DMarket and Cyberwarfare: Bridging the Virtual and Real Worlds
Abstract In this post, we explore the convergence of virtual asset trading platforms and cyberwarfare. We dive into how DMarket leverages blockchain technology to secure digital asset trading, and we examine the broader implications of cybersecurity in an increasingly digital world. We discuss core concepts such as blockchain security, smart contracts, and ethical considerations in digital marketplaces. In addition, we include real-life use cases, challenges faced by the industry, and the future outlook of integrated digital systems. This post blends technical insights with an accessible narrative, supported by authoritative resources and curated Dev.to articles. Introduction The rapid evolution of digital technologies has ushered in new forms of commerce and warfare. Platforms like DMarket not only revolutionize gaming and digital asset trading but also serve as a critical nexus between virtual economies and real-world security challenges. As the boundaries blur between cyberwarfare and everyday transactions, issues such as blockchain security and ethical digital asset management become central to discussions. In this article, we expand on the insights offered in the original article on DMarket and Cyberwarfare to provide a holistic view of this dynamic field. We’ll discuss the fundamentals of blockchain technology, its role in protecting digital marketplaces, and how cyberwarfare strategies are evolving concurrently. Our goal is to deliver technical expertise while remaining accessible to a broad audience interested in technology, cyberdefense, and open-source innovation. Background and Context DMarket and the Digital Ecosystem DMarket is more than just a marketplace for digital assets—it is a pioneering platform that integrates blockchain technology into gaming and virtual asset trading. By utilizing a decentralized framework, DMarket provides a secure and transparent environment where users can trade, collect, and manage digital assets with confidence. This technology reduces intermediary risks and enhances asset provenance. Key points about DMarket include: Transparency: Each transaction on the platform is recorded on a tamper-proof ledger. Security: Advanced blockchain protocols safeguard asset ownership and trade integrity. Interoperability: The platform’s underlying technology can integrate with various gaming ecosystems and digital marketplaces. For those unfamiliar with the technology, it is useful to explore resources such as what is blockchain for a basic primer, and the Blockchain Security Guide by IBM for deeper technical insight. Understanding Cyberwarfare Cyberwarfare involves the use of digital attacks by nation-states or non-state actors to disrupt, damage, or gain an advantage over adversaries. It encompasses a range of activities including network intrusions, data breaches, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. The cybersecurity landscape is dynamic, and institutions like the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) offer critical insights into these threats. As digital markets evolve, the intersection between cyberwarfare and digital asset trading calls for enhanced security measures. Projects like DMarket must be proactive in defending against potential cyberattacks while ensuring compliance with evolving legal and ethical standards. The Role of Open-Source in Cybersecurity Open-source projects often power the backbone of digital marketplaces. Open collaboration, transparency, and ethical software development are values that enhance cybersecurity and foster innovation. Organizations like the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) advocate for digital rights and contribute to discussions around ethical software development guidelines, ensuring that open-source projects maintain robust security standards. Core Concepts and Features Blockchain Fundamentals and Security At the heart of DMarket’s operations is blockchain technology. Blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions securely and immutably. Key features include: Decentralization: No single point of control reduces vulnerability. Transparency: Each transaction is verifiable by any network participant. Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered, ensuring data integrity. The use of smart contracts—a digital agreement that self-executes when conditions are met—is a notable core concept. Smart contracts enhance security by automating processes and reducing manual intervention, as further explored in smart contracts on blockchain. Cyberwarfare and Digital Asset Protection Cyberwarfare strategies necessitate robust defenses in digital asset platforms. Key components include: Threat Detection: Rapid identification of anomalies and breaches. Incident Response: Protocols to minimize damage and rec

Abstract
In this post, we explore the convergence of virtual asset trading platforms and cyberwarfare. We dive into how DMarket leverages blockchain technology to secure digital asset trading, and we examine the broader implications of cybersecurity in an increasingly digital world. We discuss core concepts such as blockchain security, smart contracts, and ethical considerations in digital marketplaces. In addition, we include real-life use cases, challenges faced by the industry, and the future outlook of integrated digital systems. This post blends technical insights with an accessible narrative, supported by authoritative resources and curated Dev.to articles.
