Amazon DocumentDB - Cheat Sheet
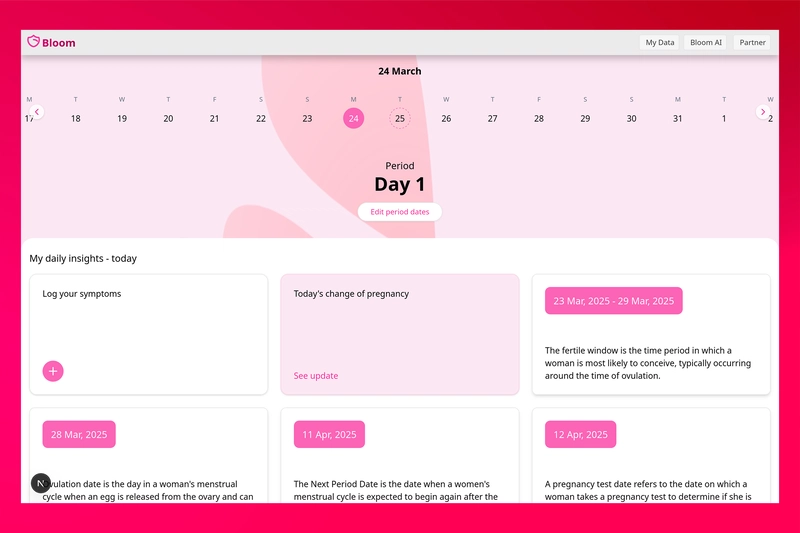
Overview Amazon DocumentDB is a fully managed, MongoDB-compatible document database service designed to store, query, and index JSON data. It provides the performance, scalability, and availability needed for modern, mission-critical MongoDB workloads. Core Concepts and Components DocumentDB is built on a distributed, fault-tolerant, self-healing storage system that automatically scales up to 64 TB per database cluster. DocumentDB ├── Cluster │ ├── Instances │ └── Storage Volume ├── Collections [1] │ ├── Documents │ └── Indexes ├── Security │ ├── IAM │ ├── Encryption │ └── VPC ├── Monitoring │ ├── CloudWatch │ └── Performance Insights └── Backup & Recovery ├── Automated Backups └── Snapshots Key Features and Specifications Feature Details Compatibility MongoDB 3.6, 4.0, and 5.0 API compatibility Storage Up to 64 TB per cluster with automatic scaling Instances Up to 16 instances per cluster for read scaling Availability Multi-AZ deployments with automatic failover Backup Automated backups with point-in-time recovery (up to 35 days) Security Encryption at rest (KMS) and in transit (TLS) Network VPC isolation, security groups, and VPC endpoints Monitoring CloudWatch metrics, Performance Insights, and Profiler Scaling Vertical scaling (instance size) and horizontal scaling (read replicas) Global Clusters Cross-region replication with up to 5 secondary regions Detailed Features and Considerations Instance Types and Sizing: Available in r5, r6g, t3, and t4g instance types Memory-optimized instances for production workloads T3/T4g instances for development and testing Storage Architecture: Separation of compute and storage 6-way replication across 3 AZs for durability Automatic storage scaling without downtime Scaling Considerations: Vertical scaling: Change instance type (requires restart) Horizontal scaling: Add read replicas (up to 15) for read-heavy workloads Storage automatically scales up to 64 TB Performance Optimization: Proper indexing is critical for query performance Use appropriate instance sizes based on workload Monitor and adjust read preference settings MongoDB Compatibility: Supports MongoDB wire protocol Compatible with MongoDB drivers, tools, and applications Some MongoDB features not supported (see limitations) Limitations and Differences from MongoDB: No support for JavaScript execution Limited support for certain MongoDB commands Different transaction implementation Security Features: IAM authentication TLS encryption in transit KMS encryption at rest VPC isolation and security groups Audit logging to CloudWatch Logs Backup and Recovery: Automated daily backups (retention up to 35 days) Manual snapshots (retained until deleted) Point-in-time recovery with 5-minute granularity Global Clusters: Primary region for writes Up to 5 secondary regions for low-latency reads Typical replication lag under 1 second Cost Optimization: Right-size instances based on workload Use T3/T4g instances for development Consider reserved instances for production workloads Data Migration Options: AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) mongodump/mongorestore mongoexport/mongoimport AWS Migration Hub Monitoring Best Practices: Monitor CPU, memory, and storage metrics Track connection count and throughput Use Performance Insights for query analysis Enable Profiler for slow query identification Performance Characteristics and Limits Service Limits: Maximum 16 instances per cluster Maximum 64 TB storage per cluster Maximum 10,000 connections per instance Maximum 100 databases per cluster Maximum 100,000 collections per cluster Throughput Considerations: Write throughput limited by primary instance capacity Read throughput scales with number of replicas Document size limit: 16 MB Index size limit: 64 KB Latency Characteristics: Single-digit millisecond read/write latency for typical operations Latency increases with document size and query complexity Global clusters add ~1 second replication lag to secondary regions Rate Limiting and Throttling: API throttling limits apply to management operations Connection limits based on instance size Implement connection pooling in applications CloudWatch Metrics for Monitoring Key CloudWatch Metrics: Metric Description Recommended Alarm CPUUtilization CPU utilization percentage > 80% for 5 minutes FreeableMemory Available RAM < 10% of total memory DatabaseConnections Number of connections > 80% of max connections ReadIOPS / WriteIOPS I/O operations per second Depends on workload baseline ReadLatency / WriteLatency Average I/O latency > 20ms for 5 minutes DiskQueueDepth Number of outstanding I/Os > 10 for 5 minutes VolumeBytesUsed Storage space used > 80% of allocated storage TransactionLogsDiskUsage Space used by transaction logs > 30% of allocated storage Performa

