Choosing the Right Oracle Solution: A Six-Dimensional Framework
Most DeFi builders put a lot of effort into choosing the right chain, finding the best way to attract liquidity, and ensuring their protocol is optimized for performance. Yet, many overlook the importance of selecting the right oracle solution. As long as the price feeds are returning a value, it’s easy to overlook the crucial role oracles play in the system. Then the unexpected strikes. The oracle suddenly feeds an incorrect price for a key asset. Automated trades fire off at distorted values, collateral is miscalculated, and positions are liquidated unexpectedly across lending platforms. A cascade of liquidations and bad trades ripples through the DeFi ecosystem. In a matter of minutes, the oracle—once taken for granted—becomes the center of attention as protocols and users scramble to contain the fallout. The fallout is immediate and painful. Users lose funds, developers are stuck in damage control, and the trust that DeFi protocols rely on takes a hit. The root of the issue? Relying on a centralized oracle—a single point of failure in an otherwise decentralized system. Suddenly, everyone is questioning the reliability of the data driving DeFi, and the vulnerability becomes impossible to ignore. Decentralized oracles step in to restore order. Instead of trusting one source or relying on a bridge for delivery, decentralized oracles integrate natively, aggregate price data from multiple sources, and verify it through a network of validators, reducing the chance of manipulation or failure. DeFi protocols start adopting decentralized oracles to ensure price accuracy and reliability, preventing future catastrophes. It’s a necessary upgrade in the pursuit of trustless finance. With decentralized oracles in place, DeFi is in a stronger position. Now, the chances of a single bad point of failure causing massive liquidations or flash crashes are dramatically reduced. The data feeding into your protocol is more secure, more reliable, and more decentralized—just like the DeFi ecosystem itself. You may not have cared before, but now, decentralized oracles are the backbone that keeps your protocol running smoothly and your users protected. Oracle decentralization is an essential element, but there is much more to consider when choosing an oracle. In this article, we will present you with a framework that you can use when choosing an oracle to power your application, this framework considers 6 important dimensions: The Oracle's Operational History Total Value Secured (TVS) Decentralization Node Operators/ Validators Data Sources Utilized Operating Cost The Oracle's Operational History When selecting a Web3 oracle for your DeFi protocol, evaluating how long the oracle has been securing assets is crucial. Oracles that have operated successfully over time demonstrate resilience and reliability, two essential qualities for securing funds in DeFi. A proven track record shows that the oracle can handle market fluctuations and scalability demands. Ultimately, opting for a well-established oracle helps safeguard your protocol by relying on an experienced data provider with a history of maintaining uptime and accuracy. Total Value Secured (TVS) Total Value Secured or TVS is also a key metric to consider when choosing an oracle. TVS indicates the amount of value reliant on the oracle's data, reflecting trust from other protocols and the market's confidence in its reliability. A high TVS demonstrates that the oracle has successfully secured a large amount of assets without security issues, which can be reassuring for new users aiming to protect funds. By choosing an oracle with substantial TVS, you’re aligning with a provider that has proven its ability to secure high-value assets, reducing the risk to your own protocol’s users. Decentralization Decentralization is essential for Web3 oracles because it aligns with the core philosophy of Web3—trustlessness, transparency, and resilience. While blockchain networks offer strong guarantees of consistency and availability within their ecosystem, the external data sources they rely on do not. APIs, databases, and external websites can be hacked, altered, or even go offline, creating potential vulnerabilities. By using a decentralized network of validators, a Web3 oracle can minimize these risks, ensuring that no single point of failure or manipulation compromises data integrity or availability. Decentralized oracles distribute responsibility across multiple nodes and tap into diverse data sources, making the oracle more robust and secure—a crucial safeguard for protecting funds and maintaining trust in DeFi and other decentralized applications. Node Operators/ Validators The validator network is at the heart of a Web3 oracle's decentralization and security. A critical question to ask when evaluating an oracle is: Who operates the nodes? If the oracle solely relies on nodes operated by its team, there is an inherent risk, even if
Most DeFi builders put a lot of effort into choosing the right chain, finding the best way to attract liquidity, and ensuring their protocol is optimized for performance. Yet, many overlook the importance of selecting the right oracle solution. As long as the price feeds are returning a value, it’s easy to overlook the crucial role oracles play in the system.
Then the unexpected strikes. The oracle suddenly feeds an incorrect price for a key asset. Automated trades fire off at distorted values, collateral is miscalculated, and positions are liquidated unexpectedly across lending platforms. A cascade of liquidations and bad trades ripples through the DeFi ecosystem. In a matter of minutes, the oracle—once taken for granted—becomes the center of attention as protocols and users scramble to contain the fallout.
The fallout is immediate and painful. Users lose funds, developers are stuck in damage control, and the trust that DeFi protocols rely on takes a hit. The root of the issue? Relying on a centralized oracle—a single point of failure in an otherwise decentralized system. Suddenly, everyone is questioning the reliability of the data driving DeFi, and the vulnerability becomes impossible to ignore.
Decentralized oracles step in to restore order. Instead of trusting one source or relying on a bridge for delivery, decentralized oracles integrate natively, aggregate price data from multiple sources, and verify it through a network of validators, reducing the chance of manipulation or failure. DeFi protocols start adopting decentralized oracles to ensure price accuracy and reliability, preventing future catastrophes. It’s a necessary upgrade in the pursuit of trustless finance.
