Why Browserless (Scrapeless scraping browser) can be the infrastructure of your AI Agent
Intro In the context of the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, AI agents are playing an increasingly important role in automating tasks, especially those that involve retrieving web information. For such tasks, efficiently and accurately scraping and parsing web content presents a significant challenge. In this article, we will explore the recently released Browser Use and Scrapeless Scraping Browser and their impact on AI agents. PART1.Browser Use: Enable AI agents to efficiently parse web pages On March 23, 2025, the startup Browser Use announced the completion of a $17 million funding round, led by Felicis Ventures with support from several well-known investment firms. Browser Use is an AI-driven browser automation agent capable of efficiently parsing web content and helping AI agents automate a variety of online tasks. The company was founded by Gregor Žunič and Magnus Müller, who initially developed a prototype within four days and successfully launched it on Hacker News, gaining widespread attention. The core technology of Browser Use is transforming each website into structured text, helping AI agents better understand and interact with webpages without relying on costly and inefficient computer vision methods. This approach allows AI agents to parse webpages as if handling databases, improving task execution efficiency and addressing common issues like IP bans and captchas. With proxy rotation and persistent session support, Browser Use ensures the stability and efficiency of tasks, enhancing the web browsing speed and accuracy of AI agents. Of course, simply enabling AI agents to "understand webpages" is not enough. In reality, websites are constantly changing and implementing various anti-scraping measures such as IP blocking, captcha triggers, and user behavior detection, creating significant obstacles for AI agents when performing tasks. While Browser Use addresses some of these issues through proxy rotation and persistent sessions, AI agents may still face challenges like fingerprint detection, dynamic rendering, and TLS anti-detection in more complex scenarios. This is where the Scrapeless Scraping Browser comes into play. Additionally, it is better suited for large-scale scraping and automation tasks, supporting parallel scraping and efficient management of large data requests to ensure task stability and efficiency. PART2.Browserless (Scrapeless Scraping Browser): The Ideal Infrastructure for AI Agents In the previous section, we explored how Browser Use helps AI agents handle web tasks more effectively through efficient webpage parsing and information structuring. However, to truly enable AI agents to perform various online tasks in a stable and intelligent manner, the Scrapeless Scraping Browser offers a more advanced and comprehensive infrastructure. PART 2.1 How to Achieve Browser Use's Capabilities and Enhance Data Scraping Performance with Scraping Browser Before diving into a detailed comparison between Scraping Browser and Browser Use, it's important to first understand their respective functionalities and technical implementations. While both involve browser automation and data scraping, they differ significantly in many aspects and are suitable for different use cases. In this section, we will analyze the differences between the two in terms of functionality, technical implementation, use cases, and ease of use, and explore how Scraping Browser can achieve the existing capabilities of Browser Use. 1.1 Functionality Overview Browser Use: As a Python library focused on automation, Browser Use is primarily aimed at developers and provides AI agents with browser control to facilitate automated tasks. It offers users a simple API that makes it easy to navigate, interact with, and scrape data from websites. Its core strength lies in its flexibility, making it ideal for developers who wish to perform customized browser operations. Scraping browser: In comparison, Scraping BrowserScraping Browser is more focused on offering efficient web scraping solutions, especially when it comes to bypassing anti-scraping technologies. With cloud fingerprinting technology, Scraping Browser simulates real user behavior to minimize the risk of being detected as a bot by target websites. Its functionality is better suited for large-scale data scraping, especially in scenarios involving complex anti-scraping measures. 1.2 Technical Implementation Next, we’ll take a deeper look at the technical differences between the two: Browser Use: Browser Use relies on powerful browser automation frameworks (such as Playwright) to perform browser operations locally or on the cloud. Its technical implementation is highly flexible, making it suitable for developers with custom needs. Users can highly customize operations according to specific requirements, such as simulating different user behaviors
Intro
In the context of the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, AI agents are playing an increasingly important role in automating tasks, especially those that involve retrieving web information. For such tasks, efficiently and accurately scraping and parsing web content presents a significant challenge. In this article, we will explore the recently released Browser Use and Scrapeless Scraping Browser and their impact on AI agents.
