3356. Zero Array Transformation II
3356. Zero Array Transformation II Difficulty: Medium Topics: Array, Binary Search, Prefix Sum You are given an integer array nums of length n and a 2D array queries where queries[i] = [li, ri, vali]. Each queries[i] represents the following action on nums: Decrement the value at each index in the range [li, ri] in nums by at most vali. The amount by which each value is decremented can be chosen independently for each index. A Zero Array is an array with all its elements equal to 0. Return the minimum possible non-negative value of k, such that after processing the first k queries in sequence, nums becomes a Zero Array. If no such k exists, return -1. Example 1: Input: nums = [2,0,2], queries = [[0,2,1],[0,2,1],[1,1,3]] Output: 2 Explanation: For i = 0 (l = 0, r = 2, val = 1): Decrement values at indices [0, 1, 2] by [1, 0, 1] respectively. The array will become [1, 0, 1]. For i = 1 (l = 0, r = 2, val = 1): Decrement values at indices [0, 1, 2] by [1, 0, 1] respectively. The array will become [0, 0, 0], which is a Zero Array. Therefore, the minimum value of k is 2. Example 2: Input: nums = [4,3,2,1], queries = [[1,3,2],[0,2,1]] Output: -1 Explanation: For i = 0 (l = 1, r = 3, val = 2): Decrement values at indices [1, 2, 3] by [2, 2, 1] respectively. The array will become [4, 1, 0, 0]. For i = 1 (l = 0, r = 2, val = 1): Decrement values at indices [0, 1, 2] by [1, 1, 0] respectively. The array will become [3, 0, 0, 0], which is not a Zero Array. Example 3: Input: nums = [0], queries = [[0,0,2],[0,0,4],[0,0,4],[0,0,3],[0,0,5]] Output: 0 Constraints: 1 Explanation: Binary Search Initialization: We start with the full range of possible k values (0 to the total number of queries). Mid-Calculation: For each midpoint in the binary search, we check if processing the first mid queries can reduce the array to zero. Difference Array Application: For each query up to mid, we update a difference array to reflect the range decrements. This allows efficient range updates and prefix sum computation. Prefix Sum Check: After applying the queries, we compute the prefix sum of the difference array to check if each element's cumulative decrement meets its initial value. If all elements meet this condition, mid is a valid candidate, and we adjust the binary search range accordingly. Result Determination: The binary search continues until the minimum valid k is found, or it is determined that no valid k exists. This approach efficiently narrows down the possible values of k using binary search and leverages the difference array technique to handle range updates and checks in linear time, making it suitable for large input sizes. Contact Links If you found this series helpful, please consider giving the repository a star on GitHub or sharing the post on your favorite social networks
3356. Zero Array Transformation II
Difficulty: Medium
Topics: Array, Binary Search, Prefix Sum
You are given an integer array nums of length n and a 2D array queries where queries[i] = [li, ri, vali].
Each queries[i] represents the following action on nums:
- Decrement the value at each index in the range
[li, ri]innumsby at mostvali. - The amount by which each value is decremented can be chosen independently for each index.
A Zero Array is an array with all its elements equal to 0.
Return the minimum possible non-negative value of k, such that after processing the first k queries in sequence, nums becomes a Zero Array. If no such k exists, return -1.
Example 1:
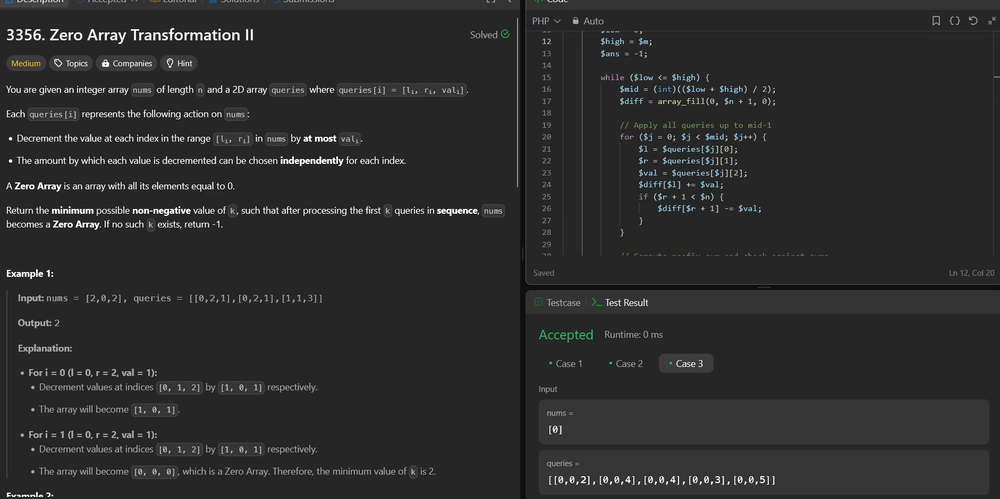
- Input: nums = [2,0,2], queries = [[0,2,1],[0,2,1],[1,1,3]]
- Output: 2
-
Explanation:
- For i = 0 (l = 0, r = 2, val = 1):
- Decrement values at indices
[0, 1, 2]by[1, 0, 1]respectively. - The array will become
[1, 0, 1]. - For i = 1 (l = 0, r = 2, val = 1):
- Decrement values at indices
[0, 1, 2]by[1, 0, 1]respectively. - The array will become
[0, 0, 0], which is a Zero Array. Therefore, the minimum value ofkis2.
Example 2:
- Input: nums = [4,3,2,1], queries = [[1,3,2],[0,2,1]]
- Output: -1
-
Explanation:
-
For i = 0 (l = 1, r = 3, val = 2):
- Decrement values at indices
[1, 2, 3]by[2, 2, 1]respectively. - The array will become
[4, 1, 0, 0].
- Decrement values at indices
-
