Building a Polyphonic Synth with Web Audio API (No Libraries Needed)
The Web Audio API is more powerful than most developers realize — it's capable of running full synth engines in the browser. This article shows how to build a basic polyphonic synthesizer from scratch using raw Web Audio primitives. Great for interactive music apps, education tools, or browser-based DAWs. What We’ll Build Multiple simultaneous notes (polyphony) ADSR envelope for smooth attack and release Keyboard input for triggering sounds Step 1: Create the Audio Context Set up your Web Audio graph entry point: const audioCtx = new (window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext)(); Step 2: Define a Note Class This encapsulates oscillator, gain (for volume), and envelope behavior: class SynthNote { constructor(freq) { this.osc = audioCtx.createOscillator(); this.gain = audioCtx.createGain(); this.osc.type = 'sawtooth'; this.osc.frequency.value = freq; this.osc.connect(this.gain); this.gain.connect(audioCtx.destination); const now = audioCtx.currentTime; this.gain.gain.setValueAtTime(0, now); this.gain.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(0.5, now + 0.01); // attack this.osc.start(now); } stop() { const now = audioCtx.currentTime; this.gain.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(0, now + 0.3); // release this.osc.stop(now + 0.3); } } Step 3: Add Keyboard Controls Trigger notes with key events and a simple mapping: const activeNotes = {}; const keyMap = { 'a': 261.63, // C4 's': 293.66, // D4 'd': 329.63, // E4 'f': 349.23, // F4 'g': 392.00, // G4 }; document.addEventListener('keydown', e => { const freq = keyMap[e.key]; if (freq && !activeNotes[e.key]) { activeNotes[e.key] = new SynthNote(freq); } }); document.addEventListener('keyup', e => { if (activeNotes[e.key]) { activeNotes[e.key].stop(); delete activeNotes[e.key]; } }); Optional: Enhance with Filters or LFO You can easily insert filters between oscillator and destination: const filter = audioCtx.createBiquadFilter(); filter.type = 'lowpass'; filter.frequency.value = 1000; this.osc.connect(filter); filter.connect(this.gain); Pros and Cons ✅ Pros Totally self-contained and fast to load Works offline — no libraries or backend required Foundation for more advanced synth engines ⚠️ Cons No MIDI support out of the box (but possible with Web MIDI API) Timing can drift slightly without clock sync Requires handling audio unlock on mobile devices

The Web Audio API is more powerful than most developers realize — it's capable of running full synth engines in the browser. This article shows how to build a basic polyphonic synthesizer from scratch using raw Web Audio primitives. Great for interactive music apps, education tools, or browser-based DAWs.
What We’ll Build
- Multiple simultaneous notes (polyphony)
- ADSR envelope for smooth attack and release
- Keyboard input for triggering sounds
Step 1: Create the Audio Context
Set up your Web Audio graph entry point:
const audioCtx = new (window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext)();Step 2: Define a Note Class
This encapsulates oscillator, gain (for volume), and envelope behavior:
class SynthNote {
constructor(freq) {
this.osc = audioCtx.createOscillator();
this.gain = audioCtx.createGain();
this.osc.type = 'sawtooth';
this.osc.frequency.value = freq;
this.osc.connect(this.gain);
this.gain.connect(audioCtx.destination);
const now = audioCtx.currentTime;
this.gain.gain.setValueAtTime(0, now);
this.gain.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(0.5, now + 0.01); // attack
this.osc.start(now);
}
stop() {
const now = audioCtx.currentTime;
this.gain.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(0, now + 0.3); // release
this.osc.stop(now + 0.3);
}
}
Step 3: Add Keyboard Controls
Trigger notes with key events and a simple mapping:
const activeNotes = {};
const keyMap = {
'a': 261.63, // C4
's': 293.66, // D4
'd': 329.63, // E4
'f': 349.23, // F4
'g': 392.00, // G4
};
document.addEventListener('keydown', e => {
const freq = keyMap[e.key];
if (freq && !activeNotes[e.key]) {
activeNotes[e.key] = new SynthNote(freq);
}
});
document.addEventListener('keyup', e => {
if (activeNotes[e.key]) {
activeNotes[e.key].stop();
delete activeNotes[e.key];
}
});
Optional: Enhance with Filters or LFO
You can easily insert filters between oscillator and destination:
const filter = audioCtx.createBiquadFilter();
filter.type = 'lowpass';
filter.frequency.value = 1000;
this.osc.connect(filter);
filter.connect(this.gain);Pros and Cons
✅ Pros
- Totally self-contained and fast to load
- Works offline — no libraries or backend required
- Foundation for more advanced synth engines
⚠️ Cons
- No MIDI support out of the box (but possible with Web MIDI API)
- Timing can drift slightly without clock sync
- Requires handling audio unlock on mobile devices





































