Arbitrum and State Channels: Innovations in Blockchain Scalability
Abstract In this post, we explore how groundbreaking technologies such as Arbitrum and state channels are reshaping blockchain scalability. We examine their origins, technical features including optimistic rollups, transaction batching, and validator mechanisms, as well as practical applications in DeFi, NFT marketplaces, gaming, and more. This holistic overview also explores challenges such as security and network dependencies while offering a peek into future trends like zero-knowledge proofs and hybrid models. Throughout, we provide clear definitions, practical examples, tables, and bullet lists to ensure that both technical experts and newcomers can appreciate how these scalability solutions enable a secure, fast, and sustainable blockchain ecosystem. Introduction Blockchain technology has revolutionized how digital transactions are handled. With ever-increasing demands for decentralization, security, and speed, scalability has emerged as one of the most crucial challenges. As decentralized applications (dApps), decentralized finance (DeFi), and NFTs become commonplace, innovative scaling solutions are needed. Arbitrum and state channels tackle these issues by processing transactions off-chain, reducing congestion on networks like Ethereum. This blog post provides an in-depth investigation into these technologies and explains why understanding them is essential for developers, investors, and enthusiasts alike. In our discussion, you can also learn more about the fundamental building blocks of blockchain from resources such as What Is Blockchain?. Background and Context Scalability challenges have plagued early blockchain systems where designs were optimized for security and decentralization, often at the expense of transaction throughput. This trade-off is commonly referred to as the blockchain trilemma. As networks like Ethereum experienced high fees and slow transaction times during peak usage, innovative second-layer solutions emerged. Arbitrum is one such solution that uses a mechanism called optimistic rollup. Essentially, multiple transactions are batched off-chain and later submitted as a single bundled update to the Ethereum mainnet. This approach takes advantage of validator nodes and fraud proofs to ensure security while drastically reducing gas fees and processing times. In parallel, state channels have allowed users to open dedicated channels for multiple transactions that occur off-chain. Only the agreed final state is committed to the blockchain, making them ideal for high-frequency, low-value transfers. Both of these technologies aim to reduce on-chain load, encourage cost-effective interactions, and improve overall network reliability. For additional insights on sustainable scaling, take a look at Sustainable Blockchain Practices. Core Concepts and Features Arbitrum: Optimistic Rollups and Validator Mechanisms Arbitrum operates as a layer-2 scaling solution that leverages optimistic rollups. Its core technical features include: EVM Compatibility: Arbitrum is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine. This allows developers to seamlessly transition their existing dApps with minimal changes. Batch Processing and Transaction Batching: Many transactions are grouped into a rollup that is processed off-chain, significantly reducing network congestion. Validator Model and Fraud Proofs: Validators monitor the rollups and can challenge fraudulent transactions using fraud proofs, thus maintaining the same high-security standards as the Ethereum blockchain. Cost-Efficiency and Speed: Since the computation is offloaded, gas fees are significantly reduced, making microtransactions and novel NFT applications more practical. To summarize these attributes, consider the table below: Feature Description Benefit Optimistic Rollup Batches transactions off-chain Reduced gas fees and network congestion EVM Compatibility Supports Ethereum-native smart contracts Easy migration for developers Validator Model & Fraud Proofs Ensures transaction validity through dispute resolution Enhanced security and reliability Cost Efficiency & Speed Off-chain computation significantly reduces fees Improved user experience Learn more about Arbitrum’s technical merits at What Is Arbitrum?. State Channels: Direct, Off-Chain Interactions State channels operate differently by establishing a private channel between parties for numerous off-chain interactions. Key benefits include: High Frequency and Low Latency: Rapid transactions without needing to record each interaction on-chain. Privacy and Cost Savings: Since only the final state is posted to the blockchain, users enjoy reduced fees and greater privacy. Versatile Use Cases: Ideal for micropayments, gaming, real-time bidding, and dynamic NFT interactions. A bullet list summarizing state channel advantages: Reduced on-chain load by batching updates into one final transa

