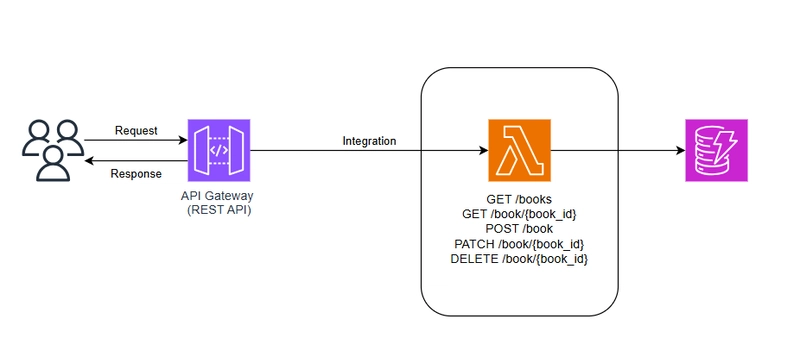
Scraping the Web with Java: Unlocking Smarter Data Extraction
Web scraping is no longer a specialized expertise; it is necessary for businesses, developers, and researchers who demand real-time data. Web scraping can be used to automate data collecting and analysis, whether you're looking to monitor competitors, acquire SEO insights, or follow eCommerce trends. Java is one of the greatest programming languages for web scraping due to its scalability and robust frameworks. But how do you use it to its full potential? Let's look at the fundamentals of web scraping with Java—what you need, the issues, and the most effective data scraping strategies. Why Java for Web Scraping? Java isn’t just for building enterprise applications—it’s a powerhouse for web scraping. Here’s why: Platform Independence – Java runs on any OS, making it ideal for large-scale scraping projects. Robust Libraries – Tools like Jsoup and Selenium simplify HTML parsing and automation. Multi-threading Support – Extract and process large amounts of data faster. Scalability – Handle complex scraping tasks without performance issues. Security & Stability – Java offers better error handling and exception management. Key Steps in Java Web Scraping 1️Sending HTTP Requests Use Java’s HttpClient or third-party libraries like Apache HttpClient to fetch web pages. Simulate browser behavior with Selenium for JavaScript-heavy websites. 2️Parsing HTML Content Extract meaningful data using Jsoup, a lightweight HTML parser. Navigate web page elements using CSS selectors or DOM traversal methods. 3️Handling Dynamic Content Many modern websites use AJAX and JavaScript to load content. Use Selenium WebDriver to automate interactions and capture fully rendered pages. 4️Avoiding Anti-Scraping Blocks Rotate user agents and IP addresses to prevent detection. Introduce time delays between requests to mimic human browsing. Use CAPTCHA-solving services if required. 5️Storing & Processing Data Save scraped data in databases (MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL) or export to JSON/CSV. Process large datasets efficiently with Java’s multithreading capabilities. 6️Handling Pagination & Infinite Scrolling Automate scrolling and clicking the ‘Load More’ buttons using Selenium. Extract paginated results by analyzing URL patterns and modifying request parameters. Advanced Web Scraping Techniques in Java Headless Browser Scraping – Use Selenium with Headless Chrome to scrape JavaScript-heavy websites without opening a UI. API Scraping as an Alternative – If a site offers an API, fetch structured data instead of scraping HTML. Web Scraping with Machine Learning – Use AI models to extract and structure data intelligently. Cloud-Based Scraping – Deploy scrapers on AWS Lambda, Google Cloud, or Azure for higher scalability. Proxy Management & IP Rotation – Avoid detection using rotating proxies and distributed scraping techniques. Common Challenges in Web Scraping & How to Overcome Them Website Blocking & CAPTCHAs – Rotate proxies and use headless browsers to bypass security. Dynamic Content Extraction – JavaScript rendering requires Selenium and advanced parsing techniques. Legal & Ethical Concerns – Always check robots.txt and adhere to data usage policies. Large-Scale Data Processing – Use multithreading and cloud-based storage solutions for efficiency. Handling Authentication & Sessions – Manage cookies and login sessions to access restricted content. Best Practices for Efficient Web Scraping in Java Respect Website Terms & Policies – Scrape responsibly and avoid overloading servers. Use Proxies & User-Agent Rotation – Prevent IP bans and simulate different devices. Optimize Code for Performance – Use Java’s multithreading for faster execution. Store Data Effectively – Choose databases based on project requirements. Error Handling & Logging – Implement error-handling mechanisms for stability. Tools & Libraries for Java Web Scraping