Introduction
The rapid evolution of digital technologies has ushered in new forms of commerce and warfare. Platforms like DMarket not only revolutionize gaming and digital asset trading but also serve as a critical nexus between virtual economies and real-world security challenges. As the boundaries blur between cyberwarfare and everyday transactions, issues such as blockchain security and ethical digital asset management become central to discussions.
In this article, we expand on the insights offered in the original article on DMarket and Cyberwarfare to provide a holistic view of this dynamic field. We’ll discuss the fundamentals of blockchain technology, its role in protecting digital marketplaces, and how cyberwarfare strategies are evolving concurrently. Our goal is to deliver technical expertise while remaining accessible to a broad audience interested in technology, cyberdefense, and open-source innovation.
Background and Context
DMarket and the Digital Ecosystem
DMarket is more than just a marketplace for digital assets—it is a pioneering platform that integrates blockchain technology into gaming and virtual asset trading. By utilizing a decentralized framework, DMarket provides a secure and transparent environment where users can trade, collect, and manage digital assets with confidence. This technology reduces intermediary risks and enhances asset provenance.
Key points about DMarket include:
- Transparency: Each transaction on the platform is recorded on a tamper-proof ledger.
- Security: Advanced blockchain protocols safeguard asset ownership and trade integrity.
- Interoperability: The platform’s underlying technology can integrate with various gaming ecosystems and digital marketplaces.
For those unfamiliar with the technology, it is useful to explore resources such as what is blockchain for a basic primer, and the Blockchain Security Guide by IBM for deeper technical insight.
Understanding Cyberwarfare
Cyberwarfare involves the use of digital attacks by nation-states or non-state actors to disrupt, damage, or gain an advantage over adversaries. It encompasses a range of activities including network intrusions, data breaches, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. The cybersecurity landscape is dynamic, and institutions like the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) offer critical insights into these threats.
As digital markets evolve, the intersection between cyberwarfare and digital asset trading calls for enhanced security measures. Projects like DMarket must be proactive in defending against potential cyberattacks while ensuring compliance with evolving legal and ethical standards.
The Role of Open-Source in Cybersecurity
Open-source projects often power the backbone of digital marketplaces. Open collaboration, transparency, and ethical software development are values that enhance cybersecurity and foster innovation. Organizations like the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) advocate for digital rights and contribute to discussions around ethical software development guidelines, ensuring that open-source projects maintain robust security standards.
Core Concepts and Features
Blockchain Fundamentals and Security
At the heart of DMarket’s operations is blockchain technology. Blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions securely and immutably. Key features include:
- Decentralization: No single point of control reduces vulnerability.
- Transparency: Each transaction is verifiable by any network participant.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered, ensuring data integrity.
The use of smart contracts—a digital agreement that self-executes when conditions are met—is a notable core concept. Smart contracts enhance security by automating processes and reducing manual intervention, as further explored in smart contracts on blockchain.
Cyberwarfare and Digital Asset Protection
Cyberwarfare strategies necessitate robust defenses in digital asset platforms. Key components include:
- Threat Detection: Rapid identification of anomalies and breaches.
- Incident Response: Protocols to minimize damage and recover control.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to legal frameworks and international guidelines.
Both DMarket’s blockchain approach and cybersecurity measures work together to protect digital assets, making the virtual marketplace less vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Comparative Overview
Below is a table comparing core aspects of blockchain technology and traditional cybersecurity measures in digital asset trading:
| Feature | Blockchain Technology | Traditional Cybersecurity |
|---|---|---|
| Decentralization | Distributed network with no central point of failure | Centralized systems often have single points of vulnerability |
| Transparency | Public, immutable ledger accessible to all users | Audit logs that can be altered or hidden |
| Smart Contract Usage | Automated execution of contracts without intermediaries | Manual processing requiring significant human oversight |
| Security | Cryptographic security measures provide tamper-proof records | Reliant on firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and patching |
| Resilience Against Cyberwarfare | Enhanced through decentralization and rapid consensus algorithms | Often requires extensive additional protective measures |
Bullet List of Key Terms
- Blockchain Technology: The backbone of decentralized digital asset trading.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing agreements embedded in blockchain.
- Cyberwarfare: Digital attacks targeting networks and critical infrastructure.
- Transparency: A characteristic that builds trust in digital systems.