PART1.Browser Use: Enable AI agents to efficiently parse web pages
On March 23, 2025, the startup Browser Use announced the completion of a $17 million funding round, led by Felicis Ventures with support from several well-known investment firms. Browser Use is an AI-driven browser automation agent capable of efficiently parsing web content and helping AI agents automate a variety of online tasks. The company was founded by Gregor Žunič and Magnus Müller, who initially developed a prototype within four days and successfully launched it on Hacker News, gaining widespread attention.
The core technology of Browser Use is transforming each website into structured text, helping AI agents better understand and interact with webpages without relying on costly and inefficient computer vision methods. This approach allows AI agents to parse webpages as if handling databases, improving task execution efficiency and addressing common issues like IP bans and captchas. With proxy rotation and persistent session support, Browser Use ensures the stability and efficiency of tasks, enhancing the web browsing speed and accuracy of AI agents.
Of course, simply enabling AI agents to "understand webpages" is not enough. In reality, websites are constantly changing and implementing various anti-scraping measures such as IP blocking, captcha triggers, and user behavior detection, creating significant obstacles for AI agents when performing tasks.
While Browser Use addresses some of these issues through proxy rotation and persistent sessions, AI agents may still face challenges like fingerprint detection, dynamic rendering, and TLS anti-detection in more complex scenarios.
This is where the Scrapeless Scraping Browser comes into play. Additionally, it is better suited for large-scale scraping and automation tasks, supporting parallel scraping and efficient management of large data requests to ensure task stability and efficiency.
PART2.Browserless (Scrapeless Scraping Browser): The Ideal Infrastructure for AI Agents
In the previous section, we explored how Browser Use helps AI agents handle web tasks more effectively through efficient webpage parsing and information structuring. However, to truly enable AI agents to perform various online tasks in a stable and intelligent manner, the Scrapeless Scraping Browser offers a more advanced and comprehensive infrastructure.
PART 2.1 How to Achieve Browser Use's Capabilities and Enhance Data Scraping Performance with Scraping Browser
Before diving into a detailed comparison between Scraping Browser and Browser Use, it's important to first understand their respective functionalities and technical implementations. While both involve browser automation and data scraping, they differ significantly in many aspects and are suitable for different use cases. In this section, we will analyze the differences between the two in terms of functionality, technical implementation, use cases, and ease of use, and explore how Scraping Browser can achieve the existing capabilities of Browser Use.
1.1 Functionality Overview
- Browser Use:
As a Python library focused on automation, Browser Use is primarily aimed at developers and provides AI agents with browser control to facilitate automated tasks. It offers users a simple API that makes it easy to navigate, interact with, and scrape data from websites.
Its core strength lies in its flexibility, making it ideal for developers who wish to perform customized browser operations.
- Scraping browser:
In comparison, Scraping BrowserScraping Browser is more focused on offering efficient web scraping solutions, especially when it comes to bypassing anti-scraping technologies. With cloud fingerprinting technology, Scraping Browser simulates real user behavior to minimize the risk of being detected as a bot by target websites.
Its functionality is better suited for large-scale data scraping, especially in scenarios involving complex anti-scraping measures.
1.2 Technical Implementation
Next, we’ll take a deeper look at the technical differences between the two:
- Browser Use:
Browser Use relies on powerful browser automation frameworks (such as Playwright) to perform browser operations locally or on the cloud. Its technical implementation is highly flexible, making it suitable for developers with custom needs.
Users can highly customize operations according to specific requirements, such as simulating different user behaviors or controlling the browser to perform specific tasks.
- Scraping browser:
Unlike Browser Use, Scraping Browser uses cloud services and fingerprint technology, employing methods like dynamic IP rotation and user agent masking to ensure simulated user behavior appears more realistic. This allows it to bypass target websites' anti-scraping measures, resulting in more efficient data scraping.
Scraping Browser’s technical advantage lies in its ability to support large-scale scraping tasks, handle complex anti-scraping mechanisms, and ensure successful data scraping even when frequently changing IPs and user agents.
Don’t let complex anti-scraping measures slow you down! Log in now and use Scrapeless Scraping Browser to enhance your web scraping tasks.
1.3 Use Cases
The differences in functionality naturally lead to different use cases:
- Browser Use:
Browser Use is more suitable for developers performing small-scale, customized automation tasks, or in scenarios where AI agents are involved. For tasks that don't require large-scale, high-frequency data scraping, Browser Use offers sufficient flexibility and customization options.
