Sensor-Based Tank Monitoring for Efficient Oil and Gas Operations
As the oil and gas industry continues its journey toward digital transformation, the adoption of advanced technologies like sensor-based tank monitoring is redefining how operations are managed, optimized, and scaled. From enhancing safety and environmental compliance to enabling predictive maintenance and cost savings, this intelligent monitoring approach is quickly becoming a global best practice. In this blog, we’ll explore how sensor-based tank monitoring systems are revolutionizing the sector, their technical advantages, and why industry leaders across continents are making it a core part of their operational strategy. Understanding Sensor-Based Tank Monitoring Sensor-based tank monitoring leverages Internet of Things (IoT) technology to track key parameters such as tank levels, pressure, temperature, and gas emissions in real time. Sensors installed on storage tanks or pipelines transmit data to centralized dashboards, often integrated with AI and analytics platforms, allowing operators to monitor conditions remotely and respond instantly to anomalies. This technology serves both upstream and downstream oil and gas segments—offering benefits ranging from leak detection in remote oilfields to inventory optimization in refineries and distribution networks. Key Components of a Sensor-Based Monitoring System **Smart Sensors **These include ultrasonic, radar, capacitive, and pressure sensors that measure variables like liquid level, temperature, and flow rate. Wireless Communication Modules Sensors transmit data via LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, or LTE-M to minimize wiring and infrastructure costs. Cloud-Based Platforms Real-time data is collected and visualized through secure, cloud-based applications that enable remote access and control. Analytics & AI Engines Data analytics tools detect patterns, forecast tank usage, and generate predictive maintenance alerts. Mobile & Desktop Dashboards User-friendly dashboards help engineers and managers visualize insights and take quick actions on the go. Why Sensor-Based Monitoring is a Game Changer The oil and gas industry is traditionally dependent on manual checks, SCADA systems, or limited automation, which often results in delayed responses, high labor costs, and safety risks. Sensor-based tank monitoring resolves these challenges through: 1. Real-Time Visibility Across Operations With sensor data continuously streamed to a centralized platform, operators no longer rely on periodic inspections. Instant alerts on pressure drops, leaks, or abnormal readings ensure that issues are resolved before they become critical. 2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency Automation of data collection eliminates manual errors and frees up skilled labor for more strategic tasks. With optimized scheduling, inventory tracking, and tank usage analysis, businesses can significantly improve overall efficiency. 3. Proactive Maintenance & Downtime Reduction Predictive maintenance is a major benefit of sensor-based monitoring. When a sensor detects an early sign of equipment wear or anomaly, maintenance can be scheduled before failure occurs—preventing unplanned downtime, saving costs, and extending asset life. 4. Improved Safety and Risk Management Accurate, real-time monitoring of volatile compounds or hazardous fluids helps minimize the risk of spills, explosions, or fire hazards. It enhances the safety of workers, assets, and the environment. 5. Regulatory Compliance and Reporting With environmental regulations growing stricter globally, sensor-based systems automatically log key parameters needed for compliance reporting—ensuring traceability and transparency for audits. Industry Use Cases Across the Globe ▪ North America: Digital Oilfields In the U.S. and Canada, operators in shale basins use tank-level sensors to monitor water and oil storage in real time, often in remote and hazardous locations. These sensors eliminate the need for manual inspection and reduce safety risks in harsh weather or terrain. ▪ Middle East: Efficient Refinery Management Refineries across the UAE and Saudi Arabia are adopting IoT tank monitoring to optimize chemical dosing, track consumption, and manage storage facilities more efficiently. Real-time analytics help maintain consistent throughput while meeting sustainability targets. ▪ Europe: Emission Control & Carbon Reduction As part of Net Zero commitments, European oil and gas companies are using sensor-based monitoring to detect methane leaks and optimize energy use—key to reducing carbon emissions and achieving environmental compliance. ▪ Asia-Pacific: Urban Distribution Optimization In densely populated regions, fuel distribution companies use smart tank systems to monitor storage levels in urban depots and coordinate replenishments more accurately—minimizing delivery delays and fuel loss. Integration with Enterprise Systems Modern tank monitoring solutions don’t operate in isolation. They integrate seamlessly with: ERP systems for inventory an
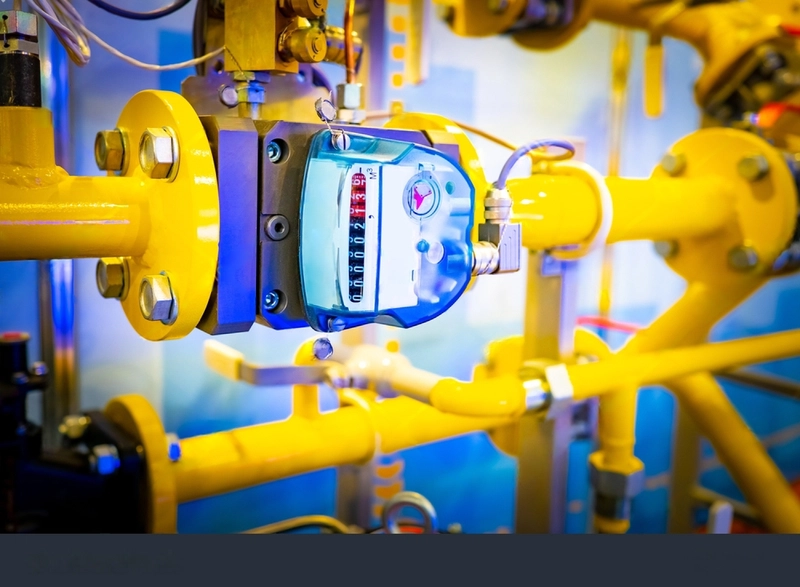