- Open-Source: Collaborative development that improves security and innovation.
Applications and Use Cases
Use Case 1: Secure Digital Asset Trading in Gaming
Platforms like DMarket enable gamers to trade in-game assets securely. By leveraging blockchain, every trade is verified and recorded, reducing disputes and fraudulent transactions. Imagine a scenario where a gamer sells a rare virtual item:
- The smart contract is deployed automatically once payment is confirmed.
- The digital asset’s provenance is recorded on the blockchain.
- Cybersecurity measures ensure that the transaction remains tamper-proof.
This process illustrates how integration of blockchain technology enhances security in the digital gaming ecosystem.
Use Case 2: Cyber Defense and Incident Response
In an era where cyberattacks are frequent, financial institutions and digital marketplaces need resilient strategies. In cyberwarfare scenarios:
- Threat Monitoring: Systems continuously scan for suspicious activity.
- Incident Management: Automated responses deployed via smart contracts help mitigate damage.
- Legal Compliance: Real-time logging and immutable records simplify regulatory audits.
For more details on cybersecurity principles, visit the blockchain security resource.
Use Case 3: Open-Source Collaboration for Ethical Software Development
The integration of open-source principles in cybersecurity ensures continuous community-led improvement. Ethical frameworks not only empower developers but also enhance the security of platforms like DMarket. Open-source projects undergo frequent peer reviews and incorporate community-sourced innovations to address vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Challenges and Limitations
Technical Challenges
Despite its benefits, blockchain technology faces several challenges:
- Scalability Issues: As transactions increase, the network may become congested.
- Interoperability: Integrating blockchain with existing systems can be complex.
- Latency: Decentralized consensus can sometimes slow transaction processing.
Additionally, while smart contracts minimize human error, vulnerabilities in their code can lead to unintended outcomes if not audited thoroughly.
Adoption and Regulatory Limitations
Digital asset marketplaces must navigate a maze of regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements. Key concerns include:
- Legal Uncertainty: Regulations concerning digital assets and cyberwarfare are still evolving.
- Market Adoption: Convincing traditional institutions to adopt decentralized systems presents challenges.
- Ethical Considerations: Balancing profit with ethical and transparent practices is paramount.
For insights into open source ethics, readers may explore ethical software development.
Cybersecurity Threats
Though blockchain provides robust security, it is not impervious. Cyber attackers continuously develop new methods to exploit vulnerabilities, whether through phishing, social engineering, or exploiting coding errors in smart contracts. The security of digital asset exchanges like DMarket relies heavily on regular updates and adherence to best practices in the industry.
Future Outlook and Innovations
Evolving Digital Marketplaces
The future of digital asset marketplaces is intertwined with advances in blockchain technology and cyber defense. Key trends include:
- Increased Interoperability: Enhanced cross-chain solutions will allow seamless exchange of assets.
- Improved Scalability: New consensus mechanisms and layer-2 solutions are emerging to reduce latency and increase throughput.
- More Robust Cyber Defenses: As cyberwarfare tactics evolve, so will countermeasures in digital asset trading platforms.
Innovations Driving Change
Technological innovations such as zero-knowledge proofs and advanced encryption methods will further secure blockchain protocols. These innovations not only improve security but also facilitate greater privacy for users. In collaboration with open-source communities, many of these advances are driven by projects that prioritize transparency and ethical development.
Dev.to Perspectives
Several Dev.to posts shed light on evolving approaches to open-source and blockchain integration. For instance, the article License Token Revolutionizing Open Source Licensing provides insights into how smart contracts and decentralized funding models are reshaping the digital landscape. Similarly, Embracing the Future: NFTs as a Game Changer in Open Source Rewards explores how tokenization offers new incentives and funding opportunities for developers.
Another noteworthy discussion, What Is the Tidelift Open Source Funding Model? An In-Depth Look, dives into innovative funding models that support community-driven development. These perspectives highlight the synergies between cybersecurity, blockchain, and ethical open-source practices.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Another emerging trend is the integration of AI with blockchain to predict and preempt cyberattacks. By analyzing data patterns, machine learning algorithms can offer predictive insights that enhance both security and operational efficiency. This proactive approach could be a game changer in defending both virtual marketplaces and critical infrastructure in the event of cyberwarfare.
