Ultimate Guide to Using NGINX as a Reverse Proxy and Load Balancer:Best Practices and Tips
What is NGINX and Why Use It? Nginx (pronounced "engine-X) is an open-source high-performance HTTP web server that can also be used as a reverse proxy. Other uses cases of nginx include Load Balancing, API Gateway,SSL/TLS Termination and Content caching. Over the years Nginx has grown to become one of the most popular and widely used webserver for its high performance, scalability, and low resource usage. Some companies that use Nginx include Uber Netflix,Instagram,Airbnb etc. This article will demonstrate how to configure and use Nginx as a Reverse proxy and a Load Balancer. We will configure nginx as reverse proxy and load balancer to distribute traffic between three django applications. Before we dive into the details of configuring nginx , lets first understand what reverse proxy and load balancer are. Understanding Reverse Proxy and Load Balancing What is a Reverse Proxy? A reverse proxy( proxy means to act on behalf ) is a special type of server that sits in front of other webservers and directs requests from clients (such as web browsers) to those servers. Reverse proxies are often used to improve security, performance, and dependability. What is Load Balancing?Load balancing is a technique of distributing computational workloads between two or more computing nodes. Load balancing is often employed to evenly distribute network traffic among several servers. This reduces the strain on each server and makes the servers more efficient, speeding up performance and reducing latency. Setting Up NGINX as a Reverse Proxy and Load Balancer Prerequisites To follow this guide, you should have A Linux OS, preferably ubuntu. Basic knowledge of using the terminal. Docker Installed. The Official documentation will guide you through how to install Docker Nginx Installed . You can follow the offical Documentation to install Nginx on your prefered OS. Step 1 Setting up docker Containers We will be setting up 3 docker Containers to server as the backend servers. The docker containers run will be running a django blog application. 1. Create a directory on your computer for the project: mkdr projects/DjangoApps 2. cd into the directory you created cd projects/Djangoapps 3. Create a docker-compose.yml file touch docker-compose.yml open the docker-compose.yml file and past this code version: '3' services: app1: image: kodecapsule/django-blog-app:dark-server container_name: dark-server ports: - "8000:8000" restart: always app2: image: kodecapsule/django-blog-app:green-server container_name: green-server ports: - "8001:8000" restart: always app3: image: kodecapsule/django-blog-app:blue-server container_name: blue-server ports: - "8002:8000" restart: always The above docker-compose.yml file setsup three Docker containers running different versions of the same Django blog application, each tagged with a different server name (dark-server, green-server, blue-server) from the Docker Hub repository kodecapsule/django-blog-app. Each container is mapped to a unique host port (8000, 8001, 8002) so they can be accessed individually, while internally all containers listen on port 8000. The restart: always policy ensures that the containers automatically restart if they fail or if the Docker service restarts. 4. Run the docker containers docker-compose up This will download and run three docker containers dark-server, green-server and blue-server.Open your browser and make sure you are able to access the three applications dark-server . green-server . blue-server Step 2 Configure NGINX as a Reverse Proxy Nginx configuration is always in nginx.conf file. The nginx.conf file is the main file that is mainly used to configure nginx behavior. By default this file is located in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf . worker_processes 1; events{ worker_connections 1024; } http{ include /etc/nginx/mime.types; upstream django_servers { server localhost:8000; server localhost:8001; server localhost:8002; } server { listen 8080; # Proxy requests to Django backend location / { proxy_pass http://django_servers; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; # Handle timeouts proxy_connect_timeout 60; proxy_read_timeout 60; } } } The server context defines all the configuration needed for nginx to act as a reverse proxy.The NGINX configuration above defines a server with the listen directive listening on port 8080. To configure Nginx as a reverse proxy the proxy_pass directive is used which enables

