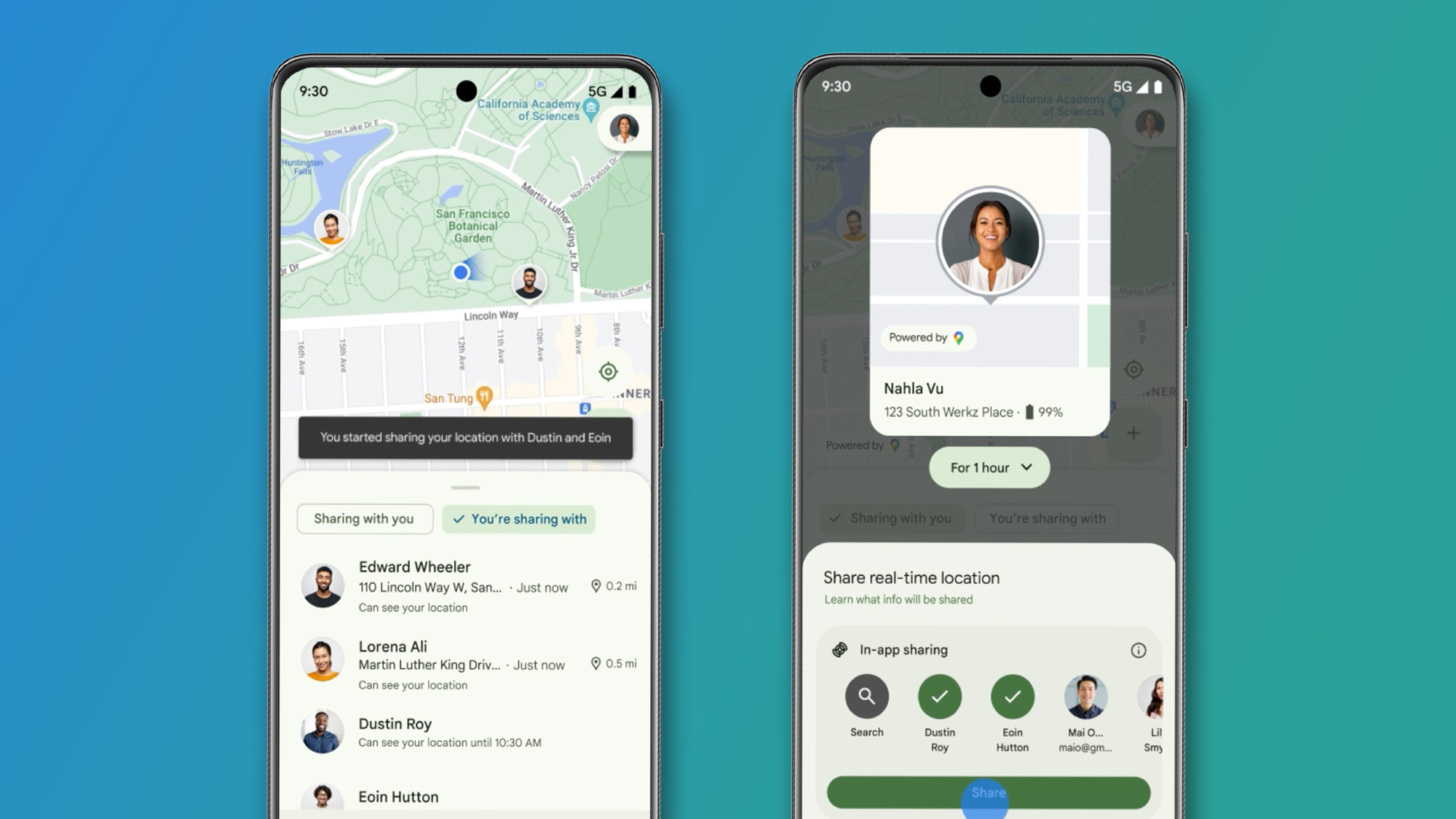
What is Zero Trust Application Access (ZTAA)?
In a world where remote work and hybrid IT environments are the new norm, traditional network-based security models are no longer sufficient. Zero Trust Application Access (ZTAA) emerges as a forward-thinking security framework, enabling organizations to secure application access through continuous verification and strict access control—regardless of user location or device. The ZTAA Philosophy: Verify First, Then Allow ZTAA operates on the core tenet of Zero Trust: never assume trust, always validate. Unlike older security paradigms that relied on perimeter-based protection, ZTAA focuses on granular application-level security. Every request—whether it comes from internal users or external connections—is assessed for identity, device posture, and context before access is granted. This ensures that access is restricted not only to authorized users but also limited to only the resources necessary for their role, drastically reducing the attack surface. ZTAA in Action: A Real-Time Verification Workflow Here’s how ZTAA functions behind the scenes: The user initiates a connection, which is intercepted by a firewall and redirected to an identity provider for verification. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is triggered when necessary. Once identity is confirmed, the user is granted session-based access—with all traffic filtered through Zero Trust policies that include malware scans and intrusion prevention. This session-aware access ensures that users cannot move laterally or access unauthorized applications, even if they are already inside the network. How ZTAA Differs from ZTNA While both Zero Trust Application Access (ZTAA) and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) share foundational security principles, their focus areas differ: ZTNA safeguards the network entry points—controlling who can access the network. ZTAA, on the other hand, governs what can be accessed within—managing user permissions on a per-application basis. Together, they provide a layered Zero Trust defense model: ZTNA protects the perimeter, while ZTAA ensures internal controls remain tight. Business Benefits of ZTAA Improved Access Governance: Enables least-privilege access for every user, device, and session. Stronger Breach Containment: Mitigates lateral movement with microsegmentation. Cross-Platform Consistency: Secures apps across cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments. Streamlined Visibility: Provides centralized monitoring and analytics for all app-level interactions. Final Takeaway ZTAA is redefining secure access in the age of distributed workforces and SaaS-heavy ecosystems. With its strict verification approach and contextual enforcement, it empowers organizations to better protect critical applications—without compromising usability or performance.


