A2A Protocol Development Guide
Overview The A2A (Agent-to-Agent) protocol is a JSON-RPC based communication protocol designed for agent interactions. This guide provides comprehensive instructions for developing both server and client components that conform to the A2A protocol specification. Table of Contents Protocol Basics Server Implementation Client Implementation Running the Coder Demo Protocol Basics The A2A protocol is built on top of JSON-RPC 2.0 and defines a set of methods for agent communication. Key components include: Message Structure All A2A messages follow the JSON-RPC 2.0 format with the following base structure: interface JSONRPCMessage { jsonrpc?: "2.0"; id?: number | string | null; method?: string; params?: unknown; result?: unknown; error?: JSONRPCError; } Protocol Flow The following sequence diagram illustrates the main interaction flow of the A2A protocol: Core Methods The protocol supports several core methods: tasks/send: Send a task message to an agent tasks/get: Retrieve task status tasks/cancel: Cancel a running task tasks/pushNotification/set: Configure push notifications for a task tasks/pushNotification/get: Get push notification configuration tasks/resubscribe: Resubscribe to task updates tasks/sendSubscribe: Send a task message and subscribe to updates Task States Tasks can be in one of the following states: submitted working input-required completed canceled failed unknown Server Implementation Core Components The server implementation consists of several key components: Server (server.ts): Main server implementation handling HTTP requests Handler (handler.ts): Request handler for processing A2A protocol messages Store (store.ts): Task storage and management Utils (utils.ts): Utility functions Error Handling (error.ts): Error definitions and handling Basic Usage (Conceptual) import { A2AServer, InMemoryTaskStore, TaskContext, TaskYieldUpdate, } from "./index"; // Assuming imports from the server package // 1. Define your agent's logic as a TaskHandler async function* myAgentLogic( context: TaskContext ): AsyncGenerator { console.log(`Handling task: ${context.task.id}`); yield { state: "working", message: { role: "agent", parts: [{ text: "Processing..." }] }, }; // Simulate work... await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000)); if (context.isCancelled()) { console.log("Task cancelled!"); yield { state: "canceled" }; return; } // Yield an artifact yield { name: "result.txt", mimeType: "text/plain", parts: [{ text: `Task ${context.task.id} completed.` }], }; // Yield final status yield { state: "completed", message: { role: "agent", parts: [{ text: "Done!" }] }, }; } // 2. Create and start the server const store = new InMemoryTaskStore(); // Or new FileStore() const server = new A2AServer(myAgentLogic, { taskStore: store }); server.start(); // Starts listening on default port 41241 console.log("A2A Server started."); The server will start on the configured port (default: 3000). Client Implementation Key Features: JSON-RPC Communication: Handles sending requests and receiving responses (both standard and streaming via Server-Sent Events) according to the JSON-RPC 2.0 specification. A2A Methods: Implements standard A2A methods like sendTask, sendTaskSubscribe, getTask, cancelTask, setTaskPushNotification, getTaskPushNotification, and resubscribeTask. Error Handling: Provides basic error handling for network issues and JSON-RPC errors. Streaming Support: Manages Server-Sent Events (SSE) for real-time task updates (sendTaskSubscribe, resubscribeTask). Extensibility: Allows providing a custom fetch implementation for different environments (e.g., Node.js). Basic Usage import { A2AClient, Task, TaskQueryParams, TaskSendParams } from "./client"; // Import necessary types import { v4 as uuidv4 } from "uuid"; // Example for generating task IDs const client = new A2AClient("http://localhost:41241"); // Replace with your server URL async function run() { try { // Send a simple task (pass only params) const taskId = uuidv4(); const sendParams: TaskSendParams = { id: taskId, message: { role: "user", parts: [{ text: "Hello, agent!" }] }, }; // Method now returns Task | null directly const taskResult: Task | null = await client.sendTask(sendParams); console.log("Send Task Result:", taskResult); // Get task status (pass only params) const getParams: TaskQueryParams = { id: taskId }; // Method now returns Task | null directly const getTaskResult: Task | null = await client.getTask(getParams); console.log("Get Task Result:", getTaskResult); } catch (error) { console.error("A2A Client Error:", error); } } run(); Streaming Usage
