What Is Network Segmentation?
In today’s digital age, organizations face a constant barrage of cyber threats. A single point of entry can compromise an entire infrastructure if the network is left wide open. That’s why network segmentation has become a critical defense mechanism. By dividing the network into isolated sections, companies can contain security breaches, reduce risk, and enhance operational control. What Is Network Segmentation? Network segmentation is the strategic practice of dividing a computer network into multiple smaller subnetworks or zones. Each segment functions independently with its own set of rules, access controls, and monitoring. This setup helps limit internal communication between systems, making it much harder for cyber attackers to move laterally within the network after breaching one part. Imagine a company office divided into departments, each with its own access restrictions—finance, HR, and IT operate independently, ensuring sensitive data isn’t freely accessible. Similarly, segmentation prevents unrestricted communication across the digital environment, reducing the overall attack surface. Why Segmentation Matters Contained Risk and Threat Isolation When a threat occurs, segmentation helps isolate the affected area, preventing malware or unauthorized access from spreading across the entire infrastructure. Optimized Network Performance Segmented environments reduce unnecessary traffic by limiting data broadcasts to their own segment. This results in better bandwidth utilization and faster response times. Compliance Made Easier Many regulatory frameworks—including HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR—require organizations to enforce strict access controls. Segmentation supports these compliance efforts by ensuring sensitive data stays within secured zones. Easier Network Management With segmentation, managing access, applying security updates, and troubleshooting issues becomes more targeted and efficient. Implementation Approaches Physical Segmentation: Uses separate hardware components (like switches and firewalls) to build isolated zones. Logical Segmentation: Achieved through technologies such as VLANs, subnets, and Software-Defined Networking (SDN), enabling segmentation within a shared physical infrastructure. Who Needs Network Segmentation? Any organization dealing with sensitive information, cloud infrastructure, or complex IT operations will benefit from segmentation. From startups to large enterprises, isolating critical assets and securing high-value systems should be a priority. Final Thought Network segmentation is more than just a security measure—it’s a foundational strategy for risk reduction, regulatory compliance, and IT efficiency. In a world where breaches are inevitable, segmentation ensures threats stay contained, systems remain resilient, and business continuity is preserved.


In today’s digital age, organizations face a constant barrage of cyber threats. A single point of entry can compromise an entire infrastructure if the network is left wide open. That’s why network segmentation has become a critical defense mechanism. By dividing the network into isolated sections, companies can contain security breaches, reduce risk, and enhance operational control.
What Is Network Segmentation?
Network segmentation is the strategic practice of dividing a computer network into multiple smaller subnetworks or zones. Each segment functions independently with its own set of rules, access controls, and monitoring. This setup helps limit internal communication between systems, making it much harder for cyber attackers to move laterally within the network after breaching one part.
Imagine a company office divided into departments, each with its own access restrictions—finance, HR, and IT operate independently, ensuring sensitive data isn’t freely accessible. Similarly, segmentation prevents unrestricted communication across the digital environment, reducing the overall attack surface.
Why Segmentation Matters
Contained Risk and Threat Isolation
When a threat occurs, segmentation helps isolate the affected area, preventing malware or unauthorized access from spreading across the entire infrastructure.
Optimized Network Performance
Segmented environments reduce unnecessary traffic by limiting data broadcasts to their own segment. This results in better bandwidth utilization and faster response times.
Compliance Made Easier
Many regulatory frameworks—including HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR—require organizations to enforce strict access controls. Segmentation supports these compliance efforts by ensuring sensitive data stays within secured zones.
Easier Network Management
With segmentation, managing access, applying security updates, and troubleshooting issues becomes more targeted and efficient.
Implementation Approaches
- Physical Segmentation: Uses separate hardware components (like switches and firewalls) to build isolated zones.
- Logical Segmentation: Achieved through technologies such as VLANs, subnets, and Software-Defined Networking (SDN), enabling segmentation within a shared physical infrastructure.
Who Needs Network Segmentation?
Any organization dealing with sensitive information, cloud infrastructure, or complex IT operations will benefit from segmentation. From startups to large enterprises, isolating critical assets and securing high-value systems should be a priority.
Final Thought
Network segmentation is more than just a security measure—it’s a foundational strategy for risk reduction, regulatory compliance, and IT efficiency. In a world where breaches are inevitable, segmentation ensures threats stay contained, systems remain resilient, and business continuity is preserved.










































