Understanding the CMDB in ServiceNow
As a backbone of IT Service Management (ITSM), the Configuration Management Database (CMDB) plays a significant role in managing complex systems and services. ServiceNow—a platform designed to manage, automate, and streamline your business requirements—is renowned for its robust CMDB. CMDB has been around for many decades, but why has CMDB ServiceNow become so popular? The answer lies in its ability to simplify a traditionally complicated concept. In this blog, we’ll explore what the CMDB is, how it works in ServiceNow, and why it’s become a game-changer for organizations worldwide. Key Takaways: Core of ITSM: The CMDB in ServiceNow organizes IT assets and their relationships, central to managing IT environments. Boosts Visibility: It maps connections, speeding up troubleshooting and decision-making. Automation Helps: ServiceNow Discovery keeps the CMDB accurate and up-to-date effortlessly. Supports IT Tasks: Integrates with incident, change, and asset management for practical use. Start Simple: Focus on key CIs and maintain data quality for success. Saves Time & Money: Reduces downtime, optimizes resources, and aids compliance. What is a CMDB? At its core, a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized repository that stores information about an organization’s IT assets and their relationships. These assets, known as Configuration Items (CIs), can include hardware (like servers and laptops), software (like applications and licenses), network components, and even documentation or facilities. The CMDB doesn’t just list these items—it maps how they connect and depend on each other, creating a dynamic picture of your IT environment. In ServiceNow, the CMDB is a foundational element of the platform, tightly integrated with ITSM processes like incident management, change management, and asset management. Just like a “single source of truth”, CMDB ServiceNow helps IT teams understand what they’re managing, troubleshoot issues faster, and make informed decisions. What Is CMDB’s Role? Imagine you’re an IT administrator and a critical application goes down. Without a CMDB, you’d be scrambling to figure out which server hosts the app, what database it relies on, or whether a recent network change caused the outage. With a well-maintained CMDB, you can quickly see the application’s dependencies, pinpoint the issue, and resolve it—minimizing downtime and frustration. In case you’re new to the definition, the key takeaway is this: a CMDB reduces chaos. It provides visibility, control, and context, enabling IT teams to manage resources proactively rather than reactively. In ServiceNow, it’s the glue that ties together various IT processes, ensuring they work harmoniously. CMDB ServiceNow CMDB ServiceNow can help you create clear, organized maps of your organization’s IT assets (like computers and software), services (like email or websites), and how they connect. These details are stored in the CMDB as Configuration Items (CIs)—think of them as records for each piece of your IT setup. By using these records, you can keep an eye on your systems, making sure everything runs smoothly, stays stable, and keeps working without interruptions. Let’s break it down into its core components and processes. 1. Configuration Items (CIs) Everything in the CMDB starts with Configuration Items, or CIs. These are the individual pieces of your IT setup, like a laptop, a server, an application, or even a printer. In ServiceNow, each CI gets its own record, packed with details—like a profile card. For example, a server’s card might list its name, IP address, who owns it, and when it was last updated. CMDB ServiceNow organizes these CIs into categories so you can easily find what you need, whether it’s hardware, software, or even a business service like your company’s email system. Hardware CIs (e.g., laptops, servers, printers) Software CIs (e.g., Microsoft Office, SAP) Cloud services CIs (e.g., AWS, Azure) Networks CIs (e.g., routers, firewalls) People CIs (e.g., employees, teams) Business services CIs (e.g., email, payroll systems) Each CI has attributes—like name, owner, location, version, or status—that provide detailed information about it. For example, a server CI might list its IP address, CPU specs, and maintenance schedule. 2. Relationships (Dependencies) What makes the CMDB truly powerful is its ability to define relationships between CIs. These relationships show how assets interact or depend on each other. For instance: A web application “runs on” a specific server. A server “connects to” a network switch. A business service “depends on” multiple applications and infrastructure components. CMDB ServiceNow visualizes these relationships in dependency views—interactive maps that let you see the ripple effects of changes or outages. 3. Discovery and Population You might be wondering: How does the CMDB get filled with all this da
As a backbone of IT Service Management (ITSM), the Configuration Management Database (CMDB) plays a significant role in managing complex systems and services. ServiceNow—a platform designed to manage, automate, and streamline your business requirements—is renowned for its robust CMDB.
CMDB has been around for many decades, but why has CMDB ServiceNow become so popular? The answer lies in its ability to simplify a traditionally complicated concept. In this blog, we’ll explore what the CMDB is, how it works in ServiceNow, and why it’s become a game-changer for organizations worldwide.