Web scraping is no longer a specialized expertise; it is necessary for businesses, developers, and researchers who demand real-time data. Web scraping can be used to automate data collecting and analysis, whether you're looking to monitor competitors, acquire SEO insights, or follow eCommerce trends.
Java is one of the greatest programming languages for web scraping due to its scalability and robust frameworks. But how do you use it to its full potential? Let's look at the fundamentals of web scraping with Java—what you need, the issues, and the most effective data scraping strategies.
Why Java for Web Scraping?
Java isn’t just for building enterprise applications—it’s a powerhouse for web scraping. Here’s why:
- Platform Independence – Java runs on any OS, making it ideal for large-scale scraping projects.
- Robust Libraries – Tools like Jsoup and Selenium simplify HTML parsing and automation.
- Multi-threading Support – Extract and process large amounts of data faster.
- Scalability – Handle complex scraping tasks without performance issues.
- Security & Stability – Java offers better error handling and exception management.
Key Steps in Java Web Scraping
1️Sending HTTP Requests
- Use Java’s HttpClient or third-party libraries like Apache HttpClient to fetch web pages.
- Simulate browser behavior with Selenium for JavaScript-heavy websites.
2️Parsing HTML Content
- Extract meaningful data using Jsoup, a lightweight HTML parser.
- Navigate web page elements using CSS selectors or DOM traversal methods.
3️Handling Dynamic Content
- Many modern websites use AJAX and JavaScript to load content.
- Use Selenium WebDriver to automate interactions and capture fully rendered pages.
4️Avoiding Anti-Scraping Blocks
- Rotate user agents and IP addresses to prevent detection.
- Introduce time delays between requests to mimic human browsing.
- Use CAPTCHA-solving services if required.
5️Storing & Processing Data
- Save scraped data in databases (MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL) or export to JSON/CSV.
- Process large datasets efficiently with Java’s multithreading capabilities.
6️Handling Pagination & Infinite Scrolling
- Automate scrolling and clicking the ‘Load More’ buttons using Selenium.
- Extract paginated results by analyzing URL patterns and modifying request parameters.
Advanced Web Scraping Techniques in Java
- Headless Browser Scraping – Use Selenium with Headless Chrome to scrape JavaScript-heavy websites without opening a UI.
- API Scraping as an Alternative – If a site offers an API, fetch structured data instead of scraping HTML.
- Web Scraping with Machine Learning – Use AI models to extract and structure data intelligently.
- Cloud-Based Scraping – Deploy scrapers on AWS Lambda, Google Cloud, or Azure for higher scalability.
- Proxy Management & IP Rotation – Avoid detection using rotating proxies and distributed scraping techniques.
Common Challenges in Web Scraping & How to Overcome Them
- Website Blocking & CAPTCHAs – Rotate proxies and use headless browsers to bypass security.
- Dynamic Content Extraction – JavaScript rendering requires Selenium and advanced parsing techniques.
- Legal & Ethical Concerns – Always check robots.txt and adhere to data usage policies.
- Large-Scale Data Processing – Use multithreading and cloud-based storage solutions for efficiency.
- Handling Authentication & Sessions – Manage cookies and login sessions to access restricted content.
Best Practices for Efficient Web Scraping in Java
- Respect Website Terms & Policies – Scrape responsibly and avoid overloading servers.
- Use Proxies & User-Agent Rotation – Prevent IP bans and simulate different devices.
- Optimize Code for Performance – Use Java’s multithreading for faster execution.
- Store Data Effectively – Choose databases based on project requirements.
- Error Handling & Logging – Implement error-handling mechanisms for stability.
Tools & Libraries for Java Web Scraping











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)























.webp?#)










_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)




































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)