WhatsApp MCP: Complete AI Integration Guide 2025
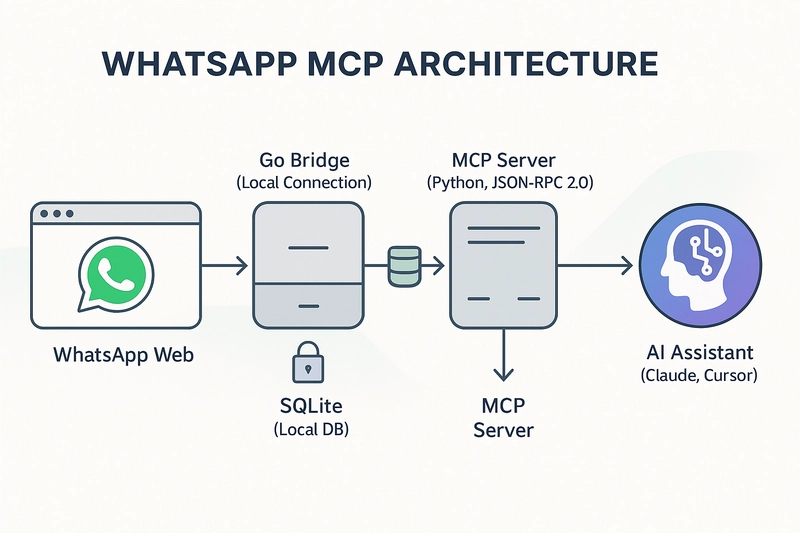
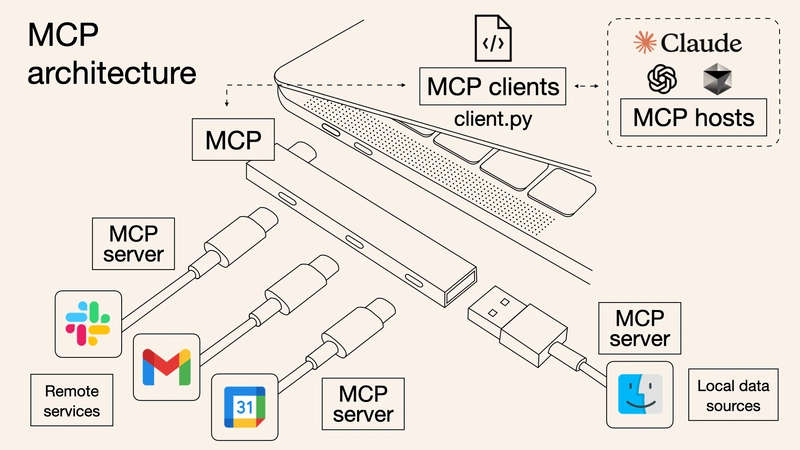
In today's rapidly evolving AI landscape, the ability to connect large language models (LLMs) with our everyday communication tools represents a significant advancement. WhatsApp, with over 2 billion users worldwide, stands as one of the most widely used messaging platforms. The WhatsApp Model Context Protocol (MCP) bridge creates a powerful connection between these two worlds, enabling AI assistants to access and interact with your WhatsApp conversations in a secure, privacy-respecting manner. What You'll Learn What WhatsApp MCP is and how it integrates with Model Context Protocol The architecture and components of WhatsApp MCP Step-by-step installation and configuration guide Core WhatsApp MCP tools and capabilities Advanced use cases and applications Troubleshooting and best practices for optimal performance Prerequisites Basic understanding of AI concepts Familiarity with messaging platforms No advanced technical knowledge required Understanding Model Context Protocol (MCP) Before diving into the specifics of WhatsApp MCP, it's important to understand the underlying technology that makes it possible. Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard designed to facilitate communication between AI models and external systems. Think of MCP as a universal translator that allows AI assistants to connect with various services, databases, and applications without requiring custom code for each integration. Unlike traditional APIs that treat each interaction as a separate event, MCP maintains conversational context, allowing AI systems to remember past interactions and learn from them over time. MCP creates a standardized way for AI systems to: Access external data sources and tools Maintain context across interactions Execute actions in external systems Preserve user privacy and security For a more detailed explanation of MCP, you can visit What is Model Context Protocol. WhatsApp MCP: Bridging WhatsApp and AI WhatsApp MCP serves as a bridge between WhatsApp Web and AI assistants like Claude and Cursor, allowing these AI systems to search, analyze, and respond to your WhatsApp messages. Instead of building custom integrations or relying on limited API functions, WhatsApp MCP leverages the standardized Model Context Protocol to create a seamless, bidirectional flow of information between WhatsApp and AI models. This integration allows you to: Search through your WhatsApp conversations Analyze message content with AI capabilities Send messages through AI assistants Maintain privacy and security of your conversations How WhatsApp MCP Works WhatsApp MCP operates on a client-server architecture with a data flow designed to maintain security while enabling powerful functionality: WhatsApp Web Connection: A Go-based bridge connects to WhatsApp Web using the same protocol your browser uses Local Data Processing: Messages and contacts are stored in a local SQLite database on your device MCP Communication: The Python MCP server implements the Model Context Protocol, allowing AI assistants to access this data AI Integration: Claude Desktop, Cursor, or other MCP-compatible clients can then search, analyze, and interact with your WhatsApp data This architecture ensures your messages never leave your device unless explicitly requested by you through the AI assistant, maintaining privacy and security throughout the process. WhatsApp MCP Components WhatsApp MCP consists of several key components working together to create a seamless integration between WhatsApp and AI assistants. Go WhatsApp Bridge The Go WhatsApp Bridge