Overview
The A2A (Agent-to-Agent) protocol is a JSON-RPC based communication protocol designed for agent interactions. This guide provides comprehensive instructions for developing both server and client components that conform to the A2A protocol specification.
Table of Contents
- Protocol Basics
- Server Implementation
- Client Implementation
- Running the Coder Demo
Protocol Basics
The A2A protocol is built on top of JSON-RPC 2.0 and defines a set of methods for agent communication. Key components include:
Message Structure
All A2A messages follow the JSON-RPC 2.0 format with the following base structure:
interface JSONRPCMessage {
jsonrpc?: "2.0";
id?: number | string | null;
method?: string;
params?: unknown;
result?: unknown;
error?: JSONRPCError;
}
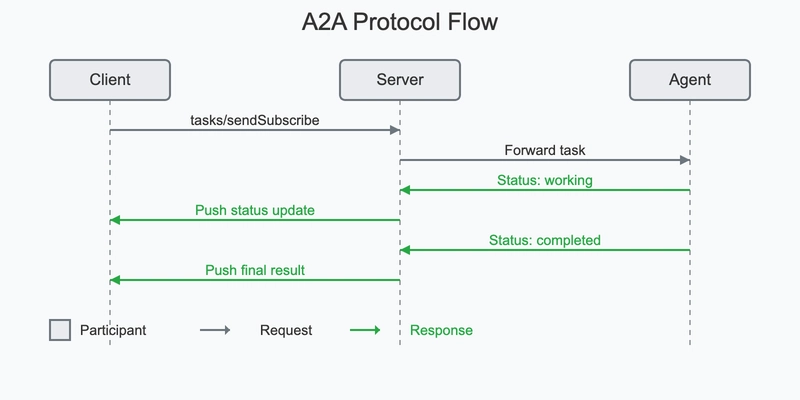
Protocol Flow
The following sequence diagram illustrates the main interaction flow of the A2A protocol:
Core Methods
The protocol supports several core methods:
-
tasks/send: Send a task message to an agent -
tasks/get: Retrieve task status -
tasks/cancel: Cancel a running task -
tasks/pushNotification/set: Configure push notifications for a task -
tasks/pushNotification/get: Get push notification configuration -
tasks/resubscribe: Resubscribe to task updates -
tasks/sendSubscribe: Send a task message and subscribe to updates
Task States
Tasks can be in one of the following states:
submittedworkinginput-requiredcompletedcanceledfailedunknown
Server Implementation
Core Components
The server implementation consists of several key components:
- Server (server.ts): Main server implementation handling HTTP requests
- Handler (handler.ts): Request handler for processing A2A protocol messages
- Store (store.ts): Task storage and management
- Utils (utils.ts): Utility functions
- Error Handling (error.ts): Error definitions and handling
Basic Usage (Conceptual)
import {
A2AServer,
InMemoryTaskStore,
TaskContext,
TaskYieldUpdate,
} from "./index"; // Assuming imports from the server package
// 1. Define your agent's logic as a TaskHandler
async function* myAgentLogic(
context: TaskContext
): AsyncGenerator<TaskYieldUpdate> {
console.log(`Handling task: ${context.task.id}`);
yield {
state: "working",
message: { role: "agent", parts: [{ text: "Processing..." }] },
};
// Simulate work...
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
if (context.isCancelled()) {
console.log("Task cancelled!");
yield { state: "canceled" };
return;
}
// Yield an artifact
yield {
name: "result.txt",
mimeType: "text/plain",
parts: [{ text: `Task ${context.task.id} completed.` }],
};
// Yield final status
yield {
state: "completed",
message: { role: "agent", parts: [{ text: "Done!" }] },
};
}
// 2. Create and start the server
const store = new InMemoryTaskStore(); // Or new FileStore()
const server = new A2AServer(myAgentLogic, { taskStore: store });
server.start(); // Starts listening on default port 41241
console.log("A2A Server started.");
The server will start on the configured port (default: 3000).
Client Implementation
Key Features:
- JSON-RPC Communication: Handles sending requests and receiving responses (both standard and streaming via Server-Sent Events) according to the JSON-RPC 2.0 specification.
-
A2A Methods: Implements standard A2A methods like
sendTask,sendTaskSubscribe,getTask,cancelTask,setTaskPushNotification,getTaskPushNotification, andresubscribeTask. - Error Handling: Provides basic error handling for network issues and JSON-RPC errors.
-
Streaming Support: Manages Server-Sent Events (SSE) for real-time task updates (
sendTaskSubscribe,resubscribeTask). -
Extensibility: Allows providing a custom
fetchimplementation for different environments (e.g., Node.js).
Basic Usage
import { A2AClient, Task, TaskQueryParams, TaskSendParams } from "./client"; // Import necessary types
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from "uuid"; // Example for generating task IDs
const client = new A2AClient("http://localhost:41241"); // Replace with your server URL
async function run() {
try {
// Send a simple task (pass only params)
const taskId = uuidv4();
const sendParams: TaskSendParams = {
id: taskId,
message: { role: "user", parts: [{ text: "Hello, agent!" }] },
};
// Method now returns Task | null directly
const taskResult: Task | null = await client.sendTask(sendParams);
console.log("Send Task Result:", taskResult);
// Get task status (pass only params)
const getParams: TaskQueryParams = { id: taskId };
// Method now returns Task | null directly
const getTaskResult: Task | null = await client.getTask(getParams);
console.log("Get Task Result:", getTaskResult);