Abstract
In this post, we explore how groundbreaking technologies such as Arbitrum and state channels are reshaping blockchain scalability. We examine their origins, technical features including optimistic rollups, transaction batching, and validator mechanisms, as well as practical applications in DeFi, NFT marketplaces, gaming, and more. This holistic overview also explores challenges such as security and network dependencies while offering a peek into future trends like zero-knowledge proofs and hybrid models. Throughout, we provide clear definitions, practical examples, tables, and bullet lists to ensure that both technical experts and newcomers can appreciate how these scalability solutions enable a secure, fast, and sustainable blockchain ecosystem.
Introduction
Blockchain technology has revolutionized how digital transactions are handled. With ever-increasing demands for decentralization, security, and speed, scalability has emerged as one of the most crucial challenges. As decentralized applications (dApps), decentralized finance (DeFi), and NFTs become commonplace, innovative scaling solutions are needed. Arbitrum and state channels tackle these issues by processing transactions off-chain, reducing congestion on networks like Ethereum. This blog post provides an in-depth investigation into these technologies and explains why understanding them is essential for developers, investors, and enthusiasts alike.
In our discussion, you can also learn more about the fundamental building blocks of blockchain from resources such as What Is Blockchain?.
Background and Context
Scalability challenges have plagued early blockchain systems where designs were optimized for security and decentralization, often at the expense of transaction throughput. This trade-off is commonly referred to as the blockchain trilemma. As networks like Ethereum experienced high fees and slow transaction times during peak usage, innovative second-layer solutions emerged.
Arbitrum is one such solution that uses a mechanism called optimistic rollup. Essentially, multiple transactions are batched off-chain and later submitted as a single bundled update to the Ethereum mainnet. This approach takes advantage of validator nodes and fraud proofs to ensure security while drastically reducing gas fees and processing times.
In parallel, state channels have allowed users to open dedicated channels for multiple transactions that occur off-chain. Only the agreed final state is committed to the blockchain, making them ideal for high-frequency, low-value transfers. Both of these technologies aim to reduce on-chain load, encourage cost-effective interactions, and improve overall network reliability.
For additional insights on sustainable scaling, take a look at Sustainable Blockchain Practices.
Core Concepts and Features
Arbitrum: Optimistic Rollups and Validator Mechanisms
Arbitrum operates as a layer-2 scaling solution that leverages optimistic rollups. Its core technical features include:
EVM Compatibility:
Arbitrum is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine. This allows developers to seamlessly transition their existing dApps with minimal changes.Batch Processing and Transaction Batching:
Many transactions are grouped into a rollup that is processed off-chain, significantly reducing network congestion.Validator Model and Fraud Proofs:
Validators monitor the rollups and can challenge fraudulent transactions using fraud proofs, thus maintaining the same high-security standards as the Ethereum blockchain.Cost-Efficiency and Speed:
Since the computation is offloaded, gas fees are significantly reduced, making microtransactions and novel NFT applications more practical.
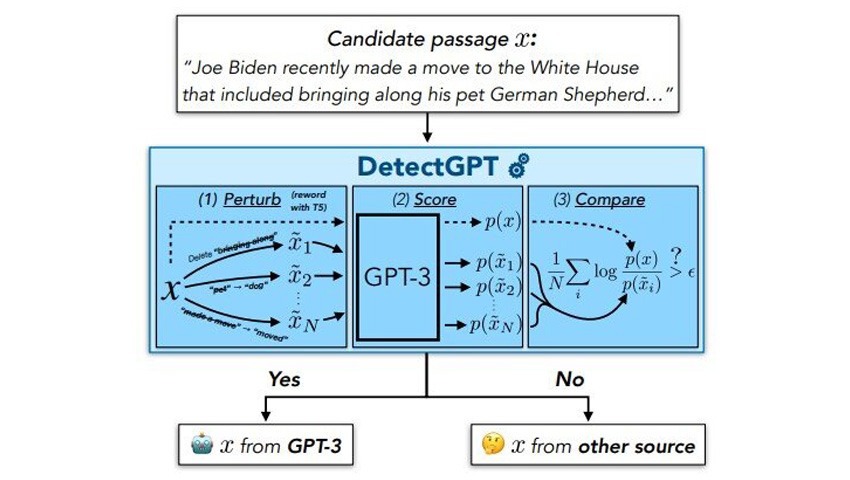
To summarize these attributes, consider the table below:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Optimistic Rollup | Batches transactions off-chain | Reduced gas fees and network congestion |
| EVM Compatibility | Supports Ethereum-native smart contracts | Easy migration for developers |
| Validator Model & Fraud Proofs | Ensures transaction validity through dispute resolution | Enhanced security and reliability |
| Cost Efficiency & Speed | Off-chain computation significantly reduces fees | Improved user experience |
Learn more about Arbitrum’s technical merits at What Is Arbitrum?.
State Channels: Direct, Off-Chain Interactions
State channels operate differently by establishing a private channel between parties for numerous off-chain interactions. Key benefits include:
High Frequency and Low Latency:
Rapid transactions without needing to record each interaction on-chain.Privacy and Cost Savings:
Since only the final state is posted to the blockchain, users enjoy reduced fees and greater privacy.Versatile Use Cases:
Ideal for micropayments, gaming, real-time bidding, and dynamic NFT interactions.
A bullet list summarizing state channel advantages:
- Reduced on-chain load by batching updates into one final transaction
- Increased transaction speed with near-instantaneous confirmations
- Cost-effective for small transactions due to minimal gas fees
- Enhanced privacy as individual transactions are not public on-chain
