Populating a RAG with data from enterprise documents repositories for Generative AI
Ingesting data from OneDrive into Milvus in order to use with generative ai. Image courtesy Milvus.io Introduction and motivation In a recent project we help our customer to populate a RAG vector database (Milvus in our case) with content ingestion from the company’s Sharepoint/OneDrive repositories, which would then be using a LLM fitting the best of the customer’s requirement on watsonx.ai platform, for instance a Granite model. This article describes the code I prepare and test locally on my computer. This code will be adapted to be used on the customer’s platform, but as usual I like to do my research beforehand… (I’m a bit a geek I guess). Local Milvus Preparation In a previous article I wrote about the difficulties I encountered on setting-up a Milvus environment on my laptop, well I guess I finally found a very straightforward and simple way to do this. Hereafter are the steps. In order to do this you need either Docker, or in my case I use Podman. # fetch the startup script curl -sfL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus/master/scripts/standalone_embed.sh -o standalone_embed.sh The next step and all you have to do is to run the script, although I have made an alias on my laptop which makes alias docker=”podman”, for the simplification in this case, I replace all ‘sudo docker’ commands to ‘sudo podman’ un the downloaded ‘standalone_embed.sh’ file which I renamed. # the original call is 'bash standalone_embed.sh start' bash standalone_podman_embed.sh start And that’s it. Your Milvus instance should be up and running. But we’re going to be sure of it. Test Milvus database connection and prepare the main application As I write the application in Python, I prepare a virtual environment (a best practice I recommend to everyone which I learnt the hard way!

Ingesting data from OneDrive into Milvus in order to use with generative ai.
Introduction and motivation
In a recent project we help our customer to populate a RAG vector database (Milvus in our case) with content ingestion from the company’s Sharepoint/OneDrive repositories, which would then be using a LLM fitting the best of the customer’s requirement on watsonx.ai platform, for instance a Granite model.
This article describes the code I prepare and test locally on my computer. This code will be adapted to be used on the customer’s platform, but as usual I like to do my research beforehand… (I’m a bit a geek I guess).
Local Milvus Preparation
In a previous article I wrote about the difficulties I encountered on setting-up a Milvus environment on my laptop, well I guess I finally found a very straightforward and simple way to do this. Hereafter are the steps.
In order to do this you need either Docker, or in my case I use Podman.
# fetch the startup script
curl -sfL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus/master/scripts/standalone_embed.sh -o standalone_embed.sh
The next step and all you have to do is to run the script, although I have made an alias on my laptop which makes alias docker=”podman”, for the simplification in this case, I replace all ‘sudo docker’ commands to ‘sudo podman’ un the downloaded ‘standalone_embed.sh’ file which I renamed.
# the original call is 'bash standalone_embed.sh start'
bash standalone_podman_embed.sh start
And that’s it. Your Milvus instance should be up and running. But we’re going to be sure of it.
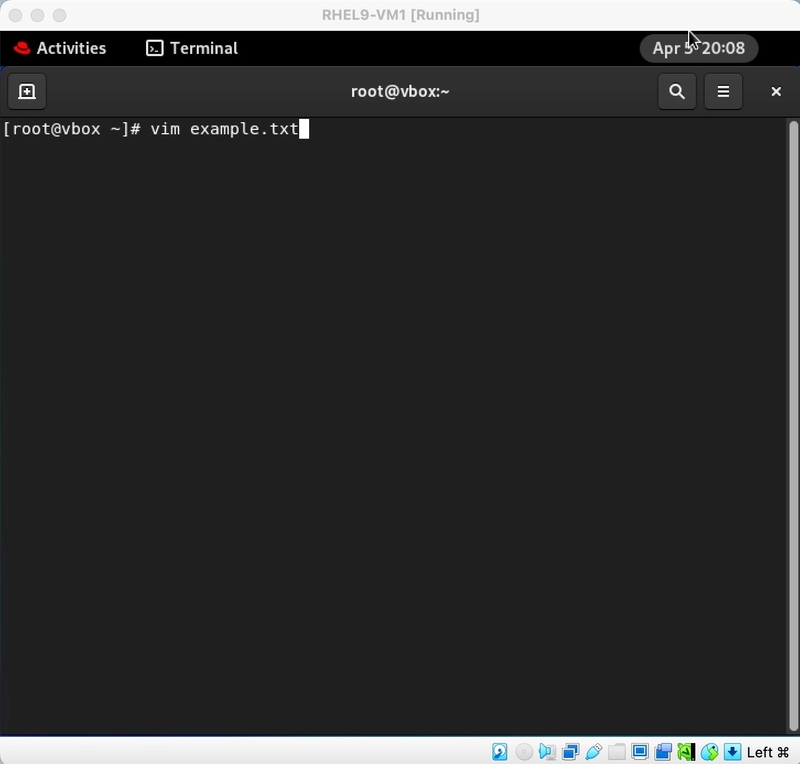
Test Milvus database connection and prepare the main application
As I write the application in Python, I prepare a virtual environment (a best practice I recommend to everyone which I learnt the hard way!












































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)


























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)








































































































.png?#)

































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
 (1).webp?#)





































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)