} catch (error) {
console.error("A2A Client Error:", error);
}
}
run();
Streaming Usage
import {
A2AClient,
TaskStatusUpdateEvent,
TaskArtifactUpdateEvent,
TaskSendParams, // Use params type directly
} from "./client"; // Adjust path if necessary
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from "uuid";
const client = new A2AClient("http://localhost:41241");
async function streamTask() {
const streamingTaskId = uuidv4();
try {
console.log(`\n--- Starting streaming task ${streamingTaskId} ---`);
// Construct just the params
const streamParams: TaskSendParams = {
id: streamingTaskId,
message: { role: "user", parts: [{ text: "Stream me some updates!" }] },
};
// Pass only params to the client method
const stream = client.sendTaskSubscribe(streamParams);
// Stream now yields the event payloads directly
for await (const event of stream) {
// Type guard to differentiate events based on structure
if ("status" in event) {
// It's a TaskStatusUpdateEvent
const statusEvent = event as TaskStatusUpdateEvent; // Cast for clarity
console.log(
`[${streamingTaskId}] Status Update: ${statusEvent.status.state} - ${
statusEvent.status.message?.parts[0]?.text ?? "No message"
}`
);
if (statusEvent.final) {
console.log(`[${streamingTaskId}] Stream marked as final.`);
break; // Exit loop when server signals completion
}
} else if ("artifact" in event) {
// It's a TaskArtifactUpdateEvent
const artifactEvent = event as TaskArtifactUpdateEvent; // Cast for clarity
console.log(
`[${streamingTaskId}] Artifact Update: ${
artifactEvent.artifact.name ??
`Index ${artifactEvent.artifact.index}`
} - Part Count: ${artifactEvent.artifact.parts.length}`
);
// Process artifact content (e.g., artifactEvent.artifact.parts[0].text)
} else {
console.warn("Received unknown event structure:", event);
}
}
console.log(`--- Streaming task ${streamingTaskId} finished ---`);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Error during streaming task ${streamingTaskId}:`, error);
}
}
streamTask();
Running the Coder Demo
The Coder Demo is an example implementation of an A2A agent that can process code-related tasks.
Setup
- Install dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/sing1ee/a2a-agent-coder.git
#or
git clone git@github.com:sing1ee/a2a-agent-coder.git
bun install
- Ensure you have the required environment variables:
# set .env first
export $(cat .env | xargs)
Running the Demo
- Start the a2a server (requires Node.js environment):
bun run agents:coder
- Start the a2a client:
bun run a2a:cli
# result
$ bun x tsx src/cli.ts
A2A Terminal Client
Agent URL: http://localhost:41241
Attempting to fetch agent card from: http://localhost:41241/.well-known/agent.json
✓ Agent Card Found:
Name: Coder Agent
Description: An agent that generates code based on natural language instructions and streams file outputs.
Version: 0.0.1
Starting Task ID: a1a608b3-3015-4404-a83f-6ccc05083761
Enter messages, or use '/new' to start a new task.
Coder Agent > You: implement binary search
Sending...
Coder Agent [4:28:00 PM]: ⏳ Status: working
Part 1: 









































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)

















































































































![[DEALS] The All-in-One Microsoft Office Pro 2019 for Windows: Lifetime License + Windows 11 Pro Bundle (89% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)





































![Is this too much for a modular monolith system? [closed]](https://i.sstatic.net/pYL1nsfg.png)






















































































































_Andreas_Prott_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)




























































































![What features do you get with Gemini Advanced? [April 2025]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/02/gemini-advanced-cover.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)













![Apple Shares Official Trailer for 'Long Way Home' Starring Ewan McGregor and Charley Boorman [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97069/97069/97069-640.jpg)
![Apple Watch Series 10 Back On Sale for $299! [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96657/96657/96657-640.jpg)
![EU Postpones Apple App Store Fines Amid Tariff Negotiations [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97068/97068/97068-640.jpg)
![Apple Slips to Fifth in China's Smartphone Market with 9% Decline [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97065/97065/97065-640.jpg)