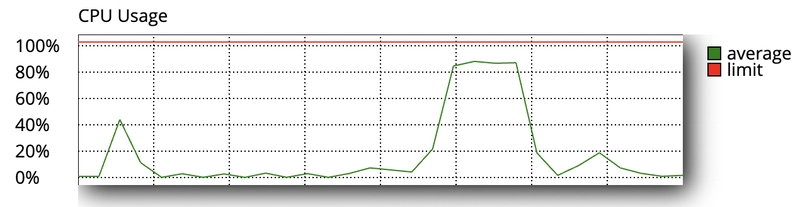
Build a Secure Static Website on AWS S3 Using Terraform
Deploying a static website on AWS S3 is easy, but making it secure, scalable, and highly available requires additional configurations. This guide will show you how to build a production-ready static website using Terraform while ensuring: Security — Restrict direct S3 access, enforce HTTPS, and follow best IAM practices. Performance — Use CloudFront CDN for fast, global content delivery. Reliability — Integrate Route 53 for domain management and DNS resolution. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a fully automated Terraform setup to launch a secure and optimized static website on AWS. Introduction In this blog, we will learn how to securely host a static website on AWS S3 using Terraform, while ensuring performance and security with CloudFront, Route 53, and IAM policies. This setup enables global content delivery, custom domain integration, and restricted S3 access via CloudFront Origin Access Control (OAC). Why Use AWS S3 for Static Websites? AWS S3 provides a highly available and scalable way to host static websites. However, to ensure security and performance, we integrate: CloudFront (CDN) — Improves global performance and security. Route 53 (DNS) — Configures a custom domain for easy access. IAM Policies — Restricts direct access to S3, allowing only CloudFront. Project Tech Stack AWS S3 — Static website hosting AWS CloudFront — Content Delivery Network (CDN) AWS Route 53 — Domain Name System (DNS) AWS IAM — Security policies Project Structure 3-tier-webapp/ │ ├── .terraform/ # Terraform’s internal files and state │ ├── .terraform.lock.hcl # Lock file for provider versions │ ├── terraform.tfstate # Current state of your infrastructure │ └── modules/ # Cached modules │ ├── backend.tf # Backend configuration for state management ├── main.tf # Main configuration file for resources ├── providers.tf # Provider configuration (e.g., AWS) ├── terraform.tfvars # Variable values for the Terraform configuration ├── variables.tf # Variable definitions │ ├── modules/ # Custom modules for organizing resources │ ├── compute/ # Module for compute resources (EC2, ALB, etc.) │ │ ├── alb.tf # ALB configuration │ │ ├── autoscaling.tf # Auto Scaling configuration │ │ ├── ec2.tf # EC2 instance configuration │ │ ├── outputs.tf # Outputs for the compute module │ │ └── variables.tf # Variables for the compute module │ │ │ ├── database/ # Module for database resources (RDS, etc.) │ │ ├── rds.tf # RDS configuration │ │ ├── outputs.tf # Outputs for the database module │ │ └── variables.tf # Variables for the database module │ │ │ └── networking/ # Module for networking resources (VPC, subnets, etc.) │ ├── vpc.tf # VPC configuration │ ├── subnets.tf # Subnet configuration │ ├── nat.tf # NAT Gateway configuration │ ├── security_groups.tf # Security Groups configuration │ ├── outputs.tf # Outputs for the networking module │ └── variables.tf # Variables for the networking module │ └── README.md Step 1: Configure S3 for Static Website Hosting Terraform Code (S3 Module) Copy Copy resource "aws_s3_bucket" "static_site" { bucket = var.bucket_name } Copy Copy resource "aws_s3_bucket_website_configuration" "website" { bucket = aws_s3_bucket.static_site.id index_document { suffix = "index.html" } }resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "allow_cloudfront" { bucket = aws_s3_bucket.static_site.id policy = jsonencode({ Statement = [{ Effect = "Allow" Principal = { Service = "cloudfront.amazonaws.com" } Action = "s3:GetObject" Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.static_site.arn}/*" }] }) }
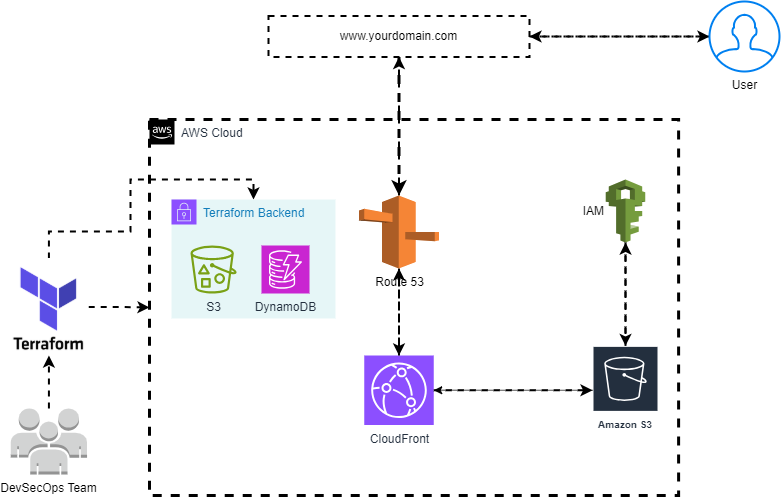

