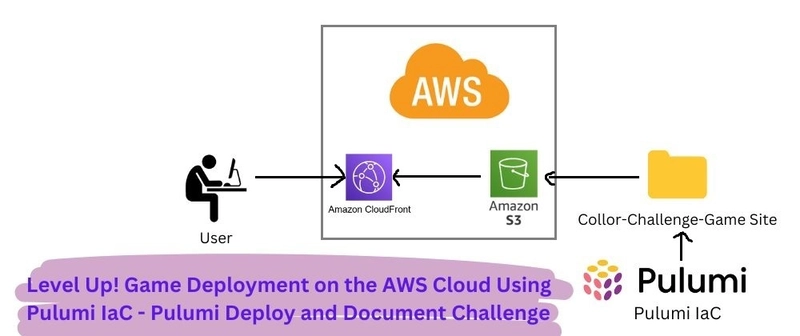
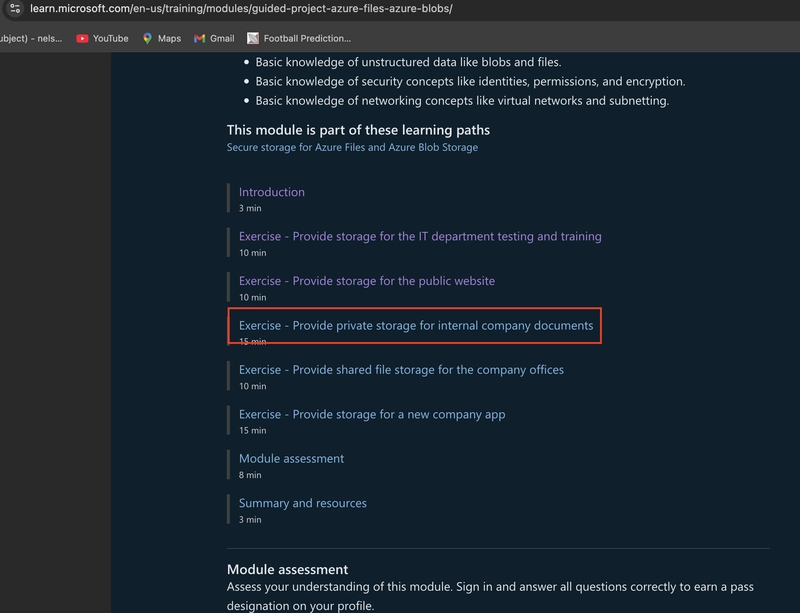
How OAuth2 Differs from API Keys: Understanding Secure API Authentication
Learn the key differences between OAuth2 and API Keys for secure API authentication In the ever-evolving landscape of software development, securing APIs is non-negotiable. With APIs acting as gateways to sensitive data and critical functionalities, choosing the right authentication method is crucial. Two common approaches dominate the field: API Keys and OAuth2. While both are used for authenticating API requests, they serve different purposes and offer varying levels of security. In this article, we'll delve into the fundamental differences between OAuth2 and API Keys, explore their respective strengths and weaknesses, and help you understand when to use each for secure API authentication. 1. What Are API Keys? Definition: An API Key is a simple, unique identifier passed along with an API request to authenticate the client making the request. Think of it as a password for your application to access an API. How API Keys Work: A developer generates an API key from the API provider. The key is included in the request header, URL, or body. The server validates the key and processes the request if it’s valid. Example: curl -H "Authorization: Api-Key YOUR_API_KEY" Pros of API Keys: Simplicity: Easy to implement and manage, especially for internal applications. Quick Setup: No need for complex token exchanges or authorization flows. Useful for Server-to-Server Communication: Effective for backend systems where security risks are minimal. Cons of API Keys: Lack of Granular Permissions: Limited control over what specific actions or data the key can access. Weak Security: Susceptible to leakage if embedded in front-end code or exposed in logs. No User Authentication: API keys authenticate the application, not the end-user. 2. What is OAuth2? Definition: OAuth2 (Open Authorization 2.0) is an industry-standard authorization framework that allows applications to obtain limited access to user resources without exposing credentials. It’s designed for delegated access, enabling third-party applications to act on behalf of a user. How OAuth2 Works: Authorization Request: The client requests access from the resource owner (user). Token Issuance: If granted, an authorization server issues an access token. API Request: The client includes the access token in API requests to authenticate. Token Validation: The API server validates the token and processes the request. Example (Bearer Token): curl -H "Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN" Pros of OAuth2: Strong Security: Tokens can be short-lived, encrypted, and scoped to specific permissions. User-Centric: Enables authentication on behalf of users, not just applications. Granular Access Control: Supports scopes and roles to define fine-grained permissions. Widely Adopted: Used by major platforms like Google, Facebook, and Microsoft. Cons of OAuth2: Complexity: Requires understanding of flows (Authorization Code, Client Credentials, etc.). Token Management Overhead: Involves handling token expiration, refresh tokens, and revocation. Overkill for Simple Use Cases: Not necessary for basic server-to-server API calls. 3. Key Differences Between API Keys and OAuth2 4. When to Use API Keys vs. OAuth2 ✅ When to Use API Keys: Internal Applications: For backend services where security risks are controlled. Server-to-Server Communication: Where user-level authentication is unnecessary. Prototyping or Quick Tests: For simple API calls during development.