Overview
Amazon DocumentDB is a fully managed, MongoDB-compatible document database service designed to store, query, and index JSON data. It provides the performance, scalability, and availability needed for modern, mission-critical MongoDB workloads.
Core Concepts and Components
DocumentDB is built on a distributed, fault-tolerant, self-healing storage system that automatically scales up to 64 TB per database cluster.
DocumentDB
├── Cluster
│ ├── Instances
│ └── Storage Volume
├── Collections [1]
│ ├── Documents
│ └── Indexes
├── Security
│ ├── IAM
│ ├── Encryption
│ └── VPC
├── Monitoring
│ ├── CloudWatch
│ └── Performance Insights
└── Backup & Recovery
├── Automated Backups
└── Snapshots
Key Features and Specifications
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Compatibility | MongoDB 3.6, 4.0, and 5.0 API compatibility |
| Storage | Up to 64 TB per cluster with automatic scaling |
| Instances | Up to 16 instances per cluster for read scaling |
| Availability | Multi-AZ deployments with automatic failover |
| Backup | Automated backups with point-in-time recovery (up to 35 days) |
| Security | Encryption at rest (KMS) and in transit (TLS) |
| Network | VPC isolation, security groups, and VPC endpoints |
| Monitoring | CloudWatch metrics, Performance Insights, and Profiler |
| Scaling | Vertical scaling (instance size) and horizontal scaling (read replicas) |
| Global Clusters | Cross-region replication with up to 5 secondary regions |
Detailed Features and Considerations
-
Instance Types and Sizing:
- Available in r5, r6g, t3, and t4g instance types
- Memory-optimized instances for production workloads
- T3/T4g instances for development and testing
-
Storage Architecture:
- Separation of compute and storage
- 6-way replication across 3 AZs for durability
- Automatic storage scaling without downtime
-
Scaling Considerations:
- Vertical scaling: Change instance type (requires restart)
- Horizontal scaling: Add read replicas (up to 15) for read-heavy workloads
- Storage automatically scales up to 64 TB
-
Performance Optimization:
- Proper indexing is critical for query performance
- Use appropriate instance sizes based on workload
- Monitor and adjust read preference settings
-
MongoDB Compatibility:
- Supports MongoDB wire protocol
- Compatible with MongoDB drivers, tools, and applications
- Some MongoDB features not supported (see limitations)
-
Limitations and Differences from MongoDB:
- No support for JavaScript execution
- Limited support for certain MongoDB commands
- Different transaction implementation
-
Security Features:
- IAM authentication
- TLS encryption in transit
- KMS encryption at rest
- VPC isolation and security groups
- Audit logging to CloudWatch Logs
-
Backup and Recovery:
- Automated daily backups (retention up to 35 days)
- Manual snapshots (retained until deleted)
- Point-in-time recovery with 5-minute granularity
-
Global Clusters:
- Primary region for writes
- Up to 5 secondary regions for low-latency reads
- Typical replication lag under 1 second
-
Cost Optimization:
- Right-size instances based on workload
- Use T3/T4g instances for development
- Consider reserved instances for production workloads
-
Data Migration Options:
- AWS Database Migration Service (DMS)
- mongodump/mongorestore
- mongoexport/mongoimport
- AWS Migration Hub
-
Monitoring Best Practices:
- Monitor CPU, memory, and storage metrics
- Track connection count and throughput
- Use Performance Insights for query analysis
- Enable Profiler for slow query identification
Performance Characteristics and Limits
-
Service Limits:
- Maximum 16 instances per cluster
- Maximum 64 TB storage per cluster
- Maximum 10,000 connections per instance
- Maximum 100 databases per cluster
- Maximum 100,000 collections per cluster
-
Throughput Considerations:
- Write throughput limited by primary instance capacity
- Read throughput scales with number of replicas
- Document size limit: 16 MB
- Index size limit: 64 KB
-
Latency Characteristics:
- Single-digit millisecond read/write latency for typical operations
- Latency increases with document size and query complexity
- Global clusters add ~1 second replication lag to secondary regions
-
Rate Limiting and Throttling:
- API throttling limits apply to management operations
- Connection limits based on instance size
- Implement connection pooling in applications
CloudWatch Metrics for Monitoring
- Key CloudWatch Metrics:
| Metric | Description | Recommended Alarm |
|---|---|---|
CPUUtilization |
CPU utilization percentage | > 80% for 5 minutes |