acts as the foundation of the WhatsApp MCP system. Written in Go for performance and reliability, this component: Connects to WhatsApp Web using the official WhatsApp Web protocol Authenticates your WhatsApp account via QR code scanning Syncs and stores messages in a local database Provides a stable API for the MCP server to access WhatsApp data The bridge is designed to be lightweight and efficient, minimizing resource usage while maintaining a persistent connection to WhatsApp Web. Python MCP Server The Python MCP server implements the Model Context Protocol specification, serving as the communication layer between the Go bridge and AI clients. Key features include: JSON-RPC 2.0 based communication Standardized message types and error handling Tool implementations for WhatsApp-specific operations Authentication and permission management This server translates generic MCP requests into specific WhatsApp operations, allowing AI assistants to interact with WhatsApp without understanding the underlying complexity of the WhatsApp Web protocol. Data Storage All WhatsApp data processed by the MCP system is stored in a local SQLite database. This approach offers several advantages: Privacy: Your data remains on your device, not in the cloud Performance: Fast local queries without network

In today's rapidly evolving AI landscape, the ability to connect large language models (LLMs) with our everyday communication tools represents a significant advancement. WhatsApp, with over 2 billion users worldwide, stands as one of the most widely used messaging platforms. The WhatsApp Model Context Protocol (MCP) bridge creates a powerful connection between these two worlds, enabling AI assistants to access and interact with your WhatsApp conversations in a secure, privacy-respecting manner.
What You'll Learn
- What WhatsApp MCP is and how it integrates with Model Context Protocol
- The architecture and components of WhatsApp MCP
- Step-by-step installation and configuration guide
- Core WhatsApp MCP tools and capabilities
- Advanced use cases and applications
- Troubleshooting and best practices for optimal performance
Prerequisites
- Basic understanding of AI concepts
- Familiarity with messaging platforms
- No advanced technical knowledge required
Understanding Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Before diving into the specifics of WhatsApp MCP, it's important to understand the underlying technology that makes it possible. Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard designed to facilitate communication between AI models and external systems.
Think of MCP as a universal translator that allows AI assistants to connect with various services, databases, and applications without requiring custom code for each integration. Unlike traditional APIs that treat each interaction as a separate event, MCP maintains conversational context, allowing AI systems to remember past interactions and learn from them over time.
MCP creates a standardized way for AI systems to:
- Access external data sources and tools
- Maintain context across interactions
- Execute actions in external systems
- Preserve user privacy and security
For a more detailed explanation of MCP, you can visit What is Model Context Protocol.
WhatsApp MCP: Bridging WhatsApp and AI
WhatsApp MCP serves as a bridge between WhatsApp Web and AI assistants like Claude and Cursor, allowing these AI systems to search, analyze, and respond to your WhatsApp messages. Instead of building custom integrations or relying on limited API functions, WhatsApp MCP leverages the standardized Model Context Protocol to create a seamless, bidirectional flow of information between WhatsApp and AI models.
