossible to make all the values equal to 2.
Example 3:
- Input: nums = [9,7,5,3], k = 1
- Output: 4
- Explanation: The operations can be performed using valid integers in the order 7, 5, 3, and 1.
Constraints:
-
1 <= nums.length <= 100 1 <= nums[i] <= 1001 <= k <= 100
Hint:
- Handle the case when the array contains an integer less than
k - Start by performing operations on the highest integer
- You can perform an operation on the highest integer using the second-highest, an operation on the second-highest using the third-highest, and so forth.
- The answer is the number of distinct integers in the array that are larger than
k.
Solution:
We need to determine the minimum number of operations required to make all elements of an array equal to a given integer k. Each operation involves selecting a valid integer h such that all elements greater than h are reduced to h. The solution must also check if it is impossible to achieve this goal and return -1 in such cases.
Approach
-
Check for Impossibility: If any element in the array is less than
k, it is impossible to make all elements equal tokbecause we cannot increase values. In this case, return-1. -
Collect Distinct Values: Identify all distinct values in the array that are strictly greater than
k. Each distinct value represents a step where we can reduce the elements to the next lower value until we reachk. -
Count Steps: The number of distinct values greater than
kdirectly corresponds to the minimum number of operations required. Each operation reduces the highest current value to the next lower distinct value until all elements arek.
Let's implement this solution in PHP: 3375. Minimum Operations to Make Array Values Equal to K
/**
* @param Integer[] $nums
* @param Integer $k
* @return Integer
*/
function minOperations($nums, $k) {
...
...
...
/**
* go to ./solution.php
*/
}
// Example 1
print_r(minOperations(array(5, 2, 5, 4, 5), 2)); // Output: 2
// Example 2
print_r(minOperations(array(2, 1, 2), 2)); // Output: -1
// Example 3
print_r(minOperations(array(9, 7, 5, 3), 1)); // Output: 4
?>
Explanation:
-
Impossibility Check: The code first iterates through the array to check if any element is less than
k. If found, it immediately returns-1as the task is impossible. -
Collecting Distinct Values: The code then iterates through the array again to collect all distinct values greater than
kusing a hash map to ensure uniqueness. -
Counting Steps: The count of these distinct values is returned as the result, representing the minimum number of operations needed. Each distinct value requires one operation to reduce it to the next lower value until all elements are
k.
This approach efficiently determines the minimum operations by leveraging the distinct values greater than k, ensuring optimal performance with a time complexity of O(n), where n is the length of the array.
Contact Links
If you found this series helpful, please consider giving the repository a star on GitHub or sharing the post on your favorite social networks






































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)



































































































































































































![Blue Archive tier list [April 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33404-1636469504/blue-archive-screenshot-2.jpg?#)


































.png?#)

































.webp?#)

























































































![[Update: Optional] Google rolling out auto-restart security feature to Android](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/google-play-services-2.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

















![Apple to Split Enterprise and Western Europe Roles as VP Exits [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97032/97032/97032-640.jpg)
![Nanoleaf Announces New Pegboard Desk Dock With Dual-Sided Lighting [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97030/97030/97030-640.jpg)








































![Security Database Used by Apple Goes Independent After Funding Cut [Updated]](https://images.macrumors.com/t/FWFeAmxnHKf7vkk_MCBh9TcNMVg=/1600x/article-new/2023/05/bug-security-vulnerability-issue-fix-larry.jpg)