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)










































































































































































































![GrandChase tier list of the best characters available [April 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33057-1637756796/grandchase-ios-android-3rd-anniversary.jpg?#)










































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
























.webp?#)
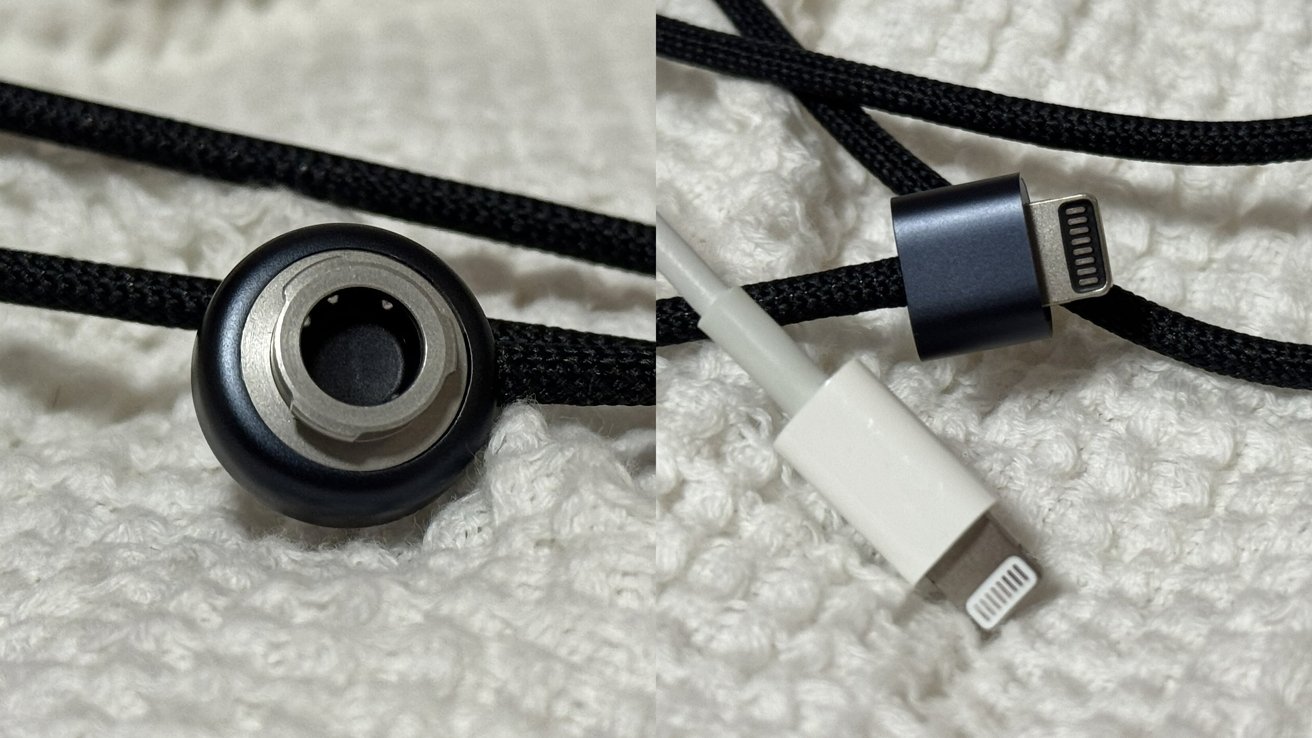





































































































![New Beats USB-C Charging Cables Now Available on Amazon [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97060/97060/97060-640.jpg)

![Apple M4 13-inch iPad Pro On Sale for $200 Off [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97056/97056/97056-640.jpg)