This integration allows you to:
- Search through your WhatsApp conversations
- Analyze message content with AI capabilities
- Send messages through AI assistants
- Maintain privacy and security of your conversations
How WhatsApp MCP Works
WhatsApp MCP operates on a client-server architecture with a data flow designed to maintain security while enabling powerful functionality:
- WhatsApp Web Connection: A Go-based bridge connects to WhatsApp Web using the same protocol your browser uses
- Local Data Processing: Messages and contacts are stored in a local SQLite database on your device
- MCP Communication: The Python MCP server implements the Model Context Protocol, allowing AI assistants to access this data
- AI Integration: Claude Desktop, Cursor, or other MCP-compatible clients can then search, analyze, and interact with your WhatsApp data
This architecture ensures your messages never leave your device unless explicitly requested by you through the AI assistant, maintaining privacy and security throughout the process.
WhatsApp MCP Components
WhatsApp MCP consists of several key components working together to create a seamless integration between WhatsApp and AI assistants.
Go WhatsApp Bridge
The Go WhatsApp Bridge acts as the foundation of the WhatsApp MCP system. Written in Go for performance and reliability, this component:
- Connects to WhatsApp Web using the official WhatsApp Web protocol
- Authenticates your WhatsApp account via QR code scanning
- Syncs and stores messages in a local database
- Provides a stable API for the MCP server to access WhatsApp data
The bridge is designed to be lightweight and efficient, minimizing resource usage while maintaining a persistent connection to WhatsApp Web.
Python MCP Server
The Python MCP server implements the Model Context Protocol specification, serving as the communication layer between the Go bridge and AI clients. Key features include:
- JSON-RPC 2.0 based communication
- Standardized message types and error handling
- Tool implementations for WhatsApp-specific operations
- Authentication and permission management
This server translates generic MCP requests into specific WhatsApp operations, allowing AI assistants to interact with WhatsApp without understanding the underlying complexity of the WhatsApp Web protocol.
Data Storage
All WhatsApp data processed by the MCP system is stored in a local SQLite database. This approach offers several advantages:
- Privacy: Your data remains on your device, not in the cloud
- Performance: Fast local queries without network latency
- Persistence: Messages remain available even when WhatsApp Web is disconnected
- Searchability: Efficient indexing for quick message retrieval
The database schema is optimized for the types of queries most commonly needed by AI assistants, such as finding conversations by contact or searching message content.
Installation and Configuration
Setting up WhatsApp MCP requires installing necessary components and configuring them to work together. This section provides a detailed guide to get you started.
System Requirements and Prerequisites
According to the official repository, you'll need:
- Go programming language
- Python 3.6+
- Anthropic Claude Desktop app (or Cursor)
-
UV (Python package manager), install with
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh -
FFmpeg (optional) - Only needed for audio messages. If you want to send audio files as playable WhatsApp voice messages, they must be in
.oggOpus format.
Windows-Specific Requirements
If you're running this project on Windows, be aware that go-sqlite3 requires CGO to be enabled in order to compile and work properly. By default, CGO is disabled on Windows, so you need to explicitly enable it and have a C compiler installed:
Install a C compiler
We recommend using MSYS2 to install a C compiler for Windows. After installing MSYS2, make sure to add theucrt64\binfolder to yourPATH.Enable CGO and run the app
cd whatsapp-bridge
go env -w CGO_ENABLED=1
go run main.go
Without this setup, you'll likely run into errors like: Binary was compiled with 'CGO_ENABLED=0', go-sqlite3 requires cgo to work.
Detailed Installation Steps
Follow these steps to install WhatsApp MCP:
1. Clone the Repository
First, clone the WhatsApp MCP repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/lharries/whatsapp-mcp.git
cd whatsapp-mcp
2. Install Go
The WhatsApp Bridge component requires Go:
For macOS (using Homebrew):
brew install go
For Windows:
Download and install Go from golang.org/dl
After installation, verify with:
go version
3. Install Python
The MCP server requires Python 3.6 or later:
For macOS (using Homebrew):
brew install python
For Windows:
Download and install Python from python.org/downloads
Verify the installation:
python --version
4. Install UV Package Manager
Install UV as specified in the prerequisites:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
5. Run the WhatsApp Bridge
Navigate to the whatsapp-bridge directory and run the Go application:
cd whatsapp-bridge
go run main.go
The first time you run it, you will be prompted to scan a QR code. Scan the QR code with your WhatsApp mobile app to authenticate. After approximately 20 days, you might need to re-authenticate.