Applications and Use Cases
Decentralized Finance and Microtransactions
Decentralized finance has quickly embraced layer-2 solutions. By using Arbitrum’s optimistic rollups, DeFi platforms can process hundreds of transactions per second. Furthermore, state channels allow for rapid microtransactions, which is critical in sectors like lending protocols and decentralized exchanges.
Example Use Case:
A decentralized exchange (DEX) may use Arbitrum to batch trade orders off-chain while simultaneously employing state channels to manage real-time, low-value transactions. This dual strategy improves both speed and cost-effectiveness.
NFT Marketplaces and Digital Art
High gas fees have historically hindered the user experience on NFT platforms. With Arbitrum reducing these costs, NFT marketplaces can offer affordable minting, buying, and selling processes. State channels add the advantage of real-time bidding in digital art auctions, ensuring a seamless experience during competitor-heavy events.
Example Use Case:
An NFT auction platform integrates Arbitrum for handling the contractual aspects and uses state channels for rapid bid updates and real-time price adjustments. This ensures artists and collectors benefit from lower fees, faster transactions, and improved security. For further reading on NFT scaling solutions, check The Sandbox Assets NFT Collection – The Sandbox Team.
Gaming and Real-Time Applications
Video games and virtual worlds, particularly those leveraging blockchain, require nearly instantaneous transaction finality. State channels provide the necessary speed, while Arbitrum secures critical updates to game states on Ethereum.
Example Use Case:
An in-game asset trading system utilizes state channels for frequent, low-value transactions such as swapping digital items. Meanwhile, important game state updates are periodically rolled up and recorded via Arbitrum, ensuring both speed and trustless security.
Other sectors such as supply chain management also benefit from these innovations, improving traceability and reducing operational costs in complex networks.
Challenges and Limitations
While Arbitrum and state channels promise significant advancements in scalability, several challenges remain:
Validator Reliance and Fraud Proof Complexities (Arbitrum)
Delayed Dispute Resolution:
When fraud proofs are raised, the resolution process can incur delays that temporarily affect transaction finality.Centralization Risks:
An over-reliance on a limited group of validators could undermine decentralization—an essential aspect of blockchain security.Economic Model Challenges:
Setting the right incentives for validators is crucial; low on-chain fees may impact their rewards, potentially threatening network stability.
Technical Difficulties and Developer Adoption (Both)
Steep Learning Curve:
Understanding off-chain computations, cryptographic proofs, and dispute resolution mechanics requires technical expertise.Integration Overhead:
Incorporating these layer-2 solutions into existing dApps may demand substantial code modifications, rigorous testing, and new security audits.
Network Dependencies and Security Concerns
Reliability of Off-Chain Communication:
State channels depend on a stable network between participants. Network interruptions can lead to synchronization issues.Reconciliation Errors:
The final state that settles back on-chain must be carefully reconciled to avoid potential data discrepancies or losses.
For detailed challenges specific to Arbitrum, visit Arbitrum Challenges.
Regulatory and Interoperability Challenges
Compliance Uncertainty:
Rapid technological advances often outpace the development of regulatory frameworks. Developers must remain ahead of potential compliance issues.Cross-Chain Integration Barriers:
As interoperability between blockchains increases, ensuring consistent standards across different networks becomes more complex.
Furthermore, discussions about regulatory impacts on blockchain scaling have been featured in community posts such as Revolutionizing Software Licensing on Dev.to.
Future Outlook and Innovations
Enhanced Privacy with Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Zero-knowledge proofs are set to revolutionize blockchain privacy. With this technology, transactions can be validated without exposing sensitive user data. As more projects implement Zero-Knowledge Proofs on Blockchain, we can expect increased trust and privacy for all blockchain users.
Evolution of Hybrid Models
The combination of optimistic rollups, state channels, and sidechains offers a flexible and resilient model for blockchain scaling. Future hybrid models may feature:
- Dynamic Transaction Routing: Intelligent systems that adjust transaction processing pathways based on current network conditions.
- Adaptive Consensus Mechanisms: Mechanisms that can change validator incentives in real time, balancing cost efficiency and security.
Open-Source Collaboration and Sustainable Funding
Open-source communities have been instrumental in driving blockchain innovation. New models for funding open-source projects, such as those discussed in Financial Backing for Open Source Projects: Sustaining Innovation and Collaboration, will ensure sustained growth and transparency.