What is NGINX and Why Use It?
Nginx (pronounced "engine-X) is an open-source high-performance HTTP web server that can also be used as a reverse proxy. Other uses cases of nginx include Load Balancing, API Gateway,SSL/TLS Termination and Content caching. Over the years Nginx has grown to become one of the most popular and widely used webserver for its high performance, scalability, and low resource usage. Some companies that use Nginx include Uber Netflix,Instagram,Airbnb etc.
This article will demonstrate how to configure and use Nginx as a Reverse proxy and a Load Balancer. We will configure nginx as reverse proxy and load balancer to distribute traffic between three django applications. Before we dive into the details of configuring nginx , lets first understand what reverse proxy and load balancer are.
Understanding Reverse Proxy and Load Balancing
What is a Reverse Proxy? A reverse proxy( proxy means to act on behalf ) is a special type of server that sits in front of other webservers and directs requests from clients (such as web browsers) to those servers. Reverse proxies are often used to improve security, performance, and dependability.
What is Load Balancing?Load balancing is a technique of distributing computational workloads between two or more computing nodes. Load balancing is often employed to evenly distribute network traffic among several servers. This reduces the strain on each server and makes the servers more efficient, speeding up performance and reducing latency.
Setting Up NGINX as a Reverse Proxy and Load Balancer
Prerequisites
To follow this guide, you should have
- A Linux OS, preferably ubuntu.
- Basic knowledge of using the terminal.
- Docker Installed. The Official documentation will guide you through how to install Docker
- Nginx Installed . You can follow the offical Documentation to install Nginx on your prefered OS.
Step 1 Setting up docker Containers
We will be setting up 3 docker Containers to server as the backend servers.
The docker containers run will be running a django blog application.
- 1. Create a directory on your computer for the project:
mkdr projects/DjangoApps
- 2. cd into the directory you created
cd projects/Djangoapps
- 3. Create a docker-compose.yml file
touch docker-compose.yml
open the docker-compose.yml file and past this code
version: '3'
services:
app1:
image: kodecapsule/django-blog-app:dark-server
container_name: dark-server
ports:
- "8000:8000"
restart: always
app2:
image: kodecapsule/django-blog-app:green-server
container_name: green-server
ports:
- "8001:8000"
restart: always
app3:
image: kodecapsule/django-blog-app:blue-server
container_name: blue-server
ports:
- "8002:8000"
restart: always
The above docker-compose.yml file setsup three Docker containers running different versions of the same Django blog application,
each tagged with a different server name (dark-server, green-server, blue-server) from the Docker Hub repository kodecapsule/django-blog-app.
Each container is mapped to a unique host port (8000, 8001, 8002) so they can be accessed individually, while internally all containers listen on port 8000. The restart: always policy ensures that the containers automatically restart if they fail or if the Docker service restarts.
- 4. Run the docker containers
docker-compose up
This will download and run three docker containers dark-server, green-server and blue-server.Open your browser and make sure you are able to access the three applications
dark-server  .
.
green-server
 .
.
blue-server

Step 2 Configure NGINX as a Reverse Proxy
Nginx configuration is always in nginx.conf file. The nginx.conf file is the main file that is mainly used to configure nginx behavior.
By default this file is located in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf .
worker_processes 1;
events{
worker_connections 1024;
}
http{
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
upstream django_servers {
server localhost:8000;
server localhost:8001;
server localhost:8002;
}
server {
listen 8080;
# Proxy requests to Django backend
location / {
proxy_pass http://django_servers;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# Handle timeouts
proxy_connect_timeout 60;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
}
}
}
The server context defines all the configuration needed for nginx to act as a reverse proxy.The NGINX configuration above defines a server with the listen directive listening on port 8080.
To configure Nginx as a reverse proxy the proxy_pass directive is used which enables nginx to forward all incoming requests to a group of backend Django servers. It sets headers like Host, X-Real-IP,
and X-Forwarded-For to pass client information to the backend servers, preserving the original request details.
Additionally, it configures timeout settings (connect and read) to control how long NGINX waits for a response from the backend servers, ensuring smooth handling of slow responses or potential server delays.
Step 3 Configure Nginx as a Load Balancer
configure nginx as load bala using round-robin
upstream django_servers {
server localhost:8000;
server localhost:8001;
server localhost:8002;
}
The upstream block defines a load balancer named django_servers, which distributes incoming requests across the three Django application instances running on ports 8000, 8001, and 8002 on localhost.
By default, NGINX uses a round-robin strategy, sending each new request to a different server in sequence to balance the load.
This setup helps improve performance and reliability, as traffic is spread across multiple instances, preventing any single server from being overwhelmed.
You can read more about Using nginx as HTTP load balancer
Open your browser and enter localhost:8080. Reload several the site several time to see how nginx is able to route the traffic between the three servers.
Other load balancing algorithms that can be used are Weighted load balancing, Least connected load balancing,ip-hash
Common Errors and Troubleshooting
Below are some list of some errors you are likely to face when











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)


































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
.webp?#)
 (1).webp?#)






































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
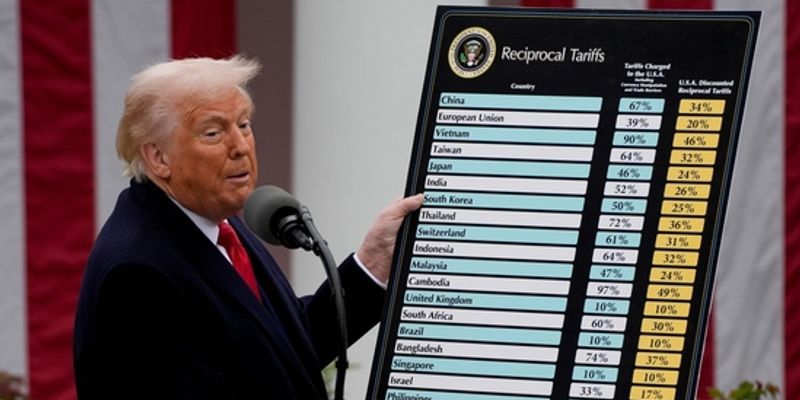
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)