6. Configure MCP Client Integration
To connect WhatsApp MCP with AI assistants like Claude Desktop or Cursor:
For Claude Desktop:
- Create a JSON configuration with the appropriate path values:
{
"mcpServers": {
"whatsapp": {
"command": "{{PATH_TO_UV}}",
"args": [
"--directory",
"{{PATH_TO_SRC}}/whatsapp-mcp/whatsapp-mcp-server",
"run",
"main.py"
]
}
}
}
- Save this as
claude_desktop_config.jsonin your Claude Desktop configuration directory:
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
For Cursor:
- Save the same configuration as
mcp.jsonin your Cursor configuration directory:
~/.cursor/mcp.json
7. Restart Claude Desktop / Cursor
Open Claude Desktop or restart Cursor, and you should now see WhatsApp as an available integration.
Common Installation Issues
If you encounter problems during installation, here are solutions to common issues:
- QR Code Not Displaying: If the QR code doesn't appear, try restarting the authentication script. If issues persist, check if your terminal supports displaying QR codes.
- WhatsApp Already Logged In: If your session is already active, the Go bridge will automatically reconnect without showing a QR code.
- Device Limit Reached: WhatsApp limits the number of linked devices. If you reach this limit, you'll need to remove an existing device from WhatsApp on your phone (Settings > Linked Devices).
- No Messages Loading: After initial authentication, it can take several minutes for your message history to load, especially if you have many chats.
-
WhatsApp Out of Sync: If your WhatsApp messages get out of sync with the bridge, delete both database files (
whatsapp-bridge/store/messages.dbandwhatsapp-bridge/store/whatsapp.db) and restart the bridge to re-authenticate.
WhatsApp MCP Tools and Features
WhatsApp MCP provides a rich set of tools for interacting with your WhatsApp data. These are divided into three main categories: chat search and management, chat analysis and interaction, and message sending and automation.
| Category | Description | Key Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Chat Search and Management | Tools for finding and organizing conversations |
search_contacts, list_messages, list_chats
|
| Chat Analysis and Interaction | Tools for analyzing and understanding conversations |
get_chat, get_direct_chat_by_contact, get_contact_chats, get_last_interaction, get_message_context
|
| Message Sending and Automation | Tools for sending messages and automating responses |
send_message, send_file, send_audio_message, download_media
|
Chat Search and Management
These tools help you find and organize your WhatsApp conversations:
search_contacts
Allows you to search for contacts by name or phone number:
search_contacts("John")
This returns matching contacts with their profile information, making it easy to find specific people in your contact list.
list_messages
Retrieves messages from a specific chat, with options for filtering and pagination:
list_messages(chat_id="123456", limit=10, before_id="msg_789")
Parameters include:
-
chat_id: The identifier for the chat -
limit: Maximum number of messages to return -
before_id/after_id: For pagination and historical lookups
list_chats
Returns a list of all available chats, including both individual and group conversations:
list_chats(limit=20, offset=0)
This tool is useful for getting an overview of all your WhatsApp conversations, sorted by recent activity.
Chat Analysis and Interaction
These tools provide deeper insights into your WhatsApp communications:
get_chat
Retrieves detailed information about a specific chat:
get_chat(chat_id="123456")
Returns comprehensive information including participants, creation date, group settings (if applicable), and message statistics.
get_direct_chat_by_contact
Finds a direct chat with a specific contact:
get_direct_chat_by_contact(contact_id="9876543210")
This is particularly useful when you know who you want to talk to but don't know the specific chat ID.
get_contact_chats
Lists all chats (both direct and groups) that include a specific contact:
get_contact_chats(contact_id="9876543210")
This helps you see all conversations where a particular person is involved.
get_last_interaction
Shows the most recent interaction with a specific contact:
get_last_interaction(contact_id="9876543210")
This provides context about when and what you last discussed with someone.
get_message_context
Retrieves messages surrounding a specific message for context:
get_message_context(message_id="msg_123", before=5, after=5)
This is particularly valuable for AI assistants to understand the conversation flow around a specific message.
Message Sending and Automation
These tools enable active participation in WhatsApp conversations:
send_message
Sends a message to a WhatsApp chat:
send_message(chat_id="123456", text="Hello, how are you?")
This function also supports sending media files, documents, and location data through additional parameters.
send_file and send_audio_message
The MCP server supports sending various media types:
- send_file: Send images, videos, documents, or raw audio files
- send_audio_message: Send audio files as playable WhatsApp voice messages (requires the file to be in .ogg Opus format or FFmpeg must be installed)
download_media
Downloads media from a WhatsApp message and returns the local file path. By default, just the metadata of media is stored in the local database, so this tool is needed to access the actual content.