Key Takaways:
- Core of ITSM: The CMDB in ServiceNow organizes IT assets and their relationships, central to managing IT environments.
- Boosts Visibility: It maps connections, speeding up troubleshooting and decision-making.
- Automation Helps: ServiceNow Discovery keeps the CMDB accurate and up-to-date effortlessly.
- Supports IT Tasks: Integrates with incident, change, and asset management for practical use.
- Start Simple: Focus on key CIs and maintain data quality for success.
- Saves Time & Money: Reduces downtime, optimizes resources, and aids compliance.
What is a CMDB?
At its core, a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized repository that stores information about an organization’s IT assets and their relationships. These assets, known as Configuration Items (CIs), can include hardware (like servers and laptops), software (like applications and licenses), network components, and even documentation or facilities. The CMDB doesn’t just list these items—it maps how they connect and depend on each other, creating a dynamic picture of your IT environment.
In ServiceNow, the CMDB is a foundational element of the platform, tightly integrated with ITSM processes like incident management, change management, and asset management. Just like a “single source of truth”, CMDB ServiceNow helps IT teams understand what they’re managing, troubleshoot issues faster, and make informed decisions.
What Is CMDB’s Role?
Imagine you’re an IT administrator and a critical application goes down. Without a CMDB, you’d be scrambling to figure out which server hosts the app, what database it relies on, or whether a recent network change caused the outage. With a well-maintained CMDB, you can quickly see the application’s dependencies, pinpoint the issue, and resolve it—minimizing downtime and frustration.
In case you’re new to the definition, the key takeaway is this: a CMDB reduces chaos. It provides visibility, control, and context, enabling IT teams to manage resources proactively rather than reactively. In ServiceNow, it’s the glue that ties together various IT processes, ensuring they work harmoniously.
CMDB ServiceNow
CMDB ServiceNow can help you create clear, organized maps of your organization’s IT assets (like computers and software), services (like email or websites), and how they connect. These details are stored in the CMDB as Configuration Items (CIs)—think of them as records for each piece of your IT setup. By using these records, you can keep an eye on your systems, making sure everything runs smoothly, stays stable, and keeps working without interruptions.
Let’s break it down into its core components and processes.
1. Configuration Items (CIs)
Everything in the CMDB starts with Configuration Items, or CIs. These are the individual pieces of your IT setup, like a laptop, a server, an application, or even a printer. In ServiceNow, each CI gets its own record, packed with details—like a profile card. For example, a server’s card might list its name, IP address, who owns it, and when it was last updated. CMDB ServiceNow organizes these CIs into categories so you can easily find what you need, whether it’s hardware, software, or even a business service like your company’s email system.
- Hardware CIs (e.g., laptops, servers, printers)
- Software CIs (e.g., Microsoft Office, SAP)
- Cloud services CIs (e.g., AWS, Azure)
- Networks CIs (e.g., routers, firewalls)
- People CIs (e.g., employees, teams)
- Business services CIs (e.g., email, payroll systems)
Each CI has attributes—like name, owner, location, version, or status—that provide detailed information about it. For example, a server CI might list its IP address, CPU specs, and maintenance schedule.
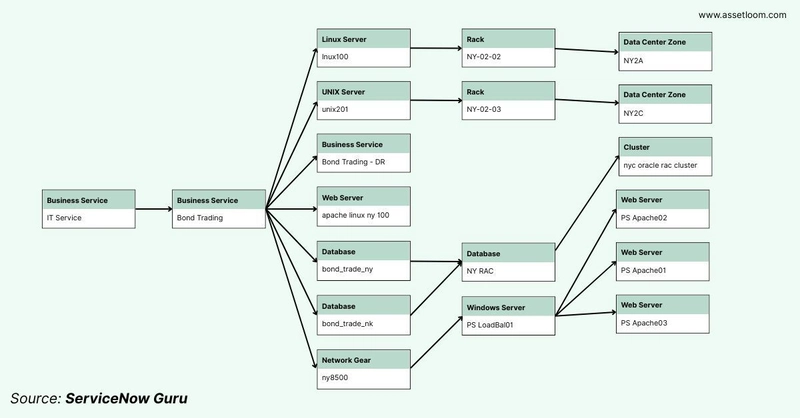
2. Relationships (Dependencies)
What makes the CMDB truly powerful is its ability to define relationships between CIs. These relationships show how assets interact or depend on each other. For instance:
- A web application “runs on” a specific server.
- A server “connects to” a network switch.
- A business service “depends on” multiple applications and infrastructure components. CMDB ServiceNow visualizes these relationships in dependency views—interactive maps that let you see the ripple effects of changes or outages.