For example, developers might use Browser Use to automate data extraction tasks from specific websites or create AI tools that integrate browser control.
- Scraping browser:
Scraping Browser shines in its adaptability, particularly in large-scale data scraping tasks that involve overcoming complex anti-scraping technologies. For tasks requiring frequent access and scraping of vast amounts of data, Scraping Browser is undoubtedly the better choice.
It is particularly useful for high-frequency, large-scale scraping tasks, such as e-commerce websites or social media data scraping, where it can effectively bypass stringent anti-scraping measures.
1.4 Ease of Use
While both tools offer automation features, there are notable differences in terms of ease of use:
- Browser Use: As a Python library aimed at developers, Browser Use provides extensive documentation, examples, and tutorials to help developers get started quickly. However, it requires users to have a certain level of programming skills to customize operations as needed.
For developers with programming experience, Browser Use's flexibility makes it an attractive choice.
- Scraping browser:
Scraping Browser typically offers a more comprehensive service where users don’t need to focus on technical details and can focus more on data scraping itself. It provides a more intuitive user interface and better usability, especially for those without programming skills.
Since it uses cloud fingerprinting technology behind the scenes, users only need to configure scraping tasks without diving deep into the technical implementation.
In summary, Browser Use is more flexible and suited for developers looking to perform customized automation tasks, while Scraping Browser focuses on efficient and secure data scraping, particularly when dealing with anti-scraping technologies. The choice of which tool to use depends on specific needs and use cases.
Start scraping smarter today! No more hassle with complex webpage parsing—use Scrapeless' scraping browser to make your AI agent tasks faster and more accurate. Log in now and begin your journey: Login Here
Overall, Browser Use is more flexible and suitable for developers to perform personalized automation operations, while Cloud Fingerprint Crawling Browser focuses on efficient and secure data capture, especially when dealing with anti-crawling technology. The choice of which tool to use depends on specific needs and usage scenarios.
PART2.2 Scraping Browser vs. Browser Use
In this section, we explore how Scraping Browser achieves the existing capabilities of Browser Use.
Optimize web scraping and boost your productivity! Let Scrapeless' scraping browser become the backbone of your AI agent, solving web scraping challenges. Log in now and experience its powerful features: Login Here
1. Strong anti-blockade capability
For most network tasks, especially data scraping tasks, preventing blocking and bypassing anti-crawling mechanisms is crucial. Scrapeless Scraping Browser provides multiple layers of protection in this regard.
- Proxy IP pool and auto-rotation
Scrapeless Scraping Browser provides a richer proxy IP pool that can automatically rotate IPs to avoid being blocked due to frequent requests from the same IP. This dynamic IP switching method greatly reduces the probability of being detected by the target website for crawlers.
- Efficient Captcha unlocking technology
Many websites employ CAPTCHA mechanisms such as reCAPTCHA or Cloudflare Turnstile Challenge to block automated tools. Scrapeless Scraping Browser has strong CAPTCHA handling capabilities, using intelligent algorithms and automated unlocking techniques to quickly bypass these challenges, ensuring that AI agents can continue scraping data without interruptions due to CAPTCHAs. This makes Scrapeless Scraping Browser highly effective and stable when working with highly secure websites.
2. Highly personified interactive simulation
To ensure that AI agents can browse a web like a real user, the Scrapeless Scraping Browser integrates multiple, anthropomorphic interaction simulation techniques.
- Dynamic Fingerprint Obfuscation Technology
This technology allows Scraping Browser to simulate user behaviors such as mouse tracks, scrolling, clicking, etc. at the Chrome kernel level , thus avoiding being recognized as an automation tool by the target website. In this way, Scrapeless Scraping Browser makes requests from AI agents appear almost identical to the behavior of ordinary users, effectively bypassing common anti-crawling strategies.
- Support dynamic rendering of JavaScript-heavy websites
Many modern websites rely on JavaScript to dynamically load content, which poses challenges to traditional crawlers. Scrapeless Scraping Browser can handle JavaScript-heavy websites, ensuring that AI agents can access all dynamically rendered content on the webpage, not just static HTML pages. This enables it to crawl more complex webpage data and meet the needs of modern internet.