Building Automated Reply Systems
By combining the above tools, you can create sophisticated automated response systems:
- Use
get_last_interactionto check for new messages - Analyze message content using AI capabilities
- Generate appropriate responses based on message context
- Send replies using the
send_messagefunction
This workflow can be customized for various scenarios, from simple auto-replies to complex conversational agents.
Advanced Application Scenarios
WhatsApp MCP enables sophisticated applications that go beyond basic messaging. This section explores advanced use cases that leverage the power of AI and WhatsApp integration.
Intelligent Conversation Analysis
By combining WhatsApp MCP with AI capabilities, you can gain deeper insights from your conversations:
Sentiment Analysis
Analyze the emotional tone of conversations to:
- Track relationship health with important contacts
- Identify potential misunderstandings before they escalate
- Understand customer satisfaction in business contexts
- Recognize patterns in communication style
For example, an AI assistant could analyze a customer service conversation and alert you to negative sentiment that requires urgent attention.
Topic Extraction
Automatically identify and categorize conversation topics to:
- Summarize long group discussions
- Track recurring themes in business communications
- Organize information from multiple conversations
- Create searchable topic indices across your chat history
This capability helps extract valuable information from the unstructured text of everyday conversations.
Key Theme Identification
Recognize important subjects and references across multiple chats:
- Track projects mentioned across different group conversations
- Identify frequently discussed topics with specific contacts
- Highlight emerging trends in your communication patterns
- Correlate topics across personal and professional conversations
Automated Message Processing Workflows
WhatsApp MCP enables the creation of sophisticated message processing systems:
- Auto-categorization: Sort incoming messages by priority, topic, or sender
- Smart Filtering: Apply custom rules to highlight important messages
- Scheduled Responses: Queue messages to be sent at optimal times
- Follow-up Reminders: Track conversations requiring action and generate reminders
- Data Extraction: Automatically collect and organize information mentioned in chats
These workflows can be customized to your specific needs, whether personal or professional.
Group Management Automation
For those who manage multiple WhatsApp groups, automation can save significant time:
- Welcome Messages: Automatically greet new members with group rules and information
- Activity Summaries: Generate periodic digests of group activity
- Moderation Assistance: Flag potentially problematic messages for review
- Poll Creation and Analysis: Simplify decision-making in groups
- Event Planning: Coordinate schedules and send reminders for group events
These tools are especially valuable for community managers, team leaders, and event organizers.
Advanced AI Assistant Integration
The combination of WhatsApp MCP with advanced AI capabilities opens up powerful possibilities:
- Multilingual Communication: Real-time translation for international conversations
- Knowledge Base Integration: Connect WhatsApp conversations with your personal or business knowledge base
- Meeting Scheduling: Let AI negotiate times and send calendar invites based on chat conversations
- Content Research: Request information from AI that's delivered directly to relevant WhatsApp chats
- Personal CRM: Build relationship intelligence by tracking interactions and important details about contacts
Chatbot Integration Examples
WhatsApp MCP can be used to create sophisticated chatbots for various purposes:
- Customer Service Bot: Handle common queries and escalate complex issues to human agents
- Appointment Scheduling: Manage bookings and send reminders through WhatsApp
- Order Processing: Allow customers to place and track orders via messaging
- Information Delivery: Create subscription-based information services delivering personalized content
- Interactive Learning: Develop educational chatbots that teach through conversation
Each of these examples demonstrates how WhatsApp MCP can transform ordinary messaging into intelligent, automated communication systems.
Appendix
Glossary
- MCP (Model Context Protocol): An open protocol standard for AI-service communication
- WhatsApp Bridge: The Go component that connects to WhatsApp Web
- MCP Server: The Python component implementing the Model Context Protocol
- QR Code Authentication: The process of linking the bridge to your WhatsApp account
- JSON-RPC 2.0: The underlying communication protocol used by MCP
- Chat ID: Unique identifier for a WhatsApp conversation
- Contact ID: Unique identifier for a WhatsApp contact
- Message Context: The surrounding messages that provide meaning to a specific message
- SQLite: The database engine used to store WhatsApp data locally
- CGO: C Go, a feature that allows Go programs to call C code, required for go-sqlite3
Learning Resources
To deepen your understanding of WhatsApp MCP and related technologies:
- GitHub Repository: github.com/lharries/whatsapp-mcp
- Model Context Protocol Guide: toolworthy.ai/blog/what-is-model-context-protocol
- Author's Video Demo: Watch Luke Harries demonstrate WhatsApp MCP in action x.com/LukeHarries_/status/1905986562388635913
- WhatsApp Developers: developers.facebook.com/docs/whatsapp
- MCP Community Forum: Discuss and share experiences with other users
These resources provide additional information and support as you explore the capabilities of WhatsApp MCP.