For i = 1 (l = 0, r = 2, val = 1):
- Decrement values at indices
[0, 1, 2]by[1, 1, 0]respectively. - The array will become
[3, 0, 0, 0], which is not a Zero Array.
- Decrement values at indices
-
For i = 0 (l = 1, r = 3, val = 2):
Example 3:
- Input: nums = [0], queries = [[0,0,2],[0,0,4],[0,0,4],[0,0,3],[0,0,5]]
- Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1050 <= nums[i] <= 5 * 1051 <= queries.length <= 105queries[i].length == 30 <= li <= ri < nums.length1 <= vali <= 5
Hint:
- Can we apply binary search here?
- Utilize a difference array to optimize the processing of queries.
Solution:
We need to determine the minimum number of queries that need to be processed in sequence to transform the given array into a zero array. Each query allows decrementing elements in a specified range by a certain value, but the actual decrement can be any amount up to the specified value. The goal is to find the earliest point where all elements in the array become zero.
Approach
The key insight is to use binary search to efficiently determine the minimum number of queries required. For each candidate number of queries (k), we check if processing the first k queries can reduce all elements to zero. This check is performed using a difference array to efficiently compute the sum of decrements applied to each element up to the k-th query.
- Binary Search: We perform binary search on the number of queries (k) from 0 to the total number of queries. The binary search helps us efficiently narrow down the minimum k.
- Difference Array: For each candidate k, we use a difference array to apply the range updates specified by the first k queries. This allows us to compute the cumulative decrements applied to each element efficiently.
- Check Feasibility: After applying the first k queries using the difference array, we compute the prefix sum to check if each element's cumulative decrement meets or exceeds its initial value. If all elements meet this condition, k is a valid candidate.
Let's implement this solution in PHP: 3356. Zero Array Transformation II
/**
* @param Integer[] $nums
* @param Integer[][] $queries
* @return Integer
*/
function minZeroArray($nums, $queries) {
...
...
...
/**
* go to ./solution.php
*/
}
// Example test cases
$nums1 = [2, 0, 2];
$queries1 = [[0, 2, 1], [0, 2, 1], [1, 1, 3]];
echo minZeroArray($nums1, $queries1) . "\n"; // Output: 2
$nums2 = [5, 3, 2, 1];
$queries2 = [[1, 3, 2], [0, 2, 1]];
echo minZeroArray($nums2, $queries2) . "\n"; // Output: -1
$nums3 = [0];
$queries3 = [[0,0,2],[0,0,4],[0,0,4],[0,0,3],[0,0,5]];
echo minZeroArray($nums3, $queries3) . "\n"; // Output: 0
?>
Explanation:
- Binary Search Initialization: We start with the full range of possible k values (0 to the total number of queries).
-
Mid-Calculation: For each midpoint in the binary search, we check if processing the first
midqueries can reduce the array to zero. -
Difference Array Application: For each query up to
mid, we update a difference array to reflect the range decrements. This allows efficient range updates and prefix sum computation. -
Prefix Sum Check: After applying the queries, we compute the prefix sum of the difference array to check if each element's cumulative decrement meets its initial value. If all elements meet this condition,
midis a valid candidate, and we adjust the binary search range accordingly. - Result Determination: The binary search continues until the minimum valid k is found, or it is determined that no valid k exists.
This approach efficiently narrows down the possible values of k using binary search and leverages the difference array technique to handle range updates and checks in linear time, making it suitable for large input sizes.
Contact Links
If you found this series helpful, please consider giving the repository a star on GitHub or sharing the post on your favorite social networks











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)























.webp?#)










_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)




































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)



































































































