Learn the key differences between OAuth2 and API Keys for secure API authentication
In the ever-evolving landscape of software development, securing APIs is non-negotiable. With APIs acting as gateways to sensitive data and critical functionalities, choosing the right authentication method is crucial. Two common approaches dominate the field: API Keys and OAuth2.
While both are used for authenticating API requests, they serve different purposes and offer varying levels of security. In this article, we'll delve into the fundamental differences between OAuth2 and API Keys, explore their respective strengths and weaknesses, and help you understand when to use each for secure API authentication.
1. What Are API Keys?
Definition:
An API Key is a simple, unique identifier passed along with an API request to authenticate the client making the request. Think of it as a password for your application to access an API.
How API Keys Work:
- A developer generates an API key from the API provider.
- The key is included in the request header, URL, or body.
- The server validates the key and processes the request if it’s valid.
Example:
curl -H "Authorization: Api-Key YOUR_API_KEY"
Pros of API Keys:
- Simplicity: Easy to implement and manage, especially for internal applications.
- Quick Setup: No need for complex token exchanges or authorization flows.
- Useful for Server-to-Server Communication: Effective for backend systems where security risks are minimal.
Cons of API Keys:
- Lack of Granular Permissions: Limited control over what specific actions or data the key can access.
- Weak Security: Susceptible to leakage if embedded in front-end code or exposed in logs.
- No User Authentication: API keys authenticate the application, not the end-user.
2. What is OAuth2?
Definition:
OAuth2 (Open Authorization 2.0) is an industry-standard authorization framework that allows applications to obtain limited access to user resources without exposing credentials. It’s designed for delegated access, enabling third-party applications to act on behalf of a user.
How OAuth2 Works:
- Authorization Request: The client requests access from the resource owner (user).
- Token Issuance: If granted, an authorization server issues an access token.
- API Request: The client includes the access token in API requests to authenticate.
- Token Validation: The API server validates the token and processes the request.
Example (Bearer Token):
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN"
Pros of OAuth2:
- Strong Security: Tokens can be short-lived, encrypted, and scoped to specific permissions.
- User-Centric: Enables authentication on behalf of users, not just applications.
- Granular Access Control: Supports scopes and roles to define fine-grained permissions.
- Widely Adopted: Used by major platforms like Google, Facebook, and Microsoft.
Cons of OAuth2:
- Complexity: Requires understanding of flows (Authorization Code, Client Credentials, etc.).
- Token Management Overhead: Involves handling token expiration, refresh tokens, and revocation.
- Overkill for Simple Use Cases: Not necessary for basic server-to-server API calls.
3. Key Differences Between API Keys and OAuth2
4. When to Use API Keys vs. OAuth2
✅ When to Use API Keys:
- Internal Applications: For backend services where security risks are controlled.
- Server-to-Server Communication: Where user-level authentication is unnecessary.
- Prototyping or Quick Tests: For simple API calls during development.











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)























.webp?#)










_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)




































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)



































































































































