Mastering UI/UX Design Principles
# Mastering UI/UX Design Principles Creating intuitive and user-friendly digital experiences requires a deep understanding of UI/UX design principles. This guide explores essential methodologies that will elevate your design skills and help you craft seamless user experiences. ## 1. Understanding UI vs. UX - **User Interface (UI):** Focuses on the aesthetics and interactive elements of a product (buttons, typography, colors, icons, etc.). - **User Experience (UX):** Encompasses the overall feel of the experience, including usability, accessibility, and user satisfaction. ## 2. Key UI/UX Design Principles ### Consistency - Maintain uniform design elements across the interface (buttons, typography, spacing, colors, etc.). - Use design systems like Material Design or Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines to ensure consistency. ### Simplicity & Clarity - Avoid unnecessary elements that could overwhelm users. - Ensure content is easy to read and understand. - Provide clear visual hierarchy to guide users naturally. ### Usability & Accessibility - Design for all users, including those with disabilities. - Follow WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) for better accessibility. - Ensure interactive elements are easily tappable/clickable. ### Visual Hierarchy - Use contrast, size, and positioning to indicate importance. - Guide users’ attention to key actions (CTA buttons, forms, etc.). ### Feedback & Response - Provide instant feedback for user actions (button clicks, form submissions, loading states, etc.). - Use microinteractions and animations to enhance user engagement. ### Mobile-First & Responsive Design - Prioritize mobile usability before scaling to larger screens. - Implement fluid grids and flexible layouts for responsiveness. ### User-Centered Design - Conduct user research to understand target audience needs. - Use wireframes and prototypes to test and iterate designs. ### Performance & Speed - Optimize images and assets to reduce loading time. - Ensure smooth interactions and avoid unnecessary animations that slow performance. ## 3. UI/UX Design Methodologies ### Design Thinking A human-centered approach to solving design problems through: 1. **Empathize** – Understand user needs. 2. **Define** – Identify user problems. 3. **Ideate** – Brainstorm solutions. 4. **Prototype** – Create interactive models. 5. **Test** – Validate with real users. ### Lean UX - Focuses on rapid prototyping and testing with minimal effort. - Encourages collaboration between designers, developers, and stakeholders. ### Agile UX - Integrates UX design within Agile development workflows. - Iterative design process with continuous feedback and improvements. ## 4. Tools for UI/UX Design - **Wireframing & Prototyping:** Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD, Balsamiq - **User Testing:** Hotjar, UsabilityHub, Maze - **Design Systems & Libraries:** Material UI, Tailwind CSS, Bootstrap ## Conclusion Mastering UI/UX principles ensures that digital experiences are not only visually appealing but also user-friendly and efficient. By applying consistency, simplicity, accessibility, and user-centered methodologies, designers can create impactful and meaningful products. Keep refining your skills, stay updated with trends, and always prioritize the end-user experience. --- *By mastering these principles, you can build designs that truly resonate with users and drive engagement.*