FreeableMemory |
Available RAM | < 10% of total memory |
DatabaseConnections |
Number of connections | > 80% of max connections |
ReadIOPS / WriteIOPS
|
I/O operations per second | Depends on workload baseline |
ReadLatency / WriteLatency
|
Average I/O latency | > 20ms for 5 minutes |
DiskQueueDepth |
Number of outstanding I/Os | > 10 for 5 minutes |
VolumeBytesUsed |
Storage space used | > 80% of allocated storage |
TransactionLogsDiskUsage |
Space used by transaction logs | > 30% of allocated storage |
-
Performance Insights Metrics:
-
DBLoad: Database load measured in average active sessions - Top SQL queries by load
- Wait event analysis
- Host and user-level metrics
-
Example Capacity Planning Calculation
-
Instance Sizing Example:
- Workload: 5,000 reads/sec, 1,000 writes/sec
- Document size: 10 KB
- Read IOPS: 5,000 × 10 KB = 50 MB/s
- Write IOPS: 1,000 × 10 KB = 10 MB/s
- Required instances: 1 primary (for writes) + 2 replicas (for reads)
- Instance type: r5.2xlarge (8 vCPU, 64 GB RAM)
-
Storage Calculation:
- Data size: 500 GB
- Indexes: 100 GB
- Growth rate: 10 GB/month
- 1-year projection: 500 GB + 100 GB + (10 GB × 12) = 720 GB
- Initial storage allocation: 1 TB (with auto-scaling enabled)
Data Ingestion and Replayability
-
Data Ingestion Patterns:
- Direct application writes using MongoDB drivers
- AWS DMS for continuous replication
- Batch loading using mongoimport/mongorestore
- Kinesis Data Firehose with Lambda transformation
-
Replayability Considerations:
- Use change streams to capture data modifications
- Store change stream events in S3 or Kinesis for replay
- Implement idempotent operations for safe replays
- Use transaction IDs or sequence numbers for tracking
Comparison with Other AWS Database Services
- DocumentDB vs. Other AWS Services:
| Feature | DocumentDB | DynamoDB | Amazon RDS for MongoDB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Document (JSON) | Key-value and document | Document (JSON) |
| Compatibility | MongoDB API | Proprietary | Native MongoDB |
| Scaling | Vertical + Read Replicas | Fully automatic | Vertical + Read Replicas |
| Global Distribution | Global Clusters | Global Tables | Not native |
| Serverless | No | Yes | No |
| Pricing Model | Instance hours + storage | Provisioned capacity or pay-per-request | Instance hours + storage |
| Max Storage | 64 TB | Unlimited | Engine dependent |
| Use Case | MongoDB workloads requiring compatibility | High-scale, low-latency applications | Self-managed MongoDB on EC2 |
-
MongoDB Compatibility Details:
- DocumentDB implements the MongoDB 3.6, 4.0, and 5.0 APIs
- Compatible with MongoDB drivers and tools
- Not a fork of MongoDB but a compatible implementation
- Some MongoDB features not supported (e.g., MapReduce)
Best Practices
-
Performance Best Practices:
- Create appropriate indexes for common queries
- Use projection to limit returned fields
- Implement connection pooling in applications
- Monitor and optimize slow queries
- Use read replicas for read-heavy workloads
-
Security Best Practices:
- Use IAM authentication when possible
- Implement least privilege access
- Enable audit logging
- Use VPC endpoints for secure access
- Rotate credentials regularly
-
Operational Best Practices:
- Set up CloudWatch alarms for key metrics
- Implement automated snapshot policies
- Test failover procedures regularly
- Use parameter groups for consistent configuration
- Implement proper backup and disaster recovery plans
-
Cost Optimization:
- Right-size instances based on workload
- Use reserved instances for production
- Scale down development environments when not in use
- Monitor and optimize storage usage
- Use T3/T4g instances for development and testing










































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)




























































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] The Kubernetes Bible, The Ultimate Linux Shell Scripting Guide & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)



![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)





































































































.png?#)





.jpg?#)
































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)








































































































![Rapidus in Talks With Apple as It Accelerates Toward 2nm Chip Production [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96937/96937/96937-640.jpg)