Understanding Spring Boot MVC
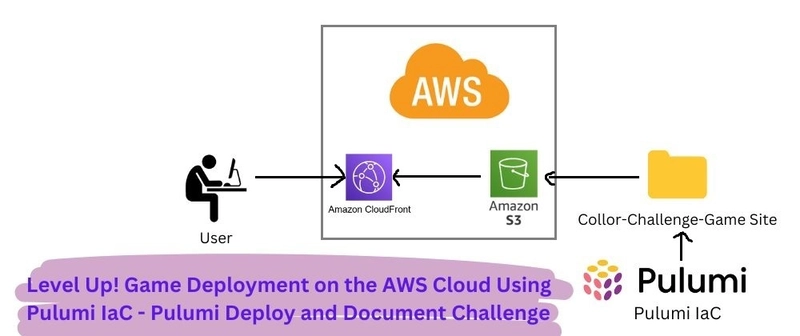
In the previous blog, we got an overview of a Basic Spring Boot Application. Now, let's dive deeper and understand how the core components work together in an MVC structure. Before Starting, We Should Know: 1. Model The Model represents the data and business logic of the application. It defines the structure of the data we are working with. Example: public class User { private Long id; private String name; private String email; // Getters and Setters } 2. Repository The Repository layer interacts with the database. It is responsible for data storage, retrieval, and query execution. Example: import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository { } 3. Service The Service layer contains business logic. It processes data before sending it to the Controller. Example: import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service public class UserService { private final UserRepository userRepository; public UserService(UserRepository userRepository) { this.userRepository = userRepository; } public List getAllUsers() { return userRepository.findAll(); } } 4. Controller The Controller handles user requests, interacts with the Service layer, and returns responses. Example: import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import java.util.List; @RestController @RequestMapping("/users") public class UserController { private final UserService userService; public UserController(UserService userService) { this.userService = userService; } @GetMapping public List getUsers() { return userService.getAllUsers(); } } 5. Exception Handling Exception handling is important to manage errors gracefully. Spring Boot provides @ControllerAdvice for centralized exception handling. Example: import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestControllerAdvice public class GlobalExceptionHandler { @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) public String handleException(Exception e) { return "Error: " + e.getMessage(); } } How Everything Works Together The Controller receives a request (e.g., /users). It calls the Service layer to process data. The Service interacts with the Repository to fetch or save data. The Repository retrieves data from the database. The Service returns the data to the Controller. The Controller sends a response to the client. If an error occurs, the Exception Handling mechanism takes care of it. This is how Spring Boot MVC works in a structured way! In the upcoming Blog, we will learn about Annotations in Spring Boot. Keep learning, keep growing!

In the previous blog, we got an overview of a Basic Spring Boot Application. Now, let's dive deeper and understand how the core components work together in an MVC structure.
Before Starting, We Should Know:
1. Model
The Model represents the data and business logic of the application. It defines the structure of the data we are working with.
Example:
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String email;
// Getters and Setters
}
2. Repository
The Repository layer interacts with the database. It is responsible for data storage, retrieval, and query execution.
Example:
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
}
3. Service
The Service layer contains business logic. It processes data before sending it to the Controller.
Example:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class UserService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
public UserService(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
}
4. Controller
The Controller handles user requests, interacts with the Service layer, and returns responses.
Example:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
private final UserService userService;
public UserController(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
@GetMapping
public List<User> getUsers() {
return userService.getAllUsers();
}
}
5. Exception Handling
Exception handling is important to manage errors gracefully. Spring Boot provides @ControllerAdvice for centralized exception handling.
Example:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public String handleException(Exception e) {
return "Error: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
How Everything Works Together
- The Controller receives a request (e.g.,
/users). - It calls the Service layer to process data.
- The Service interacts with the Repository to fetch or save data.
- The Repository retrieves data from the database.
- The Service returns the data to the Controller.
- The Controller sends a response to the client.
- If an error occurs, the Exception Handling mechanism takes care of it.
This is how Spring Boot MVC works in a structured way!
In the upcoming Blog, we will learn about Annotations in Spring Boot.
Keep learning, keep growing!











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)























.webp?#)










_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)




































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)



































































































































