The Growing Importance of Data Literacy in a Digital World Introduction
Introduction The world has experienced an exponential technological revolution in the last 40 years and this era has ushered in a massive influx of information, with data now forming the backbone of decision-making across industries. An estimate of 2.5 quintillion bytes of data is created every day, and with the rise of automation, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, this number is only set to increase. In this era AI, IoT, ML, data is like the new ‘oil’ that is required to keep these systems and engine running. From healthcare to finance, education to e-commerce, just a few to mention, data is gathered, analyzed and used to make decisions that influences every aspect of our lives. However, the ability to harness and make sense of this information effectively requires a crucial skill—data literacy Understanding Data Literacy In a world overflowing with data, our ability to understand, interpret, and utilize it effectively has never been more critical Data literacy can be defined as the capacity to read, analyze, and communicate data insights effectively. It empowers individuals and organizations to make informed decisions, identify trends, and ultimately enhance business outcomes. At the top of the list of the benefits of making data-driven decisions is that the decision is based on factual insights rather than relying solely on intuition. This approach often results in improved efficiency and stronger business strategies, giving data-driven companies a competitive edge over those that do not prioritize data in their decision-making. However, simply having access to data is not enough to guarantee success. Businesses also need skilled professionals who can analyze and interpret data effectively. As a result, there is a growing demand in the job market for professionals with strong data literacy skills Key Data Literacy Skills 1.Data Analytics Data analysis involves examining and interpreting data to extract meaningful insights. Data analysis can entail performing basic operations like reviewing patterns and drawing conclusions or as complex as applying sophisticated techniques use statistical models and machine learning algorithms. There are several types of data analysis, with four primary approaches: Descriptive analysis – Explains what has happened based on historical data. _ -Diagnostic analysis_ – Identifies reasons behind specific outcomes. Predictive analysis – Forecasts potential future trends based on patterns. Prescriptive analysis – Recommends actions to achieve desired results. Developing analytical skills is crucial for making informed business decisions and identifying opportunities for growth. 2. Data Cleaning (Wrangling) Data cleaning is the process of converting raw data into a into a usable format. This often entails removing inconsistencies, filling in missing information, and organizing data for analysis. Clean data reduces errors in decision-making and ensures accuracy in reporting.While many businesses automate this process using algorithms, employees involved in data collection and entry must also uphold data integrity standard. Most popular tools used in this stage include Power BI and Microsoft Excel. 3. Data Visualization Data visualization is the practice of transforming raw numbers into visual formats such as graphs, charts, and infographics. It plays a crucial role in making complex data more understandable, especially for stakeholders who may not have advanced data skills. Common visualization techniques include: Charts and tables for presenting trends Maps for geographic data representation Infographics for summarizing key insights Interactive dashboards for real-time data monitoring. Data specialists use popular tools like Microsoft Excel, Google Charts, Tableau, and Power BI to create compelling visualizations that drive better decision-making. 4. The Data Ecosystem A data ecosystem refers to the interconnected components that support an organization’s data management, including: - Physical infrastructure – Servers, databases, and cloud storage solutions - Software and tools – Data analysis platforms, programming languages, and AI-driven applications - Data sources– Internal and external datasets that fuel insights. Understanding an organization's data ecosystem helps professionals optimize workflows,improve efficiency, and ensure data is used effectively. 5. Data Governance Data governance is the framework that defines how an organization manages its data assets. It ensures data is accurate, secure, and used responsibly. Key areas of data governance include: Quality – Maintaining data accuracy, consistency, and completeness. Security– Protecting data from unauthorized access and breaches. Privacy – Safeguarding sensitive information, such as customer and employee records. Stewardship – Enforcing policies and best practices for ethical data handling. Many companies have formal data policies that outline rules fo

Introduction
The world has experienced an exponential technological revolution in the last 40 years and this era has ushered in a massive influx of information, with data now forming the backbone of decision-making across industries. An estimate of 2.5 quintillion bytes of data is created every day, and with the rise of automation, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, this number is only set to increase. In this era AI, IoT, ML, data is like the new ‘oil’ that is required to keep these systems and engine running. From healthcare to finance, education to e-commerce, just a few to mention, data is gathered, analyzed and used to make decisions that influences every aspect of our lives. However, the ability to harness and make sense of this information effectively requires a crucial skill—data literacy

