Linux Configuration: Hostnames, Networking, sudo and Basic of Wildcards.
Table-content:- Wildcards in Linux Hostname setup Basic network Setup sudo configuration 1.Wildcards In Linux wildcards are special character used in the command line to match multiple files or directory. They mostly used with command like ls, cp ,mv, => * match any characters, including zero charters ls *.log -> list the log files rm temp* mv *.txt directory/ => ? match the exact one character like single character 1.ls file?.txt list the file1 to file9 but to list out file10.txt 2.mv log?.txt logs/ move logs files from log1.txt to log9.txt => [] match the one character from set. 1.ls file[12].txt list out only file1.txt and file2.txt not file3.txt 2.ls [abc]*.txt list only matching character like a, b, c => [!] match any character except those inside brackets 1.ls file[!1].txt list all .txt file except file1.txt 2.ls [!abc]*.txt list all .txt except a, b ,c character => {}Expand to comma separate the values 1.touch {file1,file2,file3}.txt create mutiple fiel once 2.delete specific files rm {error,server,server}.log 3.copy the multiple file types cp *.{jpg,png,gif,txt} backupdir/ ** match file in subdirectories and ls **/*.txt find the all .txt file in all subdirectories rm **/*.log delete .log files inside any folder Escape character \ prevent wildcard: main purpose of using the escape character \ is to disable wildcard expansion or treat special characters as normal text in command. Example:- rm *text.txt -> delete all files ending in text.txt rm \*test.txt-> delete only one fie named as *text.txt **2. Hostname setup ** I. Check host name $ hostname output:- cyber.TAMIL.com II. check hostname full info ** $ hostnamectl or hostname status *III. Change hostname temporarily * $ hostname Cyber.TAMIL.com **IV. Change hostname permanently in terminal $ hostnamectl set-hostname Cyber.TAMIL.com V. Change hostname permanently in configuration file $ sudo vim /etc/hostname Output:- Centos.TAMIL.com => you can press i button (insert mode) then Esc , save :wq then , sudo reboot or exec bash(refresh the shell) VI. /etc/hosts (hostname ip mapping) *This file maps hostnames to ip address for local name resolution not applicable for Network-wide Resolution. Example:- $ sudo vim /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 oldhostname you can modify:- 127.0.0.1 newhostname For real network-wide hostname resolution: Set up a DNS server (like BIND, dnsmasq, or Unbound).Configure all machines to use the DNS server for hostname resolution. 3. Basic network Setup:- I.# nmclid d -> shows all network iterface. II. # nmcli d show eth0s3(my interface_name) -> Display details of eth0s3 III. Set the Static ip address $sudo systemctl restart Networkmanger or $nmcli networking off && nmcli networking on Restart on specific Network interface. sudo ifdown eth0 && sudo ifup eth0 id=eth0 -> name of the network connection. uuid= -> unique identifier (auto generated) type=ethernet -> wired ethernet connection autoconnect=true -> the system automatically connect the interface on boot interface-name=eth0 → Ensures the settings apply only to eth0. permissions=-> Restrict who can modify this connection (empty means restricted) permissions=username1;username2; -> only can access specific user timestamp=0 -> last modification timestamp(optional) 2 [ethernet] Section mac-address= -> mac address of your network card, optional but useful for binding configuration. 