Deploying a static website on AWS S3 is easy, but making it secure, scalable, and highly available requires additional configurations. This guide will show you how to build a production-ready static website using Terraform while ensuring:
Security — Restrict direct S3 access, enforce HTTPS, and follow best IAM practices.
Performance — Use CloudFront CDN for fast, global content delivery.
Reliability — Integrate Route 53 for domain management and DNS resolution.
By the end of this tutorial, you will have a fully automated Terraform setup to launch a secure and optimized static website on AWS.
Introduction
In this blog, we will learn how to securely host a static website on AWS S3 using Terraform, while ensuring performance and security with CloudFront, Route 53, and IAM policies. This setup enables global content delivery, custom domain integration, and restricted S3 access via CloudFront Origin Access Control (OAC).
Why Use AWS S3 for Static Websites?
AWS S3 provides a highly available and scalable way to host static websites. However, to ensure security and performance, we integrate:
- CloudFront (CDN) — Improves global performance and security.
- Route 53 (DNS) — Configures a custom domain for easy access.
- IAM Policies — Restricts direct access to S3, allowing only CloudFront.
Project Tech Stack
AWS S3 — Static website hosting
AWS CloudFront — Content Delivery Network (CDN)
AWS Route 53 — Domain Name System (DNS)
AWS IAM — Security policies
Project Structure
3-tier-webapp/
│
├── .terraform/ # Terraform’s internal files and state
│ ├── .terraform.lock.hcl # Lock file for provider versions
│ ├── terraform.tfstate # Current state of your infrastructure
│ └── modules/ # Cached modules
│
├── backend.tf # Backend configuration for state management
├── main.tf # Main configuration file for resources
├── providers.tf # Provider configuration (e.g., AWS)
├── terraform.tfvars # Variable values for the Terraform configuration
├── variables.tf # Variable definitions
│
├── modules/ # Custom modules for organizing resources
│ ├── compute/ # Module for compute resources (EC2, ALB, etc.)
│ │ ├── alb.tf # ALB configuration
│ │ ├── autoscaling.tf # Auto Scaling configuration
│ │ ├── ec2.tf # EC2 instance configuration
│ │ ├── outputs.tf # Outputs for the compute module
│ │ └── variables.tf # Variables for the compute module
│ │
│ ├── database/ # Module for database resources (RDS, etc.)
│ │ ├── rds.tf # RDS configuration
│ │ ├── outputs.tf # Outputs for the database module
│ │ └── variables.tf # Variables for the database module
│ │
│ └── networking/ # Module for networking resources (VPC, subnets, etc.)
│ ├── vpc.tf # VPC configuration
│ ├── subnets.tf # Subnet configuration
│ ├── nat.tf # NAT Gateway configuration
│ ├── security_groups.tf # Security Groups configuration
│ ├── outputs.tf # Outputs for the networking module
│ └── variables.tf # Variables for the networking module
│
└── README.md
Step 1: Configure S3 for Static Website Hosting
Terraform Code (S3 Module)
Copy
Copy
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "static_site" {
bucket = var.bucket_name
}
Copy
Copy
resource "aws_s3_bucket_website_configuration" "website" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.static_site.id
index_document {
suffix = "index.html"
}
}resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "allow_cloudfront" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.static_site.id
policy = jsonencode({
Statement = [{
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = { Service = "cloudfront.amazonaws.com" }
Action = "s3:GetObject"
Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.static_site.arn}/*"
}]
})
}











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)























.webp?#)










_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)




































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)