3. Advanced anti-detection mechanism
Scrapeless Scraping Browser uses various technologies to hide the crawling features of AI agents, avoiding recognition and blocking by target websites.
- TLS Fingerprint Forgery Technology
Through TLS fingerprint forgery, Scrapeless Scraping Browser can disguise itself as a normal browser access, avoiding the detection of crawler tools by target websites. TLS (Transport Layer Security Protocol) fingerprint forgery is an advanced security technology that simulates the unique identity of the browser during connection, increasing the anti-interference ability of anti-crawling technology.
- Real browser environment for anti-detection
In order to avoid being recognized by crawlers, Scrapeless Scraping Browser makes the browser environment as close as possible to the behavior of real users, using a real browser environment to perform tasks. Unlike crawlers that use Computer Vision and image recognition, this method can effectively reduce the risk of recognition and interception, ensuring that requests from AI agents are not marked as malicious by the target website.
4. Real-time data statistics and session management
Scrapeless Scraping Browser introduces real-time data statistics to ensure efficient and controllable Data Acquisition process. Users can track session status in real-time, view the progress of each browser session (such as running, success, failure), and intuitively grasp the status of task execution to ensure smooth data capture.
In addition, Scrapeless has enhanced session management capabilities, including:
- Chat list and records: Users can easily view historical and current conversations, and easily manage and monitor all conversations.
- Session stop function: Through the dashboard, users can directly terminate running sessions without manual intervention, greatly improving operational efficiency and flexibility.
Start scraping smarter today! No more hassle with complex webpage parsing—use Scrapeless' scraping browser to make your AI agent tasks faster and more accurate. Log in now and begin your journey: Login Here
PART 2.3 Use Cases of Scraping Browser
To more clearly demonstrate the powerful capabilities of Scraping Browser, let's look at a few typical use cases and how AI agents enable more intelligent data scraping.
1. E-Commerce Website Data Collection and Price Monitoring
Use Case: Cross-border e-commerce companies need to regularly monitor product prices and stock information on competitor websites to optimize their own pricing strategies.
Challenges: The target website employs strict anti-scraping mechanisms, including dynamic IP blocking, CAPTCHA detection, and JavaScript-rendered pages.
Solution:
- Dynamic IP Rotation: Use Scraping Browser’s proxy pool functionality to regularly change IPs and avoid being blocked.
- Advanced Fingerprint Simulation: Implement dynamic fingerprint obfuscation to make the browsing behavior resemble that of a real user.
- Automatic JavaScript Parsing: Ensure the scraped pages include all dynamically rendered content.
Whether you're monitoring eCommerce prices or collecting real-time travel data, Scrapeless is the solution you need. Log in now and streamline your data scraping with advanced automation.
2. Travel Industry Information Scraping and Price Comparison Analysis
Use Case: A travel booking platform wants to scrape real-time price information from multiple airline and hotel websites to provide the best booking recommendations.
Challenges: Many travel websites use dynamic loading technologies and have strict anti-scraping measures, such as TLS fingerprint detection and CAPTCHA validation.
Solution:
- TLS Fingerprint Spoofing: Scraping Browser simulates TLS fingerprints from different devices and browsers, making requests appear to come from real users.
- Intelligent CAPTCHA Solving: Use Scraping Browser’s CAPTCHA solution to automatically handle CAPTCHAs during login and query processes.
- Parallel Scraping: Improve the speed of data collection through multithreading and distributed architecture.
- AI Agent Predictive Analysis: Combine AI Agent to predict price trends and provide users with more accurate booking recommendations.
PART3. Bonus Tip: Bypass Cloudflare using Scraping Browser and Puppeteer
We firmly protect the privacy of the website. All data in this blog is public and is only used as a demonstration of the crawling process. We do not save any information and data.
