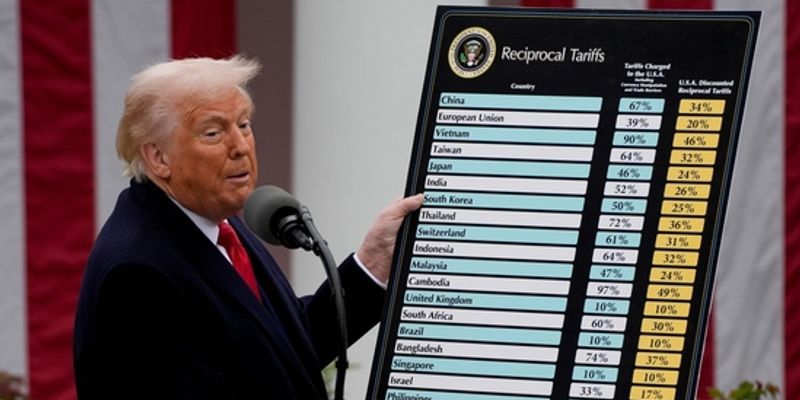
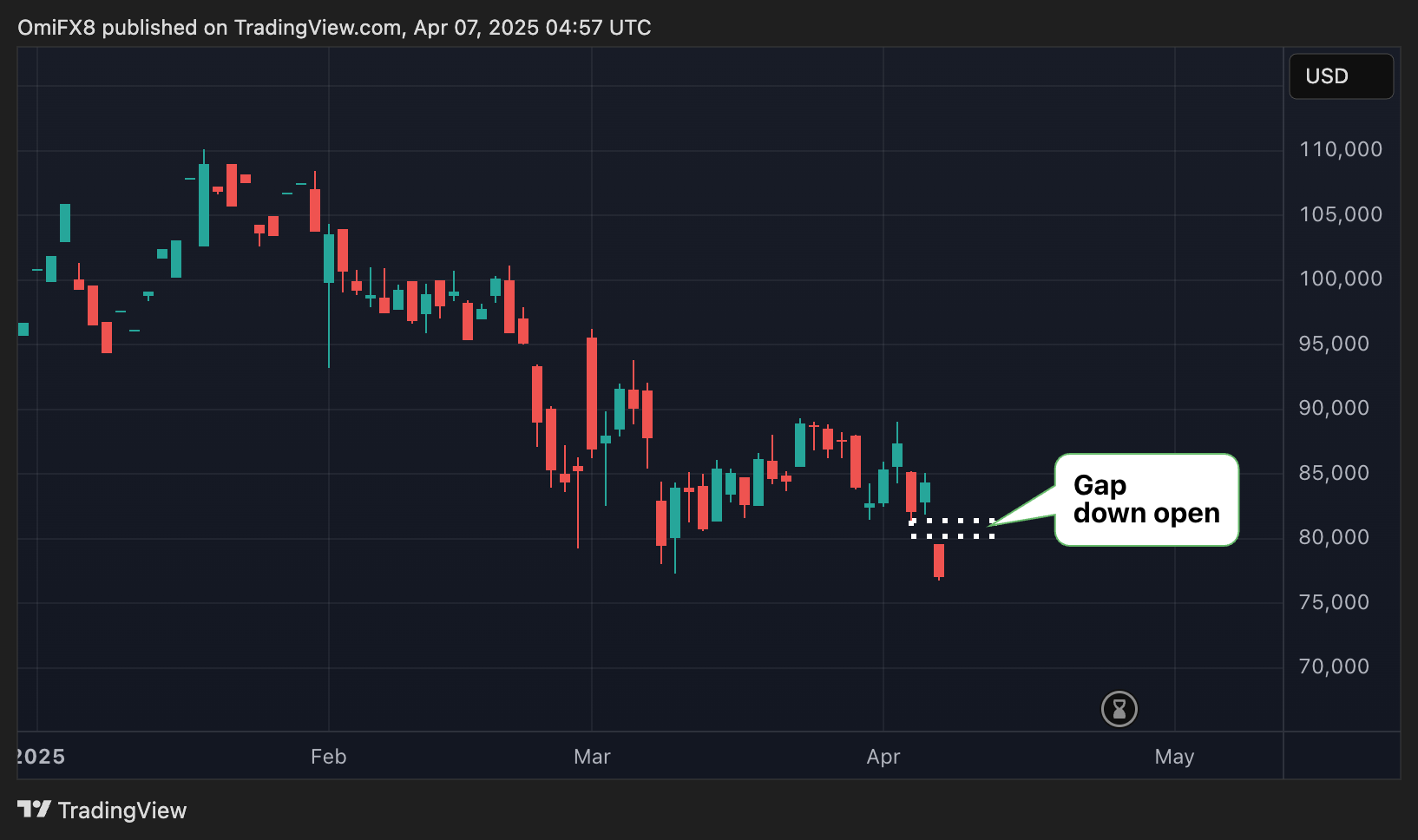
Deutsche Bank's Path to Sustainable Banking: A Deep Dive into Sustainable Innovations
Abstract This post takes a comprehensive look at Deutsche Bank’s bold move toward sustainable banking practices. We examine the background, core initiatives, technological integration, and industry implications of the bank’s journey to achieve net-zero emissions and foster sustainable finance. In addition, the post analyzes related trends in digital transformation and sustainability frameworks within the financial sector. With key tables, bullet lists, and carefully woven hyperlinks to authoritative sources and related discussions on platforms like Dev.to, this piece offers a technical yet accessible overview for both industry experts and curious readers. Introduction Sustainability in banking is no longer a future prospect—it has become a strategic imperative. Global banks are increasingly aligning their business models with environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices. Deutsche Bank is at the forefront of this movement. The bank’s initiatives range from reducing its overall carbon footprint to funding projects that generate global environmental and social impact. In this post, we explore Deutsche Bank's sustainable banking journey and investigate how digital innovations, regulatory pressures, and modern investor expectations are reshaping the financial industry. Background and Context The Rise of Sustainable Banking Sustainable banking emerged from the recognition that economic growth and environmental protection should coexist. Recent decades have witnessed heightened awareness about climate change, prompting regulators, investors, and consumers to demand a balance between financial profitability and environmental stewardship. Deutsche Bank’s commitment, seen alongside similar movements by other financial institutions, marks an important pivot from traditional banking models. Evolution of Regulatory and Investor Demands Key drivers for sustainable banking include: Climate Change Awareness: Governments and investors now require businesses to account for and reduce their carbon emissions. Regulatory Demands: New and evolving policies push banks to adopt greener operations. For example, regional regulators often enforce emissions reduction targets. Investor Expectations: Investors increasingly integrate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria into their decision-making. Projects like blockchain and environmental impact highlight the intersection between technology and sustainability. Market Demand for Green Products: Consumers expect financial institutions to offer environmentally friendly products and services, spurring innovations such as green bonds and sustainable loans. Deutsche Bank’s comprehensive