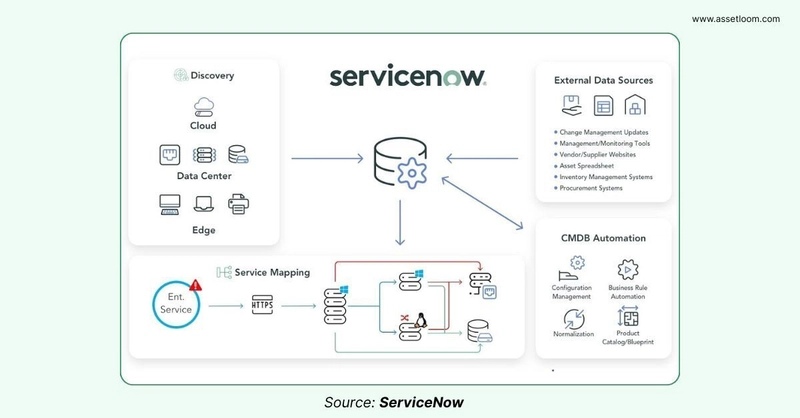
3. Discovery and Population
You might be wondering: How does the CMDB get filled with all this data? Manually entering thousands of CIs would be a nightmare. That’s where ServiceNow Discovery comes in. Discovery is an automated tool that scans your IT environment—networks, cloud resources, virtual machines—and populates the CMDB with accurate, up-to-date information.
Manual entry is still an option for smaller setups or specific CIs, but automation is the key to keeping the CMDB current and reliable.
To summarize, the CMDB ServiceNow can be populated through:
- Automated Discovery: ServiceNow Discovery automatically scans your network to identify and gather information about CIs.
- Service Mapping: This feature maps the underlying IT infrastructure to the business services they support, providing a service-centric view.
- Integrations: You can integrate the CMDB with other systems (e.g., asset management, monitoring tools) to pull in data.
- Manual Input: While not ideal for large environments, you can manually create and update CI records.
- Import Sets: Allows importing data from external sources like spreadsheets.
4. Integration with ITSM Processes
The CMDB isn’t a standalone tool—it’s deeply integrated into ServiceNow’s ITSM modules. Take this scenario as an example. If someone reports a slow app (an incident), you check the CMDB to see which server it runs on and fix the issue fast. Planning to update that server (a change)? The CMDB warns you that the app might be affected, so you’re prepared. It even tracks assets, like how many licenses you’ve got left.
- Incident Management (If a server crashes, the CMDB helps find affected services).
- Change Management (Before making changes, check dependencies/relationships to avoid issues).
- Asset Management (Track costs, warranties, and ownership of IT assets).
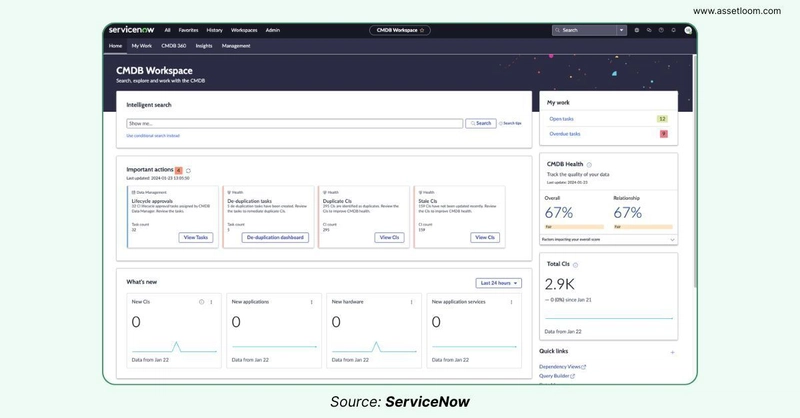
CMDB ServiceNow: The CMDB Workspace
The ServiceNow CMDB Workspace serves as your main control center for handling the CMDB. It offers simple access to dashboards and tools to help with different tasks. You can look up Configuration Items (CIs) and check a clear, visual overview of the CMDB’s condition.
Key features of CMDB ServiceNow Workspace (Homepage) to name a few:
Intelligent Search
The Intelligent Search feature within the ServiceNow CMDB Workspace offers a sophisticated yet accessible method for querying the CMDB. Leveraging a Natural Language Query (NLQ) approach, it enables users to search for Configuration Items (CIs) using intuitive language, complemented by advanced options such as the Query Builder for complex inquiries and conditional filters for precise results. The feature also provides visibility into recent and sample queries, ensuring efficient navigation of CI classes and related data tables.