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)































































































































![[DEALS] Sterling Stock Picker: Lifetime Subscription (85% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)












































































































































_Olekcii_Mach_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)













































































































![M4 MacBook Air Drops to New All-Time Low of $912 [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97108/97108/97108-640.jpg)
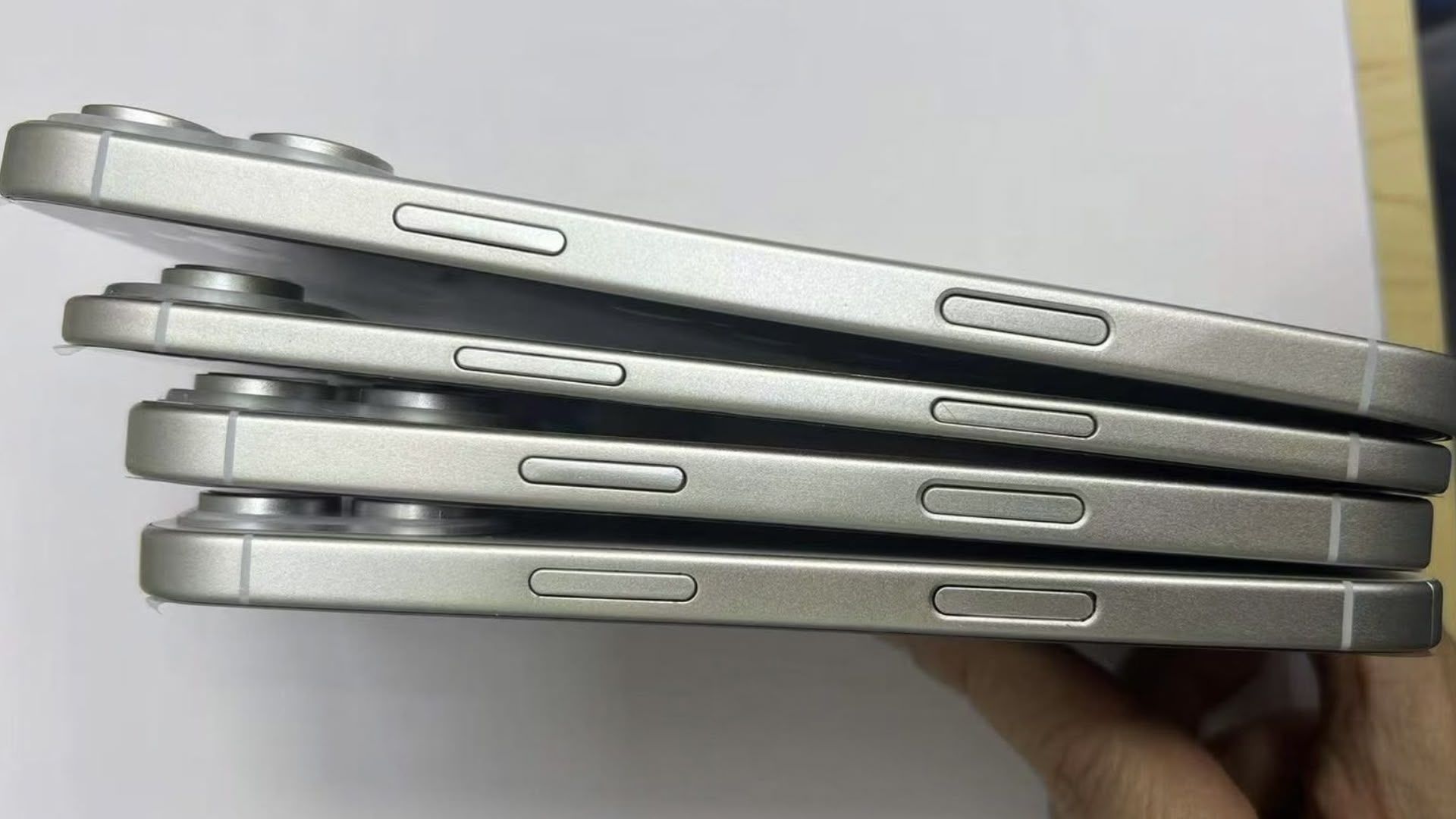
![New iPhone 17 Dummy Models Surface in Black and White [Images]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97106/97106/97106-640.jpg)