approach demonstrates an awareness of these trends, setting the stage for industry-wide transformation. Technology Integration in Sustainability Digital innovations, including data analytics and blockchain, are essential for measuring and improving sustainability metrics. Deutsche Bank is leveraging these tools to monitor ESG performance and develop digital platforms for green investing. Practices such as sustainable blockchain practices enable improved transparency and efficiency in environmental initiatives. Core Concepts and Features Carbon Footprint Reduction Initiatives Deutsche Bank’s strategy to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 primarily focuses on: Green Operations: Transitioning to energy-efficient facilities and renewable energy sources. Sustainable Supply Chains: Prioritizing eco-friendly procurement through stringent vendor criteria. Innovative Data Analytics: Leveraging digital tools to track carbon emissions, thus enabling precise ESG monitoring. Below is a table summarizing key sustainability initiatives at Deutsche Bank: Initiative Description Key Technology Green Operations Investing in energy-efficient and renewable energy-powered facilities Data Analytics, IoT Sensors Sustainable Supply Chain Engaging eco-friendly suppliers and circular procurement strategies Blockchain, Digital Identity Green Financial Products Issuing green bonds and evaluating credits based on ESG criteria Financial Modeling, AI Analytics Employee and Stakeholder Engagement Training programs and collaborative projects to further sustainability Digital Platforms, Online Education Sustainable Finance and Investment Deutsche Bank has played a pivotal role in channeling investments toward environmentally beneficial projects. The bank endeavours to: Issue Green Bonds: Funding projects such as renewable energy infrastructure. Incorporate ESG Criteria: Evaluating loan applications with a focus on environmental impact. Engage in Stakeholder Collaboration: Promoting sustainability through partnerships with governments, NGOs, and industry bodies. A bullet list of sustainable finance benefits includes: Enhanced Transparency: Better ESG reporting frames tru

Abstract
This post takes a comprehensive look at Deutsche Bank’s bold move toward sustainable banking practices. We examine the background, core initiatives, technological integration, and industry implications of the bank’s journey to achieve net-zero emissions and foster sustainable finance. In addition, the post analyzes related trends in digital transformation and sustainability frameworks within the financial sector. With key tables, bullet lists, and carefully woven hyperlinks to authoritative sources and related discussions on platforms like Dev.to, this piece offers a technical yet accessible overview for both industry experts and curious readers.