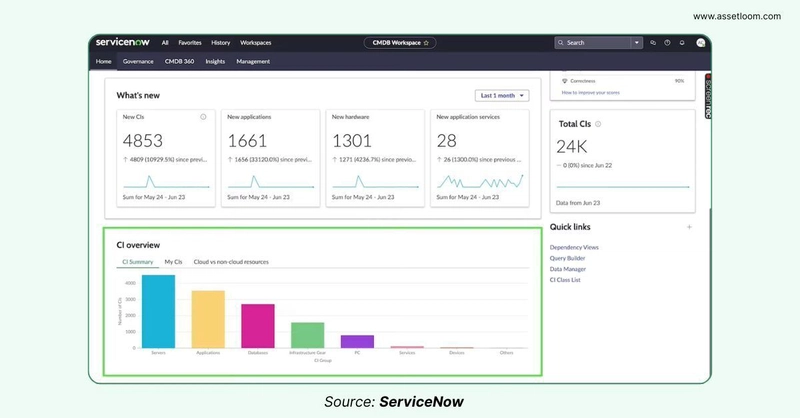
CI Overview
The CI Overview delivers a structured and detailed perspective of the IT environment managed within the CMDB. It categorizes Configuration Items (CIs) into logical groups—such as hardware, software, or cloud-based assets—offering insights into ownership, distribution, and type. Accessible through a centralized dashboard, this feature provides a consolidated view of managed CIs. As a result, it enables IT teams to assess the scope and composition of their infrastructure effectively.
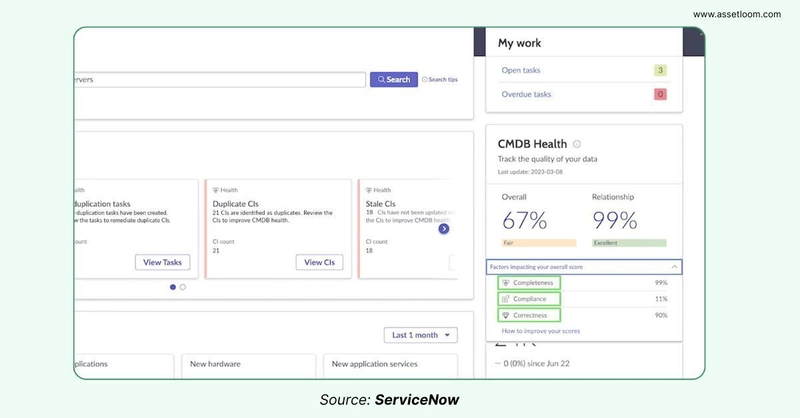
CMDB Health Monitoring
This feature provides a comprehensive assessment of Configuration Items (CIs) and their interconnections. It displays health metrics as percentage scores, which users can click to access the CMDB Health and CMDB Relationship Health dashboards for deeper insights. The overall health percentage reflects the condition of all CIs, evaluated against three essential criteria: correctness (data accuracy), compliance (adherence to defined standards), and completeness (presence of required information). Additionally, the Relationship percentage measures the integrity of CI relationships, accounting for issues such as orphaned connections, duplicates, and stale links.
Benefits of Using the CMDB ServiceNow
The ServiceNow CMDB enhances IT management with a range of practical advantages. Below are the core benefits driving its value.
- Enhanced Visibility: CI Overview and Unified Map provide a clear view of assets and relationships, improving control.
- Increased Efficiency: Intelligent Search and Discovery streamline data access, speeding up IT tasks.
- Reliable Data: CMDB Health Monitoring ensures accurate, complete CI information for decision-making.
- Reduced Risk: Relationship mapping and health checks minimize downtime and disruptions.
- Compliance Made Easy: A single source of truth simplifies audits and regulatory adherence.
- Cost Savings: Asset insights help optimize resource use and cut unnecessary expenses.
- Process Integration: Seamless ITSM connectivity enhances operational workflows.
Conclusion
The CMDB ServiceNow is more than just a database—it’s a strategic tool that brings order to the complexity of IT environments. By understanding its components, features, and benefits, you’re well on your way to mastering this cornerstone of ITSM. Whether you’re troubleshooting an outage or planning a major change, the CMDB is your trusted ally—so dive in, explore, and watch your IT operations transform!











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)



























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)

































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)





































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)