3. [ipv4] Section (Static IP Settings) method=manual -> assign the static ip address addresses=192.168.1.100/24; ip address -> 192.168.1.100 sub netmask -> /24 gateway=192.168.1.1 -> Default router IP dns=8.8.8.8;1.1.1.1; if you want to dynamic ip set only [ipv4] method=auto dns=8.8.8.8;1.1.1.1; ignore-auto-dns=true -> google 8.8.8.8 & 1.1.1.1 Cloudflare servers,ignore-auto-dns=true -> prevent Dhcp fri changing your dns settings, use always manual Dns settings. may-fail=false -> Forces the system to wait for a network connection before booting. I f network fails ,the system won't start until it's connected, it useful for server , may-fail=true the system will boot even if the network fails, it useful for desktop ,computer. 4. [ipv6] Section (Disabling IPv6) method=ignore -> Disable the IPv6 completely. or method=auto -> automatically get an ipv6 address. Network manger GUI( CentOS, RHEL, Fedora) $nmtui(text based gui ) (you can set Ip adress like static and dynamic) 4.Sudo configuration:- $sudo -l (check the who has the sudo access) $sudo -l -U username $sudo useradd username $sudo gpasswd -a username wheel or $sudo usermod -aG wheel username (add the user to wheel group) $sudo gpasswd -d username wheel (disabling the user to wheel group) whell = defaul admin group of centos/RHEL os $sudo visudo (edit the sudoers file) (or) $sudo visudo /etc/sudoers I added user prasanth362k to give allow to root run any commands
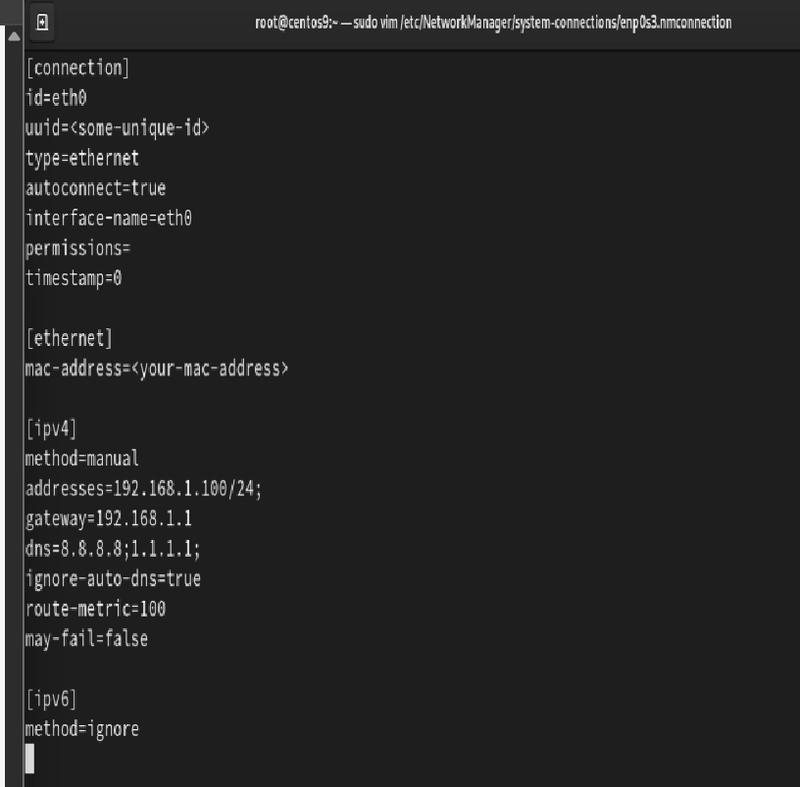
Table-content:-
- Wildcards in Linux
- Hostname setup
- Basic network Setup
- sudo configuration
1.Wildcards
- In Linux wildcards are special character used in the command line to match multiple files or directory. They mostly used with command like ls, cp ,mv,
=> * match any characters, including zero charters
-
ls *.log-> list the log files rm temp*mv *.txt directory/
=> ? match the exact one character like single character
1.ls file?.txt
list the file1 to file9 but to list out file10.txt
2.mv log?.txt logs/
move logs files from log1.txt to log9.txt
=> [] match the one character from set.
1.ls file[12].txt
list out only file1.txt and file2.txt not file3.txt
2.ls [abc]*.txt
list only matching character like a, b, c
=> [!] match any character except those inside brackets
1.ls file[!1].txt
list all .txt file except file1.txt
2.ls [!abc]*.txt
list all .txt except a, b ,c character
=> {}Expand to comma separate the values
1.touch {file1,file2,file3}.txt
create mutiple fiel once
2.delete specific files
rm {error,server,server}.log
3.copy the multiple file types
cp *.{jpg,png,gif,txt} backupdir/
** match file in subdirectories and
-
ls **/*.txtfind the all .txt file in all subdirectories -
rm **/*.logdelete .log files inside any folder
Escape character \ prevent wildcard:
- main purpose of using the escape character \ is to disable wildcard expansion or treat special characters as normal text in command.
Example:-
rm *text.txt -> delete all files ending in text.txt
rm \*test.txt-> delete only one fie named as *text.txt
**2. Hostname setup
**
I. Check host name
$ hostname
output:-
cyber.TAMIL.com
II. check hostname full info
**
$ hostnamectl or hostname status
*III. Change hostname temporarily
*
$ hostname Cyber.TAMIL.com
**IV. Change hostname permanently in terminal
$ hostnamectl set-hostname Cyber.TAMIL.com
V. Change hostname permanently in configuration file
$ sudo vim /etc/hostname
Output:-
Centos.TAMIL.com
=> you can press i button (insert mode) then Esc , save :wq then , sudo reboot or exec bash(refresh the shell)
VI. /etc/hosts (hostname <-> ip mapping)
*This file maps hostnames to ip address for local name resolution not applicable for Network-wide Resolution.
Example:-
$ sudo vim /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 oldhostname
you can modify:-
127.0.0.1 newhostname
For real network-wide hostname resolution:
- Set up a DNS server (like BIND, dnsmasq, or Unbound).Configure all machines to use the DNS server for hostname resolution.
3. Basic network Setup:-
I.# nmclid d -> shows all network iterface.
