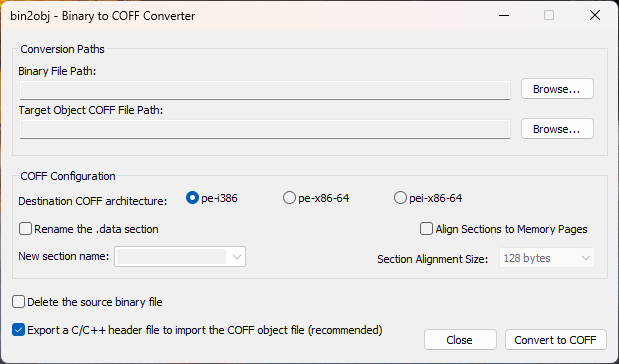
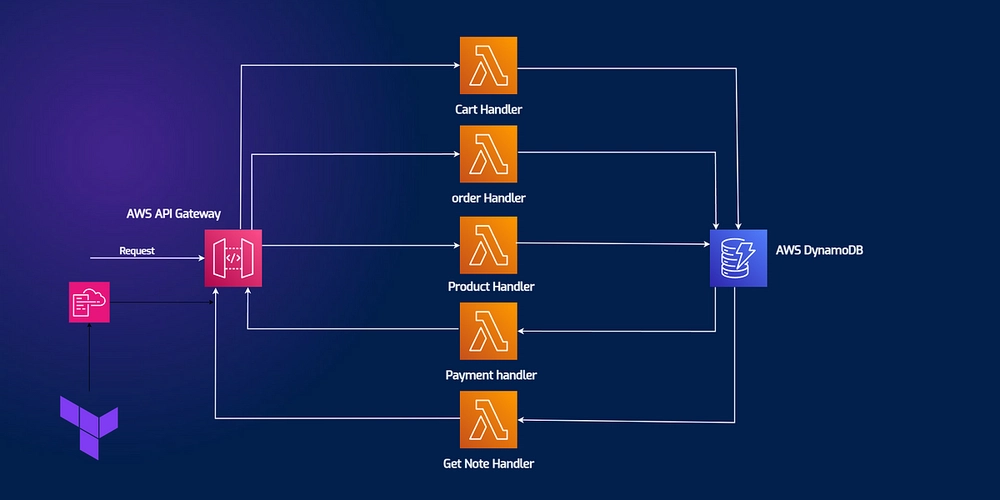
How to Embed Binary Data into a Win32 Executable File in 4 Methods
This Gist covers 4 methods to embed arbitrary binary files (images, data, etc.) inside an executable. From standard approaches (byte arrays) to low-level hacks like binary appending (copy /b), each method includes ready-to-use examples in Visual C++. Use cases: Single-file deployment (no external resources). Hiding data inside .exe/.elf (no encryption). Quick prototyping or educational purposes. ⚠️ Note: Methods 1-3 are "clean" and portable. Method 4 (copy /b) is a hack and may cause problems with checksums or antivirus. All examples assume x86_64 context (adaptable for other architectures). Method 1: Using Win32 Resource Files (.rc) Best for: Native Windows executables where you want integrated resource handling Step 1: Add resource files in Visual Studio Right-click project → Add → Resource... Choose "Import..." and select your binary file (e.g., data.bin) Set resource type as RCDATA and assign an ID (e.g., IDR_MY_DATA) Visual Studio will automatically: Generate/modify resource.h with your ID Create/update the .rc file with: IDR_MY_DATA RCDATA "file.bin" Step 2: Access the resource from code This will be the code to access the resources: main.cpp #include #include "resource.h" // Auto-generated by VS void LoadEmbeddedData() { HRSRC hRes = FindResource(nullptr, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDR_MY_DATA), RT_RCDATA); DWORD dataSize = SizeofResource(nullptr, hRes); HGLOBAL hData = LoadResource(nullptr, hRes); const BYTE* pData = static_cast(LockResource(hData)); // Use pData (read-only) and dataSize... // Note: LockResource doesn't need unlocking } Key Notes:
This Gist covers 4 methods to embed arbitrary binary files (images, data, etc.) inside an executable.
From standard approaches (byte arrays) to low-level hacks like binary appending (copy /b), each method includes ready-to-use examples in Visual C++.
Use cases:
- Single-file deployment (no external resources).
- Hiding data inside .exe/.elf (no encryption).
- Quick prototyping or educational purposes.
⚠️ Note:
- Methods 1-3 are "clean" and portable.
- Method 4 (
copy /b) is a hack and may cause problems with checksums or antivirus. - All examples assume x86_64 context (adaptable for other architectures).
Method 1: Using Win32 Resource Files (.rc)
Best for: Native Windows executables where you want integrated resource handling
Step 1: Add resource files in Visual Studio
- Right-click project → Add → Resource...
- Choose "Import..." and select your binary file (e.g.,
data.bin) - Set resource type as
RCDATAand assign an ID (e.g.,IDR_MY_DATA)
Visual Studio will automatically:
- Generate/modify
resource.hwith your ID - Create/update the
.rcfile with:
IDR_MY_DATA RCDATA "file.bin"
Step 2: Access the resource from code
This will be the code to access the resources:
main.cpp
#include 








































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The All-in-One Microsoft Office Pro 2019 for Windows: Lifetime License + Windows 11 Pro Bundle (89% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


















































































































































_Andreas_Prott_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
































































































![What features do you get with Gemini Advanced? [April 2025]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/02/gemini-advanced-cover.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![Apple Shares Official Trailer for 'Long Way Home' Starring Ewan McGregor and Charley Boorman [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97069/97069/97069-640.jpg)
![Apple Watch Series 10 Back On Sale for $299! [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96657/96657/96657-640.jpg)
![EU Postpones Apple App Store Fines Amid Tariff Negotiations [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97068/97068/97068-640.jpg)