With decentralized oracles in place, DeFi is in a stronger position. Now, the chances of a single bad point of failure causing massive liquidations or flash crashes are dramatically reduced. The data feeding into your protocol is more secure, more reliable, and more decentralized—just like the DeFi ecosystem itself. You may not have cared before, but now, decentralized oracles are the backbone that keeps your protocol running smoothly and your users protected.
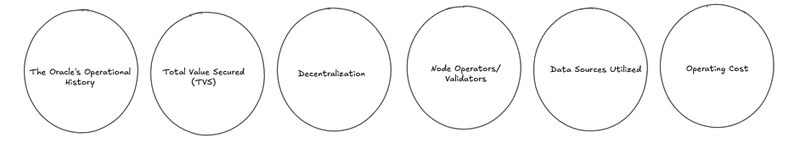
Oracle decentralization is an essential element, but there is much more to consider when choosing an oracle. In this article, we will present you with a framework that you can use when choosing an oracle to power your application, this framework considers 6 important dimensions:
The Oracle's Operational History
Total Value Secured (TVS)
Decentralization
Node Operators/ Validators
Data Sources Utilized
Operating Cost
The Oracle's Operational History
When selecting a Web3 oracle for your DeFi protocol, evaluating how long the oracle has been securing assets is crucial. Oracles that have operated successfully over time demonstrate resilience and reliability, two essential qualities for securing funds in DeFi. A proven track record shows that the oracle can handle market fluctuations and scalability demands. Ultimately, opting for a well-established oracle helps safeguard your protocol by relying on an experienced data provider with a history of maintaining uptime and accuracy.
Total Value Secured (TVS)
Total Value Secured or TVS is also a key metric to consider when choosing an oracle. TVS indicates the amount of value reliant on the oracle's data, reflecting trust from other protocols and the market's confidence in its reliability. A high TVS demonstrates that the oracle has successfully secured a large amount of assets without security issues, which can be reassuring for new users aiming to protect funds. By choosing an oracle with substantial TVS, you’re aligning with a provider that has proven its ability to secure high-value assets, reducing the risk to your own protocol’s users.
Decentralization
Decentralization is essential for Web3 oracles because it aligns with the core philosophy of Web3—trustlessness, transparency, and resilience. While blockchain networks offer strong guarantees of consistency and availability within their ecosystem, the external data sources they rely on do not. APIs, databases, and external websites can be hacked, altered, or even go offline, creating potential vulnerabilities. By using a decentralized network of validators, a Web3 oracle can minimize these risks, ensuring that no single point of failure or manipulation compromises data integrity or availability. Decentralized oracles distribute responsibility across multiple nodes and tap into diverse data sources, making the oracle more robust and secure—a crucial safeguard for protecting funds and maintaining trust in DeFi and other decentralized applications.
Node Operators/ Validators
The validator network is at the heart of a Web3 oracle's decentralization and security. A critical question to ask when evaluating an oracle is: Who operates the nodes? If the oracle solely relies on nodes operated by its team, there is an inherent risk, even if the intentions are sound. Relying exclusively on internal nodes introduces a single point of failure and reduces resilience, as any technical failure, malicious attack, or simple human error could disrupt the service.
In contrast, a decentralized validator network consisting of independent, reputable entities promises high levels of data integrity and network security. With multiple validators, no single entity can compromise or influence the data delivered to smart contracts, reducing the chance of manipulation or error. Validators from varied geographical locations and operating different infrastructure setups add resilience, distributing risk across a diversified network.
Data Sources Utilized
When evaluating oracle networks, it’s essential to scrutinize the quality and integrity of their data sources. Key questions include: What sources does the oracle network rely on? Does it leverage tier-one, reputable data sources with established credibility, high liquidity, and a proven track record? Does it use primary sources, or secondary sources such as data aggregators? For oracle networks using onchain data sources, such as DEXs, are there at least 2-3 reliable data sources—ideally with at least two on the same chain—to enable MEV bots to arbitrage and prevent market manipulation?
High-quality data sources are fundamental to minimizing the risk of inaccuracies or exploitation. Oracle networks must prioritize Tier 1 data sources with healthy liquidity that are resistant to manipulation. In contrast, reliance on low-quality or low-liquidity sources can be prone to market manipulation, undermining the security of the system.
Operating Cost
Lastly, cost is a critical factor when evaluating oracles. By design, oracles are gas-intensive, and during periods of network congestion, fluctuating gas prices can make them prohibitively expensive to operate.
On Ethereum, the annual cost of running an oracle network can exceed $500,000, making high-quality oracles a luxury accessible only to the wealthiest protocols. Even on a Layer 2, the operating cost can be very expensive when you are updating many data feeds, multiple times per day.
One way to reduce costs is by lowering the frequency of oracle updates, but this comes at the expense of accuracy. While it may provide short-term relief, sacrificing data freshness for cost is a short-sighted approach that fails to scale.
An effective oracle solution should strike a balance, employing mechanisms that reduce costs without compromising data freshness. Reliable and cost-efficient oracles ensure both performance and accessibility at scale.
Final Thoughts
As DeFi continues to mature, the importance of carefully selecting an oracle cannot be overstated. An oracle might seem like just another tool, but it holds the power to make or break your protocol. This six-dimensional framework offers a comprehensive approach to making informed decisions when assessing an oracle solution.
By treating your oracle provider as a core component rather than an afterthought, you lay the groundwork for robust, scalable, and secure operations that can withstand the test of time and market volatility.











































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)



























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)

































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)





































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)