Scrapeless requires puppeteer-core, a Puppeteer version that doesn't download the Chrome binary. So, ensure you install it:
npm install puppeteer-core
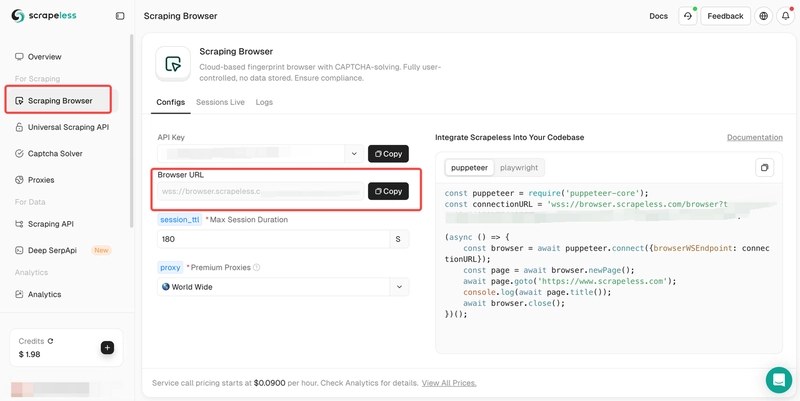
Step 1. Sign up for Scrapeless, click API Key Management > Create API Key to create your Scrapeless API Key.
Sign up for Scrapeless and get a free trial. If you have any questions, you can also contact Liam via Discord
Step 2. Then, go to Scraping Browser and copy your Browser URL.
Integrate the copied browser URL into your Puppeteer script like so:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer-core');
const connectionURL = 'wss://browser.scrapeless.com/browser?token=&session_ttl=180&proxy_country=ANY';
(async () => {// set up browser environmentconst browser = await puppeteer.connect({browserWSEndpoint: connectionURL,
});
// create a new pageconst page = await browser.newPage();
// navigate to a URLawait page.goto('https://www.scrapingcourse.com/cloudflare-challenge', {waitUntil: 'networkidle0',
});
// wait for the challenge to resolveawait new Promise(function (resolve) {setTimeout(resolve, 10000);
});
//take page screenshotawait page.screenshot({ path: 'screenshot.png' });// close the browser instanceawait browser.close();
})();
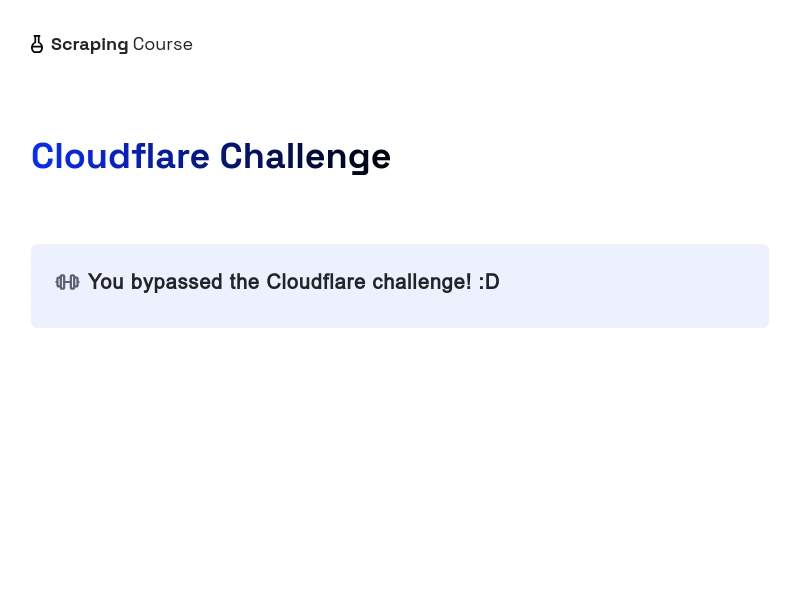
You need to replace https://www.scrapingcourse.com/cloudflare-challenge with any website with cloudflare-challenge; Also replace your Scrapeless API Key in the token part.
The above code accesses and screenshots the protected page. See the result below:
Congratulations












































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)









































































































.png?#)

































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)




































































































![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)