Introduction
Sustainability in banking is no longer a future prospect—it has become a strategic imperative. Global banks are increasingly aligning their business models with environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices. Deutsche Bank is at the forefront of this movement. The bank’s initiatives range from reducing its overall carbon footprint to funding projects that generate global environmental and social impact. In this post, we explore Deutsche Bank's sustainable banking journey and investigate how digital innovations, regulatory pressures, and modern investor expectations are reshaping the financial industry.
Background and Context
The Rise of Sustainable Banking
Sustainable banking emerged from the recognition that economic growth and environmental protection should coexist. Recent decades have witnessed heightened awareness about climate change, prompting regulators, investors, and consumers to demand a balance between financial profitability and environmental stewardship. Deutsche Bank’s commitment, seen alongside similar movements by other financial institutions, marks an important pivot from traditional banking models.
Evolution of Regulatory and Investor Demands
Key drivers for sustainable banking include:
- Climate Change Awareness: Governments and investors now require businesses to account for and reduce their carbon emissions.
- Regulatory Demands: New and evolving policies push banks to adopt greener operations. For example, regional regulators often enforce emissions reduction targets.
- Investor Expectations: Investors increasingly integrate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria into their decision-making. Projects like blockchain and environmental impact highlight the intersection between technology and sustainability.
- Market Demand for Green Products: Consumers expect financial institutions to offer environmentally friendly products and services, spurring innovations such as green bonds and sustainable loans.
Deutsche Bank’s comprehensive approach demonstrates an awareness of these trends, setting the stage for industry-wide transformation.
Technology Integration in Sustainability
Digital innovations, including data analytics and blockchain, are essential for measuring and improving sustainability metrics. Deutsche Bank is leveraging these tools to monitor ESG performance and develop digital platforms for green investing. Practices such as sustainable blockchain practices enable improved transparency and efficiency in environmental initiatives.
Core Concepts and Features
Carbon Footprint Reduction Initiatives
Deutsche Bank’s strategy to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 primarily focuses on:
- Green Operations: Transitioning to energy-efficient facilities and renewable energy sources.
- Sustainable Supply Chains: Prioritizing eco-friendly procurement through stringent vendor criteria.
- Innovative Data Analytics: Leveraging digital tools to track carbon emissions, thus enabling precise ESG monitoring.
Below is a table summarizing key sustainability initiatives at Deutsche Bank:
| Initiative | Description | Key Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Green Operations | Investing in energy-efficient and renewable energy-powered facilities | Data Analytics, IoT Sensors |
| Sustainable Supply Chain | Engaging eco-friendly suppliers and circular procurement strategies | Blockchain, Digital Identity |
| Green Financial Products | Issuing green bonds and evaluating credits based on ESG criteria | Financial Modeling, AI Analytics |
| Employee and Stakeholder Engagement | Training programs and collaborative projects to further sustainability | Digital Platforms, Online Education |
Sustainable Finance and Investment
Deutsche Bank has played a pivotal role in channeling investments toward environmentally beneficial projects. The bank endeavours to:
- Issue Green Bonds: Funding projects such as renewable energy infrastructure.