In a world where remote work and hybrid IT environments are the new norm, traditional network-based security models are no longer sufficient. Zero Trust Application Access (ZTAA) emerges as a forward-thinking security framework, enabling organizations to secure application access through continuous verification and strict access control—regardless of user location or device.
The ZTAA Philosophy: Verify First, Then Allow
ZTAA operates on the core tenet of Zero Trust: never assume trust, always validate. Unlike older security paradigms that relied on perimeter-based protection, ZTAA focuses on granular application-level security. Every request—whether it comes from internal users or external connections—is assessed for identity, device posture, and context before access is granted.
This ensures that access is restricted not only to authorized users but also limited to only the resources necessary for their role, drastically reducing the attack surface.
ZTAA in Action: A Real-Time Verification Workflow
Here’s how ZTAA functions behind the scenes:
- The user initiates a connection, which is intercepted by a firewall and redirected to an identity provider for verification.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is triggered when necessary.
- Once identity is confirmed, the user is granted session-based access—with all traffic filtered through Zero Trust policies that include malware scans and intrusion prevention.
This session-aware access ensures that users cannot move laterally or access unauthorized applications, even if they are already inside the network.
How ZTAA Differs from ZTNA
While both Zero Trust Application Access (ZTAA) and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) share foundational security principles, their focus areas differ:
- ZTNA safeguards the network entry points—controlling who can access the network.
- ZTAA, on the other hand, governs what can be accessed within—managing user permissions on a per-application basis.
Together, they provide a layered Zero Trust defense model: ZTNA protects the perimeter, while ZTAA ensures internal controls remain tight.
Business Benefits of ZTAA
- Improved Access Governance: Enables least-privilege access for every user, device, and session.
- Stronger Breach Containment: Mitigates lateral movement with microsegmentation.
- Cross-Platform Consistency: Secures apps across cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments.
- Streamlined Visibility: Provides centralized monitoring and analytics for all app-level interactions.
Final Takeaway
ZTAA is redefining secure access in the age of distributed workforces and SaaS-heavy ecosystems. With its strict verification approach and contextual enforcement, it empowers organizations to better protect critical applications—without compromising usability or performance.































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)



























































































































![[DEALS] Koofr Cloud Storage: Lifetime Subscription (1TB) (80% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)
























![Is this too much for a modular monolith system? [closed]](https://i.sstatic.net/pYL1nsfg.png)







































































































![M4 MacBook Air Drops to Just $849 - Act Fast! [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97140/97140/97140-640.jpg)












_roibu_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)




 CISO’s Core Focus.webp?#)




































































































![Apple Smart Glasses Not Close to Being Ready as Meta Targets 2025 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97139/97139/97139-640.jpg)
![iPadOS 19 May Introduce Menu Bar, iOS 19 to Support External Displays [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97137/97137/97137-640.jpg)