# Mastering UI/UX Design Principles
Creating intuitive and user-friendly digital experiences requires a deep understanding of UI/UX design principles. This guide explores essential methodologies that will elevate your design skills and help you craft seamless user experiences.
## 1. Understanding UI vs. UX
- **User Interface (UI):** Focuses on the aesthetics and interactive elements of a product (buttons, typography, colors, icons, etc.).
- **User Experience (UX):** Encompasses the overall feel of the experience, including usability, accessibility, and user satisfaction.
## 2. Key UI/UX Design Principles
### Consistency
- Maintain uniform design elements across the interface (buttons, typography, spacing, colors, etc.).
- Use design systems like Material Design or Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines to ensure consistency.
### Simplicity & Clarity
- Avoid unnecessary elements that could overwhelm users.
- Ensure content is easy to read and understand.
- Provide clear visual hierarchy to guide users naturally.
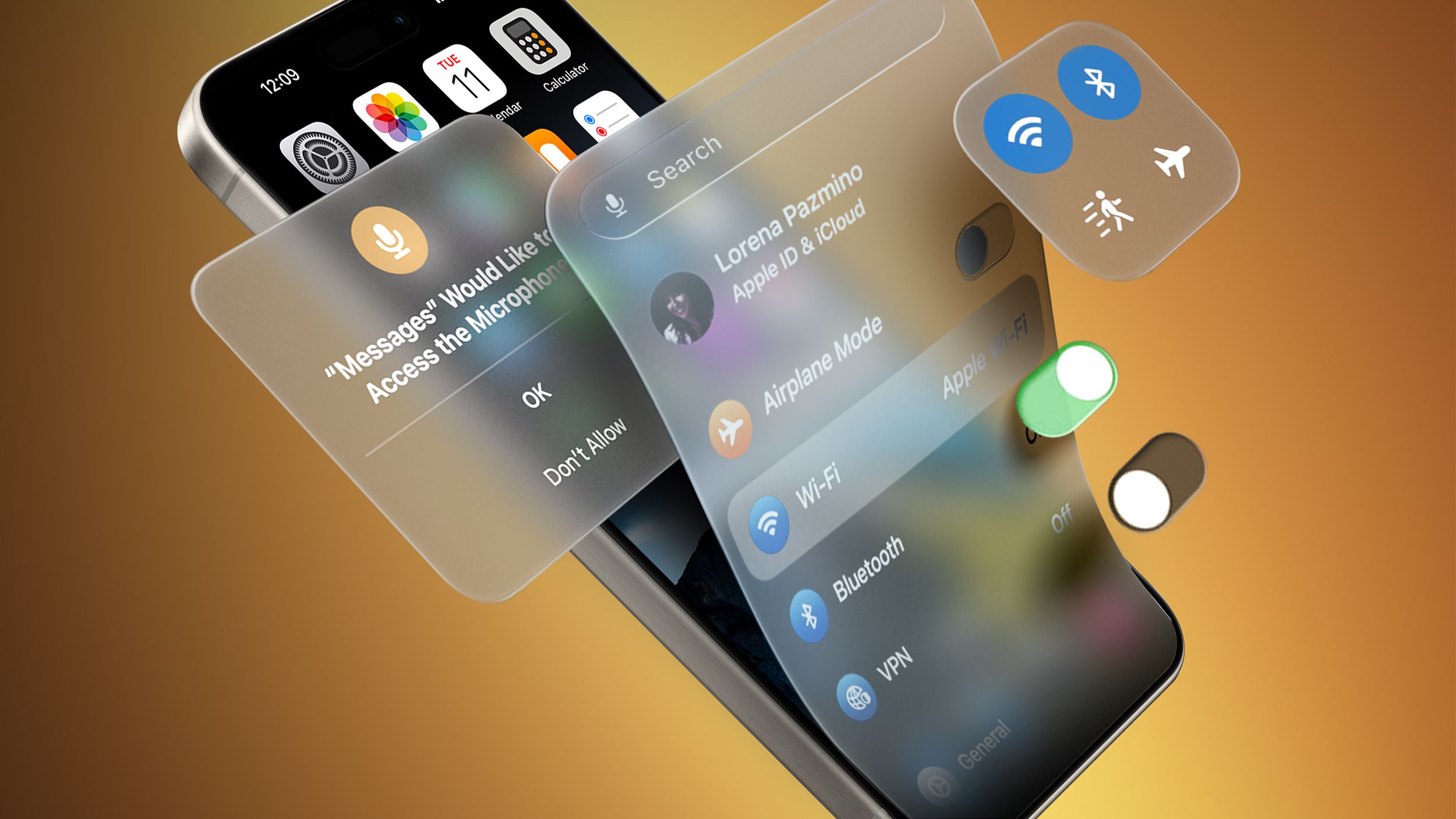
### Usability & Accessibility
- Design for all users, including those with disabilities.
- Follow WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) for better accessibility.
- Ensure interactive elements are easily tappable/clickable.
### Visual Hierarchy
- Use contrast, size, and positioning to indicate importance.
- Guide users’ attention to key actions (CTA buttons, forms, etc.).
### Feedback & Response
- Provide instant feedback for user actions (button clicks, form submissions, loading states, etc.).
- Use microinteractions and animations to enhance user engagement.
### Mobile-First & Responsive Design
- Prioritize mobile usability before scaling to larger screens.
- Implement fluid grids and flexible layouts for responsiveness.
### User-Centered Design
- Conduct user research to understand target audience needs.
- Use wireframes and prototypes to test and iterate designs.
### Performance & Speed
- Optimize images and assets to reduce loading time.
- Ensure smooth interactions and avoid unnecessary animations that slow performance.
## 3. UI/UX Design Methodologies
### Design Thinking
A human-centered approach to solving design problems through:
1. **Empathize** – Understand user needs.
2. **Define** – Identify user problems.
3. **Ideate** – Brainstorm solutions.
4. **Prototype** – Create interactive models.
5. **Test** – Validate with real users.
### Lean UX
- Focuses on rapid prototyping and testing with minimal effort.
- Encourages collaboration between designers, developers, and stakeholders.
### Agile UX
- Integrates UX design within Agile development workflows.
- Iterative design process with continuous feedback and improvements.
## 4. Tools for UI/UX Design
- **Wireframing & Prototyping:** Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD, Balsamiq
- **User Testing:** Hotjar, UsabilityHub, Maze
- **Design Systems & Libraries:** Material UI, Tailwind CSS, Bootstrap
## Conclusion
Mastering UI/UX principles ensures that digital experiences are not only visually appealing but also user-friendly and efficient. By applying consistency, simplicity, accessibility, and user-centered methodologies, designers can create impactful and meaningful products. Keep refining your skills, stay updated with trends, and always prioritize the end-user experience.
---
*By mastering these principles, you can build designs that truly resonate with users and drive engagement.*






































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)






























































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)










































































































.jpg?#)































_ArtemisDiana_Alamy.jpg?#)


 (1).webp?#)







































































-xl.jpg)













![Yes, the Gemini icon is now bigger and brighter on Android [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/02/Gemini-on-Galaxy-S25.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![Apple Rushes Five Planes of iPhones to US Ahead of New Tariffs [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96967/96967/96967-640.jpg)
![Apple Vision Pro 2 Allegedly in Production Ahead of 2025 Launch [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96965/96965/96965-640.jpg)