Understanding Data Literacy
In a world overflowing with data, our ability to understand, interpret, and utilize it effectively has never been more critical Data literacy can be defined as the capacity to read, analyze, and communicate data insights effectively. It empowers individuals and organizations to make informed decisions, identify trends, and ultimately enhance business outcomes. At the top of the list of the benefits of making data-driven decisions is that the decision is based on factual insights rather than relying solely on intuition. This approach often results in improved efficiency and stronger business strategies, giving data-driven companies a competitive edge over those that do not prioritize data in their decision-making.
However, simply having access to data is not enough to guarantee success. Businesses also need skilled professionals who can analyze and interpret data effectively. As a result, there is a growing demand in the job market for professionals with strong data literacy skills
Key Data Literacy Skills
1.Data Analytics
Data analysis involves examining and interpreting data to extract meaningful insights. Data analysis can entail performing basic operations like reviewing patterns and drawing conclusions or as complex as applying sophisticated techniques use statistical models and machine learning algorithms. There are several types of data analysis, with four primary approaches:
- Descriptive analysis – Explains what has happened based on historical data. _ -Diagnostic analysis_ – Identifies reasons behind specific outcomes.
- Predictive analysis – Forecasts potential future trends based on patterns.
-
Prescriptive analysis – Recommends actions to achieve desired results.
Developing analytical skills is crucial for making informed business decisions and identifying opportunities for growth.
 2. Data Cleaning (Wrangling)
2. Data Cleaning (Wrangling)
Data cleaning is the process of converting raw data into a into a usable format. This often entails removing inconsistencies, filling in missing information, and organizing data for analysis.
Clean data reduces errors in decision-making and ensures accuracy in reporting.While many businesses automate this process using algorithms, employees involved in data collection and entry must also uphold data integrity standard. Most popular tools used in this stage include Power BI and Microsoft Excel.
3. Data Visualization
Data visualization is the practice of transforming raw numbers into visual formats such as graphs, charts, and infographics. It plays a crucial role in making complex data more understandable, especially for stakeholders who may not have advanced data skills. Common visualization techniques include:
- Charts and tables for presenting trends
- Maps for geographic data representation
- Infographics for summarizing key insights
- Interactive dashboards for real-time data monitoring.
Data specialists use popular tools like Microsoft Excel, Google Charts, Tableau, and Power BI to create compelling visualizations that drive better decision-making.
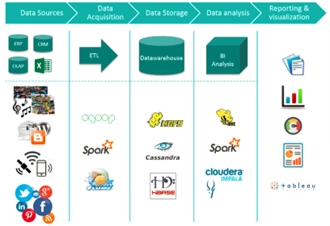
4. The Data Ecosystem
A data ecosystem refers to the interconnected components that support an organization’s data management, including:
- Physical infrastructure – Servers, databases, and cloud storage solutions
- Software and tools – Data analysis platforms, programming languages, and AI-driven applications
- Data sources– Internal and external datasets that fuel insights.
Understanding an organization's data ecosystem helps professionals optimize workflows,improve efficiency, and ensure data is used effectively.
5. Data Governance
Data governance is the framework that defines how an organization manages its data assets. It ensures data is accurate, secure, and used responsibly. Key areas of data governance include:
- Quality – Maintaining data accuracy, consistency, and completeness.
- Security– Protecting data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Privacy – Safeguarding sensitive information, such as customer and employee records.
-
Stewardship – Enforcing policies and best practices for ethical data handling.
 Many companies have formal data policies that outline rules for employees, ensuring compliance with legal and industry standards
Many companies have formal data policies that outline rules for employees, ensuring compliance with legal and industry standards
6. The Data Team
Understanding the roles within a data team can help professionals collaborate effectively. Most organizations have:
- Data Scientists– Experts in advanced analytics, machine learning, and predictive modeling.
- Data Engineers – Developers who build and maintain data infrastructures, ensuring seamless data processing.
- Data Analysts– Specialists who conduct analyses, generate reports, and provide actionable insights. Each of these roles contributes to turning raw data into valuable business intelligence, helping organizations remain competitive in a data-driven world.









































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)






























































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)


























































































![Switch 2 Pre-Order Rules Are Some BS: Here's How They Work [Update]](https://i.kinja-img.com/image/upload/c_fill,h_675,pg_1,q_80,w_1200/485ec87fd3cea832387b2699e4cbd2a1.jpg)












.png?#)


.jpeg?#)
(1).jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)




-Mario-Kart-World-Hands-On-Preview-Is-It-Good-00-08-36.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)























_NicoElNino_Alamy.png?#)
_Igor_Mojzes_Alamy.jpg?#)

.webp?#)
.webp?#)











































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)