As the oil and gas industry continues its journey toward digital transformation, the adoption of advanced technologies like sensor-based tank monitoring is redefining how operations are managed, optimized, and scaled. From enhancing safety and environmental compliance to enabling predictive maintenance and cost savings, this intelligent monitoring approach is quickly becoming a global best practice.
In this blog, we’ll explore how sensor-based tank monitoring systems are revolutionizing the sector, their technical advantages, and why industry leaders across continents are making it a core part of their operational strategy.
Understanding Sensor-Based Tank Monitoring
Sensor-based tank monitoring leverages Internet of Things (IoT) technology to track key parameters such as tank levels, pressure, temperature, and gas emissions in real time. Sensors installed on storage tanks or pipelines transmit data to centralized dashboards, often integrated with AI and analytics platforms, allowing operators to monitor conditions remotely and respond instantly to anomalies.
This technology serves both upstream and downstream oil and gas segments—offering benefits ranging from leak detection in remote oilfields to inventory optimization in refineries and distribution networks.
Key Components of a Sensor-Based Monitoring System
**Smart Sensors
**These include ultrasonic, radar, capacitive, and pressure sensors that measure variables like liquid level, temperature, and flow rate.
Wireless Communication Modules
Sensors transmit data via LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, or LTE-M to minimize wiring and infrastructure costs.
Cloud-Based Platforms
Real-time data is collected and visualized through secure, cloud-based applications that enable remote access and control.
Analytics & AI Engines
Data analytics tools detect patterns, forecast tank usage, and generate predictive maintenance alerts.
Mobile & Desktop Dashboards
User-friendly dashboards help engineers and managers visualize insights and take quick actions on the go.
Why Sensor-Based Monitoring is a Game Changer
The oil and gas industry is traditionally dependent on manual checks, SCADA systems, or limited automation, which often results in delayed responses, high labor costs, and safety risks. Sensor-based tank monitoring resolves these challenges through:
1. Real-Time Visibility Across Operations
With sensor data continuously streamed to a centralized platform, operators no longer rely on periodic inspections. Instant alerts on pressure drops, leaks, or abnormal readings ensure that issues are resolved before they become critical.
2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Automation of data collection eliminates manual errors and frees up skilled labor for more strategic tasks. With optimized scheduling, inventory tracking, and tank usage analysis, businesses can significantly improve overall efficiency.
3. Proactive Maintenance & Downtime Reduction
Predictive maintenance is a major benefit of sensor-based monitoring. When a sensor detects an early sign of equipment wear or anomaly, maintenance can be scheduled before failure occurs—preventing unplanned downtime, saving costs, and extending asset life.
4. Improved Safety and Risk Management
Accurate, real-time monitoring of volatile compounds or hazardous fluids helps minimize the risk of spills, explosions, or fire hazards. It enhances the safety of workers, assets, and the environment.
5. Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
With environmental regulations growing stricter globally, sensor-based systems automatically log key parameters needed for compliance reporting—ensuring traceability and transparency for audits.
Industry Use Cases Across the Globe
▪ North America: Digital Oilfields
In the U.S. and Canada, operators in shale basins use tank-level sensors to monitor water and oil storage in real time, often in remote and hazardous locations. These sensors eliminate the need for manual inspection and reduce safety risks in harsh weather or terrain.
▪ Middle East: Efficient Refinery Management