II. # nmcli d show eth0s3(my interface_name) -> Display details of eth0s3
III. Set the Static ip address
$sudo systemctl restart Networkmanger
or
$nmcli networking off && nmcli networking on
Restart on specific Network interface.
sudo ifdown eth0 && sudo ifup eth0
id=eth0 -> name of the network connection.
uuid= -> unique identifier (auto generated)
type=ethernet -> wired ethernet connection
autoconnect=true -> the system automatically connect the interface on boot
interface-name=eth0 → Ensures the settings apply only to eth0.
permissions=-> Restrict who can modify this connection (empty means restricted)
permissions=username1;username2; -> only can access specific user
timestamp=0
2 [ethernet] Section
mac-address= -> mac address of your network card, optional but useful for binding configuration.
3. [ipv4] Section (Static IP Settings)
method=manual -> assign the static ip address
addresses=192.168.1.100/24;
ip address -> 192.168.1.100
sub netmask -> /24
gateway=192.168.1.1 -> Default router IP
dns=8.8.8.8;1.1.1.1;
if you want to dynamic ip set only
[ipv4]
method=auto
dns=8.8.8.8;1.1.1.1;
ignore-auto-dns=true
-> google 8.8.8.8 & 1.1.1.1 Cloudflare servers,ignore-auto-dns=true -> prevent Dhcp fri changing your dns settings, use always manual Dns settings.
may-fail=false -> Forces the system to wait for a network connection before booting. I f network fails ,the system won't start until it's connected, it useful for server , may-fail=true the system will boot even if the network fails, it useful for desktop ,computer.
4. [ipv6] Section (Disabling IPv6)
method=ignore
or
method=auto -> automatically get an ipv6 address.
Network manger GUI( CentOS, RHEL, Fedora)
$nmtui(text based gui )
(you can set Ip adress like static and dynamic)
4.Sudo configuration:-
$sudo -l (check the who has the sudo access)
$sudo -l -U username
$sudo useradd username
$sudo gpasswd -a username wheel
or
$sudo usermod -aG wheel username
(add the user to wheel group)
$sudo gpasswd -d username wheel (disabling the user to wheel group)
whell = defaul admin group of centos/RHEL os
$sudo visudo (edit the sudoers file)
(or)
$sudo visudo /etc/sudoers
- I added user prasanth362k to give allow to root run any commands.
6.ALLOW a user to run only specific sudo commands :-
- Restrict sudo access to only commands improves security and limits risks.
- add the end of the file of
/etc/sudoerswithout # - Allowing a user to run only specific commands:-
-
Tamil ALL= NOPASSWD: /bin/systemctl restart apache2( restart service with out password) -
English ALL= PASSWD: /bin/systemctl restart apache2,/bin/systemctl restart nginx( restart service with password) -Akash ALL = PASSWD /sbin/ifconfig, /sbin/ip-Amala_paul ALL= NOPASSWD: /bin/mount, /bin/umount - think about ,one multination company is there work over 100000 employ , how it possible each user can set permission level . we can create group then we will restrict the group which command can execute and not execute.
Example:-
$ sudo groupadd it_team
%it_team ALL = NOPASSWD: /bin/systemctl restart apache2
%network_admin = PASSWD: /sbin/ip, /sbin/iptables
%hr_team ALL= NOPASSWD: /bin/cat /etc/payroll.conf
%dev_team ALL= NOPASSWD: /bin/git pull, /bin/systemctl restart app-service
/bin = permit only normal user can execute the small tasks like nano cat ,systemctl.
/sbin= permit only admin user can execute the system level tasks like reboot, ifconfig ,iptables.
Tamil ALL= NOPASSWD: /bin/cat =>only user Tamil environent execute command
Samantha ALL=(root) PASSWD : /bin/cat =>Samantha can run the specified command as root,password require when using sudo.
Trisha ALL=(ALL) PASSWD : /bin/cat => only Trish user can execute the command,She can run the command as any user(not regular human user) (including root) using sudo -u. password required, does not mean any user.
Example:-
sudo -u root /bin/systemctl restart apache2
sudo -u apache /bin/systemctl restart apache2
sudo -u www-data /bin/systemctl restart apache2
- you can aks me question apche ,ww-data is user ?
- This users all system service related specific user.
Example:-
www-data-> user all webservice like apache, nginx (debian/ubuntu)
mysql -> user for MYSQL
postgres-> user for PostgreSQL
=> Validate the sudoers file before applying changes:
$sudo visudo -c ( Check for syntax)











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)























.webp?#)










_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)




































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)