Top 5 CMDB Best Practices for Beginners
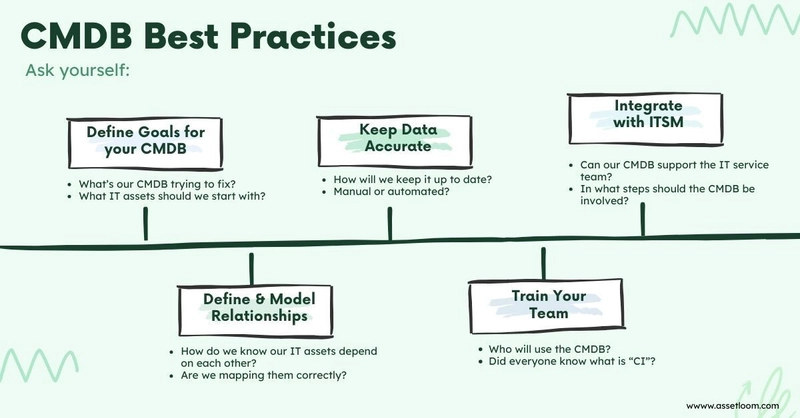
You may have heard that the Configuration Management Database (CMDB) offers a clear, up-to-date map of your entire IT environment, every server, application, and connection, all in one place. It helps you manage your IT infrastructure. But here’s the brutal truth: a CMDB can’t run itself. It needs care and a solid plan to stay useful. Not sure how to do it? Let’s review these 5 CMDB best practices to make sure your CMDB is on the right track. Key Takeaway A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a powerful tool for mapping your IT environment, but it needs a clear plan to deliver value. These 5 CMDB best practices answer critical questions to guide your success: What’s our CMDB trying to fix? Set a specific goal (e.g., reduce outages) to focus your efforts and avoid a data mess. How will we keep our CMDB up to date? Use automated tools and regular checks to ensure data reflects reality. Are we mapping how our IT assets depend on each other? Link assets (e.g., servers to apps) to troubleshoot faster and plan smarter. How can our CMDB support our IT processes? Connect it to incident, problem, and change management for quicker fixes and fewer disruptions. How will we get everyone using the CMDB? Train IT and non-IT teams to make the CMDB a go-to resource. Learn More. CMDB Best Practices #1: Define Clear Goal for Your CMDB Just like any plan, your CMDB needs a clear goal to point the way, guiding your team and the CMDB to collect just the right data. A good goal keeps everyone focused on what matters. Without clear goals, you might collect too much data, or too little, turning into nothing more than a messy spreadsheet. For example, if you want to cut down on system outages, your CMDB should prioritize critical systems, like servers and applications, and how they’re connected. To keep from chewing more than you can swallow, here’s a tip: sit down with stakeholders. Include your IT staff, managers, and business units like marketing or finance, then ask what challenges they face that a CMDB could solve. So how do you know if your goal is specific and measurable? Imagine you’re at a retail company trying to prevent website crashes during holiday sales. A strong goal might be: “Map all components of our e-commerce platform, including servers, databases, and external services, to ensure 99.9% uptime during Black Friday.” With that goal, the CMDB can focus on collecting data about these systems first, allowing the IT team to respond quickly if issues arise. CMDB Best Practices #2: Keep Data Accurate A CMDB is only reliable if its data is correct and current. Outdated or wrong information can lead to mistakes, like upgrading the wrong server or missing a key dependency. Regular updates and checks keep your CMDB trustworthy, especially in fast-changing IT environments where new devices or software are added often. One of the most effective ways to ensure data accuracy is by leveraging discovery tools. These automated solutions can scan your IT environment to identify and record hardware, software, and their configurations. Sure, your team sets the rules for what gets discovered and keeps the tools running smoothly. They also add business insights to the data. But for sheer accuracy and up-to-the-minute info, you can't beat automated discovery. If you’re looking for a trusted tool, consider ServiceNow Discovery, or BMC Helix Discovery (integrated with BMC Helix CMDB). They offer the ability to automatically map your IT infrastructure, providing a real-time view of your assets and their relationships. CMDB Best Practices #3: Model Relationships Effectively It is well known that the power of a CMDB comes from understanding how Configuration Items (CIs) relate to each other. For example, knowing that a server hosts a specific application and that application depends on a database helps IT teams troubleshoot issues, plan changes, and avoid disruptions. Without clear relationship mapping, a CMDB is just a list of assets, missing the “big picture” that makes it valuable. How to Do It: Map Dependencies: Identify and document relationships between CIs, like which servers support which applications or which networks connect to which devices. Use a Framework: Follow a well-established standard ITIL or the Common Service Data Model (CSDM)) to guide how you define and structure relationships. Validate Relationships: Use stakeholder input or automated tools to confirm that relationships are accurate and up-to-date. CMDB Best Practices #4: Integrate with ITSM Processes Let's be real, a CMDB sitting on its own isn't doing you much good. It becomes a powerhouse when it works with other IT Service Management (ITSM) processes. From incident and problem management to change management, the CMDB can be involved at every step. Here's how it works: Within Incident Management: When an issue pops up with an application (which is a CI in your CMDB), the sy