- Incorporate ESG Criteria: Evaluating loan applications with a focus on environmental impact.
- Engage in Stakeholder Collaboration: Promoting sustainability through partnerships with governments, NGOs, and industry bodies.
A bullet list of sustainable finance benefits includes:
- Enhanced Transparency: Better ESG reporting frames trust and accountability.
- Improved Risk Management: Tracking and mitigating environmental risks.
- Increased Investment Attraction: Aligning portfolios to meet investor preferences.
- Broadened Social Impact: Funding projects that yield long-term societal benefits.
Embracing Digital Innovations
Digital transformation remains critical for both service delivery and sustainability. Deutsche Bank is investing in state-of-the-art digital platforms to:
- Enhance ESG Data Analytics: Using cloud computing and big data algorithms to monitor performance.
- Develop Digital Products: Platforms facilitating green investments as well as digital identity verification, as detailed in blockchain and digital identity.
These innovations help bridge traditional banking methods with modern, sustainable practices.
Applications and Use Cases
Case Study 1: Green Bond Issuance
Deutsche Bank’s green bond issuance exemplifies how financial instruments can simultaneously serve investment and environmental goals. These bonds:
- Enable funding for renewable energy projects.
- Provide investors with opportunities to finance environmentally sustainable initiatives.
- Boost the bank’s reputation as a leader in sustainable finance.
Case Study 2: Data-Driven ESG Monitoring
By implementing advanced data analytics tools, Deutsche Bank monitors its sustainability performance more effectively. Applications include:
- Real-Time Carbon Emission Tracking: Using IoT sensors and blockchain to log and verify emissions data.
- Enhanced Reporting Frameworks: Transparent and verifiable ESG metrics allow for improved investor decision-making.
Case Study 3: Digital Platforms for Sustainable Investments
The bank is developing platforms that empower individual investors to support green technology and sustainable projects. These platforms offer:
- User-friendly interfaces for transparent investment opportunities.
- Tools to track environmental impact alongside financial returns.
- Integration with blockchain technology for secure and verifiable transactions.
These cases highlight that sustainable banking is not just about cost reduction—it is also a competitive edge that drives innovation and growth.
Challenges and Limitations
While Deutsche Bank’s sustainable initiatives have broad support, challenges remain:
- Profitability vs. Sustainability: Balancing short-term financial returns with long-term environmental goals can be complex.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating varying global sustainability regulations demands specific, agile strategies. See blockchain regulation for insights on managing diverse regulatory regimes.
- Measuring ESG Metrics: Establishing clear and standardized sustainability metrics poses technical challenges. Enhanced data analytics and digital tools help but remain resource-intensive.
- Technology Gaps: Bridging the divide between legacy systems and modern digital solutions is necessary to facilitate smooth sustainability transitions. This includes addressing concerns highlighted in blockchain technology for open source security.
A bullet list of primary challenges includes:
- Cost Management: High upfront investments.
- Complex Compliance: Differing regulations across regions.
- Metric Standardization: Need for industry-wide, transparent ESG benchmarks.
- Integration Barriers: Legacy systems hindering rapid digital transformation.
Future Outlook and Innovations
Trends in Sustainable Banking
The future of sustainable banking appears promising with several anticipated advancements:
- Circular Economy Support: Banks will increasingly finance projects that promote the reuse and recycling of materials, enhancing a circular economic model.
- Enhanced Transparency: Leveraging blockchain for immutable records of ESG performance will become a standard practice.
- Innovative Product Offerings: New financial products that combine environmental benefits with digital innovation are expected. For instance, emerging solutions in blockchain for open source funding will blend social responsibility with technology.
- Collaborative Industry Efforts: Cross-industry partnerships will further promote sustainable transformation in finance. Collaborative platforms and shared tools are key to this evolution.
Digital Transformation Impact
Digital platforms and blockchain technology will continue to reshape the financial industry:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Integration with decentralized systems is likely to drive a new wave of financial products that are both secure and sustainable.