Cross-Chain Interoperability and Global Integration
The evolution of cross-chain bridges and interoperability protocols promises a future where assets and data flow seamlessly between blockchains. This global resource sharing will create a unified digital economy where scalability innovations like Arbitrum play a critical role. For further reading on cross-chain efforts, check out Arbitrum and Cross-Chain Messaging: Pioneering Blockchain Interoperability.
Technical Standardization and Regulatory Adaptation
The path forward involves not only technological breakthroughs but also standardizing protocols across different networks. As regulators catch up with the pace of innovation, clearer frameworks will emerge—ensuring that scalability solutions are compliant, secure, and widely adopted.
Summary
Arbitrum and state channels represent two innovative approaches to resolving the scalability challenges faced by modern blockchains. By offloading transaction processing from the congested Ethereum mainnet, these solutions enable high-speed and cost-efficient interactions while retaining the security and decentralization critical to blockchain technology. Arbitrum uses optimistic rollups, supported by robust validator mechanisms and fraud proofs, making it ideal for complex DeFi protocols and NFT applications. In contrast, state channels offer near-instantaneous transaction finality for repetitive, low-value operations—a perfect match for gaming and micropayments.
Despite the promise of these technologies, challenges remain. Issues related to validator centralization, technical complexity, network reliability, and regulatory uncertainties need to be addressed. Nevertheless, the future is bright. Advances in zero-knowledge proofs, hybrid scaling models, and cross-chain interoperability will pave the way for even more sophisticated blockchain ecosystems.
For developers and business leaders looking to harness these innovations, now is the time to explore their practical applications. By combining the strengths of both approaches, projects can create dApps that are not only scalable and efficient but also secure and sustainable.
Additional insights into blockchain fundamentals can be found in What Is Blockchain? and for more on open-source funding models, consider exploring community discussions on Dev.to such as Unlocking Blockchain Innovation with Web3py.
Key Takeaways
- Arbitrum’s Optimistic Rollups: Batches transactions off-chain to reduce congestion and gas fees while maintaining security.
- State Channels: Facilitate high-speed, low-cost transactions in a private off-chain environment, ideal for micropayments and gaming.
- Challenges: Include validator centralization risks, technical complexity, reconciliation errors, and regulatory uncertainties.
- Future Innovations: Are expected to focus on zero-knowledge proofs, hybrid scaling models, and enhanced interoperability across blockchains.
By combining these advanced scaling techniques with sustainable open-source funding and collaboration efforts, the blockchain world is set for a transformative era that will further unlock its potential in finance, gaming, art, and beyond.
For more detailed technical insights, visit the original article Arbitrum and State Channels: Innovations in Blockchain Scalability.
In conclusion, both Arbitrum and state channels are critical components in addressing the scalability trilemma. Their roles in reducing gas fees, accelerating transactions, and maintaining high security make them indispensable for the future of decentralized applications. As the blockchain ecosystem evolves, adapting these technologies will be key to building a more interconnected, efficient, and secure digital economy.






























































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)

























































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] AI and Business Rule Engines for Excel Power Users, Machine Learning Hero & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)






































































































































































































































![Hostinger Horizons lets you effortlessly turn ideas into web apps without coding [10% off]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/04/IMG_1551.png?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)




![This new Google TV streaming dongle looks just like a Chromecast [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/04/thomson-cast-150-google-tv-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)












![Apple Drops New Immersive Adventure Episode for Vision Pro: 'Hill Climb' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97133/97133/97133-640.jpg)

![Most iPhones Sold in the U.S. Will Be Made in India by 2026 [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97130/97130/97130-640.jpg)