Summary
In this post, we navigated the intricate relationship between DMarket, blockchain technology, and the realities of cyberwarfare. We started by exploring the underlying technology powering digital asset trading platforms like DMarket and how smart contracts contribute to a secure and immutable ledger system. Alongside this, we examined the evolving landscape of cyberwarfare and the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures in protecting digital assets.
Key takeaways include:
- Blockchain Fundamentals: The decentralization, transparency, and immutability that underpin secure digital transactions.
- Cyber Defense Techniques: From threat detection and response to regulatory compliance, the integration of cybersecurity measures is vital in today’s digital marketplace.
- Practical Use Cases: Real-world examples from gaming asset trading, incident response in cyberwarfare scenarios, and the ethical challenges of open-source software development.
- Challenges Ahead: Scalability, regulatory hurdles, and evolving cyber threats remain significant challenges that require ongoing innovation and collaboration.
- Future Innovations: Advanced technologies like zero-knowledge proofs, layer-2 scaling solutions, and AI integration promise a future where digital asset trading is even more secure and efficient.
As digital marketplaces continue to expand, the convergence of blockchain security and cyberwarfare strategies will be critical. By fostering open-source collaboration and embracing innovative funding models—as demonstrated in Dev.to discussions—platforms like DMarket can remain at the forefront of the innovation curve.
For further reading and to deepen your understanding, explore resources such as blockchain security and the official DMarket website. Additionally, consider insights from authoritative bodies such as the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Final Thoughts
Bridging the gap between the virtual and real worlds is no longer science fiction—it is our everyday reality. By embedding robust blockchain technology within digital asset marketplaces and adopting a vigilant approach to cybersecurity, platforms like DMarket are leading by example. As threats evolve and technological innovations continue to emerge, the synergy between these domains will shape the future of safe, transparent, and ethical digital commerce.
Key Terms:
Blockchain Technology, Cyberwarfare, Smart Contracts, Digital Asset Trading, Open-Source Ethics.
Further Resources:
- DMarket and Cyberwarfare: Bridging the Virtual and Real Worlds
- What is Blockchain
- Smart Contracts on Blockchain
- Ethical Software Development
By staying informed and adopting best practices, both developers and end users can contribute to a more secure digital future. The blend of blockchain innovation with cyberwarfare countermeasures offers tremendous promise for transforming digital marketplaces into resilient bastions of trust and efficiency.
Additional Dev.to Insights:
- License Token Revolutionizing Open Source Licensing
- Embracing the Future: NFTs as a Game Changer in Open Source Rewards
- What Is the Tidelift Open Source Funding Model? An In-Depth Look
This comprehensive analysis serves as a guide to understanding how blockchain and cybersecurity intersect in today's digital asset ecosystem. With continued innovation and community collaboration, the path forward is not only promising but also essential for ensuring sustainable digital markets in our increasingly interconnected world.











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)


































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
.webp?#)
 (1).webp?#)






































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
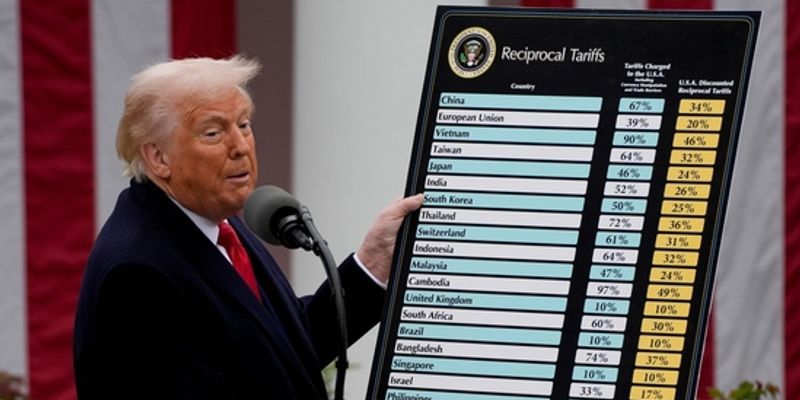
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)