- Data Analytics Evolution: Improved data analytics tools will allow banks to better predict environmental risks and tailor investment products accordingly.
- Regulatory Technology (RegTech): Emerging regulatory technology will ease the compliance burden by automating many aspects of reporting and data verification.
Industry Collaborations and Research
Collaborative models that involve financial institutions, technology companies, and policymakers are vital. Recent commentary, such as the insightful piece Deutsche Bank's embrace of open source revolutionizing financial technology on Dev.to, highlights the potential of open financing and digital collaboration for sustainable growth. Additionally, discussions on decentralized finance in articles like Arbitrum Token Distribution: A Deep Dive into Decentralized Finance underscore trends that could further empower sustainable banking.
Summary
Deutsche Bank’s journey toward sustainable banking embodies a broader industry imperative—a move to balance economic growth with environmental priorities. By investing in green operations, sustainable financial products, and transforming digital technologies, Deutsche Bank is setting a benchmark for responsible banking. Although challenges remain in terms of regulatory compliance, cost, and technological integration, the bank’s bold initiatives and forward-thinking strategies pave the way for a future where sustainability and profitability coexist.
Key takeaways include:
- Sustainable Finance is Rising: Driven by regulatory pressures, investor expectations, and market demand.
- Digital Innovations are Critical: Technologies such as blockchain and data analytics empower transparent ESG monitoring.
- Collaboration is Key: Industry-wide partnerships and open source funding models help create standardized, effective solutions.
- Future Trends: The rise of DeFi, enhanced transparency through digital platforms, and increased focus on circular economy models signal robust growth and innovation.
For additional insights on sustainable banking and technology integration, check out the Original Article on Deutsche Bank's Sustainable Banking. Other authoritative resources like blockchain and environmental impact and blockchain for open source funding further enrich the discussion.
Furthermore, industry thought leaders continue to contribute to this conversation on various platforms. For instance, articles such as Unveiling a New Era in Open Source Licensing and other discussions hosted on Dev.to provide valuable context regarding the evolution of funding and licensing models which, when combined with sustainable practices, create a comprehensive framework for future banking innovations.
Concluding Thoughts
By aligning financial growth with ecological responsibility, Deutsche Bank is not only reshaping its own operations but is also setting a precedent for the global banking industry. Using a blend of green operations, sustainable supply chains, and cutting-edge data technology, the bank demonstrates that sustainable banking is both viable and essential for long-term prosperity.
In summary:
- Innovative Practices: Adoption of ESG metrics, green bonds, and digital platforms has turned sustainability from a buzzword into actionable strategy.
- Overcoming Challenges: Despite hurdles such as technology gaps and complex regulation, Deutsche Bank's progressive measures offer a replicable model.
- Looking Ahead: Advances in digital technology, collaboration between stakeholders, and evolving financial products will continue to propel sustainable banking into the mainstream.
The path forward is clear: by embracing transparent, data-driven sustainability practices, banks can foster not only their own growth but also contribute to a healthier, more equitable global economy.
Embracing sustainability, leveraging technology, and nurturing transparent financial practices are the pillars that will define the future of banking—and Deutsche Bank is clearly leading the charge.
Additional Resources:
- Blockchain Regulation: Learn more about navigating regulatory challenges in the digital space at blockchain regulation.
- Digital Identity and Security: Explore innovations in digital identity in banking by visiting blockchain and digital identity.
- Open Source Funding Models: Gain further insights into funding models for open source and sustainable projects on Dev.to, where discussions such as Arbitrum Mainnet: A Leap Forward in Ethereum Scalability add perspective to new financing methods.
Through technical innovation, regulatory adaptation, and collaborative industry efforts, sustainable banking is set to revolutionize not only the financial sector but also the global agenda for responsible and inclusive growth.












































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)



























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)

![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)


































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)


.webp?#)





































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)