Useful Resource Links
- WhatsApp MCP GitHub Repository
- Model Context Protocol Specification
- Go Programming Language
- Python Programming Language
- SQLite Database Engine
- Claude Desktop Application
- Cursor IDE
- WhatsApp Web
Related MCP Server List
- File System MCP: Access local files and directories
- GitHub MCP: Interact with GitHub repositories
- Weather MCP: Get weather information
- Browser MCP: Control web browsing
- PostgreSQL MCP: Connect to PostgreSQL databases
- Memory MCP: Store and retrieve information between sessions
- Slack MCP: Integrate with Slack messaging
- Google Drive MCP: Access Google Drive files
- Email MCP: Send and receive emails
- Calendar MCP: Manage calendar events
Tool Command Reference
| Command | Description | Required Parameters | Optional Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| search_contacts | Find contacts by name or number | query | limit, offset |
| list_messages | Get messages from a chat | chat_id | limit, before_id, after_id |
| list_chats | List available chats | limit, offset | |
| get_chat | Get detailed chat information | chat_id | |
| get_direct_chat_by_contact | Find chat with specific contact | contact_id | |
| get_contact_chats | List all chats with a contact | contact_id | |
| get_last_interaction | See recent interaction with contact | contact_id | |
| get_message_context | Get surrounding messages | message_id | before, after |
| send_message | Send a WhatsApp message | chat_id, text | media_url, caption, reply_to |
| send_file | Send a file (image, video, document) | chat_id, file_path | caption |
| send_audio_message | Send a voice message | chat_id, audio_path | |
| download_media | Download media from a message | message_id, chat_jid |
This reference table provides a quick overview of the most commonly used WhatsApp MCP tools.




























![[Webinar] AI Is Already Inside Your SaaS Stack — Learn How to Prevent the Next Silent Breach](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiOWn65wd33dg2uO99NrtKbpYLfcepwOLidQDMls0HXKlA91k6HURluRA4WXgJRAZldEe1VReMQZyyYt1PgnoAn5JPpILsWlXIzmrBSs_TBoyPwO7hZrWouBg2-O3mdeoeSGY-l9_bsZB7vbpKjTSvG93zNytjxgTaMPqo9iq9Z5pGa05CJOs9uXpwHFT4/s1600/ai-cyber.jpg?#)











































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)





























































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] Machine Learning Hero, AI-Assisted Programming for Web and Machine Learning & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)








































































![Rogue Company Elite tier list of best characters [April 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33136-1657102075/rogue-company-ios-android-tier-cover.jpg?#)







































































_Andreas_Prott_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)


























































































![What’s new in Android’s April 2025 Google System Updates [U: 4/18]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/google-play-services-3.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)










![Apple Watch Series 10 Back On Sale for $299! [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96657/96657/96657-640.jpg)
![EU Postpones Apple App Store Fines Amid Tariff Negotiations [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97068/97068/97068-640.jpg)
![Apple Slips to Fifth in China's Smartphone Market with 9% Decline [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97065/97065/97065-640.jpg)