Refineries across the UAE and Saudi Arabia are adopting IoT tank monitoring to optimize chemical dosing, track consumption, and manage storage facilities more efficiently. Real-time analytics help maintain consistent throughput while meeting sustainability targets.
▪ Europe: Emission Control & Carbon Reduction
As part of Net Zero commitments, European oil and gas companies are using sensor-based monitoring to detect methane leaks and optimize energy use—key to reducing carbon emissions and achieving environmental compliance.
▪ Asia-Pacific: Urban Distribution Optimization
In densely populated regions, fuel distribution companies use smart tank systems to monitor storage levels in urban depots and coordinate replenishments more accurately—minimizing delivery delays and fuel loss.
Integration with Enterprise Systems
Modern tank monitoring solutions don’t operate in isolation. They integrate seamlessly with:
ERP systems for inventory and billing synchronization
SCADA systems for holistic plant control
Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) for automated work order generation
Environmental Monitoring Platforms for emission reporting and sustainability dashboards
This ecosystem integration ensures that data flows across departments—enabling enterprise-wide visibility and smarter decision-making.
Key Considerations for Implementation
Before deploying a sensor-based tank monitoring system, companies should consider:
Tank Type & Fluid Properties – Ensure sensors are compatible with corrosive, volatile, or pressurized materials.
Network Connectivity – In remote areas, choose low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN) like LoRaWAN or satellite-based systems.
Data Security & Compliance – Implement encrypted communication, role-based access, and data redundancy.
Scalability – Choose a platform that can grow with your operational footprint—across sites, geographies, and use cases.
Training & Change Management – Equip teams with the skills and support to interpret data and act on insights.
A Sustainable and Future-Ready Investment
With environmental and operational pressures mounting, sensor-based tank monitoring is a strategic investment that pays off in multiple ways. It contributes to:
Lower carbon emissions through energy optimization
Reduced product loss via leak detection
Improved asset performance through timely maintenance
Greater worker safety and reduced compliance risk
Streamlined operations across global facilities
As oil and gas companies accelerate their digital transformation, smart monitoring solutions like these will become indispensable to achieving resilience, profitability, and sustainability.
Final Thoughts
Sensor-based tank monitoring is more than just a technological upgrade—it's a transformative enabler for modern oil and gas operations. By delivering real-time intelligence, improving safety, and supporting environmental goals, it helps companies stay competitive in an evolving global energy landscape.
Early adopters are already seeing significant ROI through reduced downtime, lower emissions, and optimized resource usage. As the industry shifts toward automation and sustainability, this innovation is no longer optional—it’s essential.







































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)
































































































































![From Art School Drop-out to Microsoft Engineer with Shashi Lo [Podcast #170]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1746203291209/439bf16b-c820-4fe8-b69e-94d80533b2df.png?#)








































































































(1).jpg?#)






























_Inge_Johnsson-Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)








































































































![Apple Developing AI 'Vibe-Coding' Assistant for Xcode With Anthropic [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97200/97200/97200-640.jpg)
![Apple's New Ads Spotlight Apple Watch for Kids [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97197/97197/97197-640.jpg)