You may have heard that the Configuration Management Database (CMDB) offers a clear, up-to-date map of your entire IT environment, every server, application, and connection, all in one place. It helps you manage your IT infrastructure.
But here’s the brutal truth: a CMDB can’t run itself. It needs care and a solid plan to stay useful. Not sure how to do it? Let’s review these 5 CMDB best practices to make sure your CMDB is on the right track.
Key Takeaway
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a powerful tool for mapping your IT environment, but it needs a clear plan to deliver value. These 5 CMDB best practices answer critical questions to guide your success:
- What’s our CMDB trying to fix? Set a specific goal (e.g., reduce outages) to focus your efforts and avoid a data mess.
- How will we keep our CMDB up to date? Use automated tools and regular checks to ensure data reflects reality.
- Are we mapping how our IT assets depend on each other? Link assets (e.g., servers to apps) to troubleshoot faster and plan smarter.
- How can our CMDB support our IT processes? Connect it to incident, problem, and change management for quicker fixes and fewer disruptions.
- How will we get everyone using the CMDB? Train IT and non-IT teams to make the CMDB a go-to resource.
CMDB Best Practices #1: Define Clear Goal for Your CMDB
Just like any plan, your CMDB needs a clear goal to point the way, guiding your team and the CMDB to collect just the right data. A good goal keeps everyone focused on what matters. Without clear goals, you might collect too much data, or too little, turning into nothing more than a messy spreadsheet. For example, if you want to cut down on system outages, your CMDB should prioritize critical systems, like servers and applications, and how they’re connected.
To keep from chewing more than you can swallow, here’s a tip: sit down with stakeholders. Include your IT staff, managers, and business units like marketing or finance, then ask what challenges they face that a CMDB could solve.
So how do you know if your goal is specific and measurable? Imagine you’re at a retail company trying to prevent website crashes during holiday sales. A strong goal might be: “Map all components of our e-commerce platform, including servers, databases, and external services, to ensure 99.9% uptime during Black Friday.” With that goal, the CMDB can focus on collecting data about these systems first, allowing the IT team to respond quickly if issues arise.
CMDB Best Practices #2: Keep Data Accurate
A CMDB is only reliable if its data is correct and current. Outdated or wrong information can lead to mistakes, like upgrading the wrong server or missing a key dependency. Regular updates and checks keep your CMDB trustworthy, especially in fast-changing IT environments where new devices or software are added often.
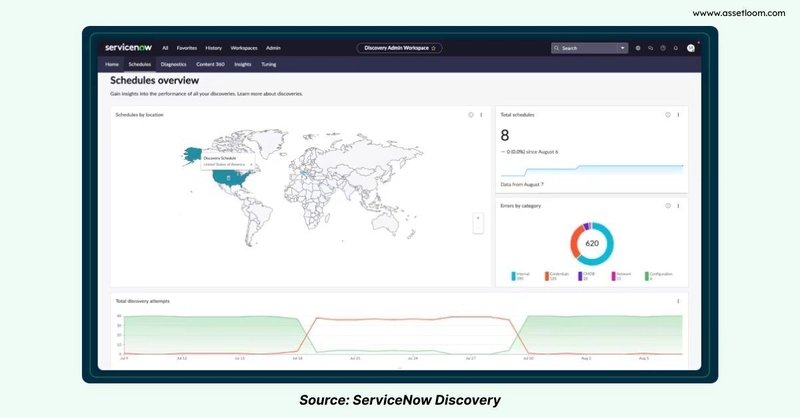
One of the most effective ways to ensure data accuracy is by leveraging discovery tools. These automated solutions can scan your IT environment to identify and record hardware, software, and their configurations. Sure, your team sets the rules for what gets discovered and keeps the tools running smoothly. They also add business insights to the data. But for sheer accuracy and up-to-the-minute info, you can't beat automated discovery.
If you’re looking for a trusted tool, consider ServiceNow Discovery, or BMC Helix Discovery (integrated with BMC Helix CMDB). They offer the ability to automatically map your IT infrastructure, providing a real-time view of your assets and their relationships.
CMDB Best Practices #3: Model Relationships Effectively
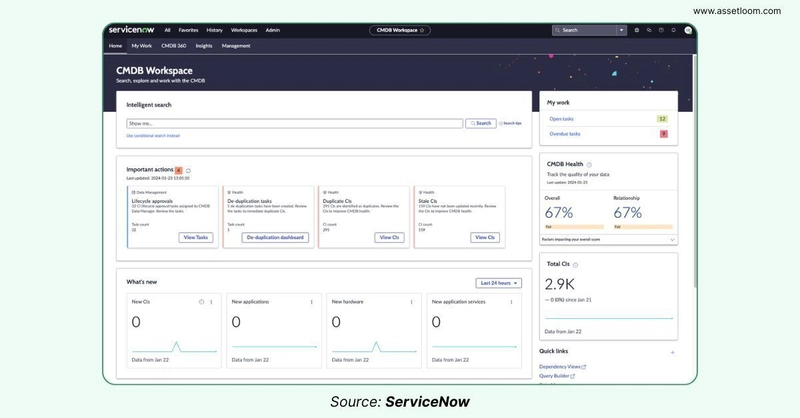
It is well known that the power of a CMDB comes from understanding how Configuration Items (CIs) relate to each other. For example, knowing that a server hosts a specific application and that application depends on a database helps IT teams troubleshoot issues, plan changes, and avoid disruptions. Without clear relationship mapping, a CMDB is just a list of assets, missing the “big picture” that makes it valuable.
How to Do It:
- Map Dependencies: Identify and document relationships between CIs, like which servers support which applications or which networks connect to which devices.
- Use a Framework: Follow a well-established standard ITIL or the Common Service Data Model (CSDM)) to guide how you define and structure relationships.
- Validate Relationships: Use stakeholder input or automated tools to confirm that relationships are accurate and up-to-date.
CMDB Best Practices #4: Integrate with ITSM Processes
Let's be real, a CMDB sitting on its own isn't doing you much good. It becomes a powerhouse when it works with other IT Service Management (ITSM) processes. From incident and problem management to change management, the CMDB can be involved at every step. Here's how it works:
Within Incident Management:
When an issue pops up with an application (which is a CI in your CMDB), the system pulls up all the related info. The agent instantly sees the server it lives on, the database it connects to. This means:
- Knowing the Damage: The CMDB shows which business services are hit by the broken app, so the agent knows how big of a deal it is and can prioritize right.
- Faster Fixes: Seeing all the linked components helps pinpoint the problem faster.
- Getting the Right Help: The CMDB knows which teams are responsible for the different parts, so the ticket gets to the right experts ASAP.
Within Problem Management:
Problem management is about figuring out why things keep breaking. By looking at incidents tied to specific items in the CMDB, you can see trends and find the underlying causes. That weird application error that keeps happening? The CMDB might show it's always linked to a specific version of a database server. This makes finding a permanent fix much easier. Plus, when you do fix it, the CMDB helps you see everything that might be affected by your fix.
Within Change Management:
Before you make a change, the CMDB shows you everything that could be impacted, what depends on what. This lets you:
- See the Risks: Understand the potential fallout of your change and plan accordingly.
- Plan Smart: Make sure you consider all the connected pieces to avoid conflicts and failures.
- Keep Track: After the change, update the CMDB to reflect the new setup. This gives you a history of changes and helps if something goes wrong later.
Pro tip: Many modern CMDB solutions come with these integrations to popular ITSM tools already built-in or readily available. This significantly simplifies the process of linking your configuration data with your day-to-day IT operations, making the CMDB a truly integral and valuable part of your service management framework.
Explore the top 10 CMDB tools here.
CMDB Best Practices #5: Keep Everyone on the Same Page
Basically, making sure everyone is on the same page about the CMDB – what it is, why it matters, and how to use it. CMDB can be complicated, especially for beginners. As a central repository for all things IT, it can feel overwhelming with its interconnected data and specific terminology. That's precisely why keeping everyone on the same page through training and education is absolutely vital for a CMDB to be effective. If users don't understand its purpose or how to navigate it, the investment in the tool will likely fall flat.
Get your IT staff up to speed on all things CMDB: the processes, the tools, and why it makes their lives easier (fewer mistakes, faster fixes, etc.). Make sure they know how to find information and update it correctly.
Final Thoughts
A well-managed CMDB reduces risks, saves time, and improves decisions. These CMDB best practices should ensure your CMDB is a reliable, easy-to-use tool that supports both IT and business goals. Good luck mastering your CMDB!








































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)



































































































































![From fast food worker to cybersecurity engineer with Tae'lur Alexis [Podcast #169]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1745242807605/8a6cf71c-144f-4c91-9532-62d7c92c0f65.png?#)























![BPMN-procesmodellering [closed]](https://i.sstatic.net/l7l8q49F.png)



















































































.jpg?#)
.jpg?#)






























































































































![CarPlay app with web browser for streaming video hits App Store [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2024/11/carplay-apple.jpeg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

![What’s new in Android’s April 2025 Google System Updates [U: 4/21]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/google-play-services-3.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![Apple Releases iOS 18.5 Beta 3 and iPadOS 18.5 Beta 3 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97076/97076/97076-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds visionOS 2.5 Beta 3 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97077/97077/97077-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds tvOS 18.5 Beta 3 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97078/97078/97078-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds watchOS 11.5 Beta 3 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97079/97079/97079-640.jpg)