IGMP Snooping: A Comprehensive Networking Multicast Guide
In today’s interconnected world, efficient network management is a key component of delivering smooth user experiences and optimized bandwidth usage. IGMP Snooping is a network feature that helps manage multicast traffic effectively by reducing unnecessary flooding of multicast packets. Summary What is IGMP Snooping? IGMP Snooping identifies devices in multicast groups to optimize traffic delivery. It minimizes unnecessary multicast packet flooding by directing data to relevant devices. How IGMP Snooping Works: The switch monitors IGMP messages between hosts and routers. A multicast forwarding table is created, mapping ports to multicast group memberships. Multicast traffic is sent only to the necessary ports, preventing VLAN-wide flooding. What is IGMP Snooping? IGMP snooping (Internet Group Management Protocol Snooping) is a process used by switches to identify specific multicast groups—a set of devices that receive the same network traffic. By doing so, switches are able to forward packets to the right devices within a network in the most effective manner. IGMP is a network layer protocol that allows multiple devices to be configured with the same multicast IP address so that they all can receive the same data transmission. Devices use IGMP to join or leave multicast groups, which are identified by a single multicast IP address. Typically, network switches operate at Layer 2 and do not interpret Layer 3 protocols like IGMP. As such, they cannot naturally determine which devices belong to which multicast group. IGMP Snooping solves this issue by enabling switches to "listen in" on IGMP messages and dynamically update their internal multicast forwarding tables. Although not part of the IGMP protocol itself, IGMP Snooping is a widely supported feature on managed network switches. How IGMP Snooping Works When a multicast router sends multicast traffic, traditional switches would flood it across all ports within the VLAN. IGMP Snooping changes this behavior by allowing the switch to listen for IGMP messages exchanged between hosts and multicast routers. It then uses this information to construct a multicast forwarding table. Example Workflow: A host sends an IGMP membership report to join a multicast group. The switch records this report and updates its multicast table with the port for that group. When the multicast stream is sent, the switch forwards the traffic only to the port(s) with active members of that group. This targeted delivery minimizes bandwidth usage and eliminates unnecessary traffic across the network. Benefits of IGMP Snooping 1. Prevents Traffic Floods IGMP Snooping ensures that multicast traffic is only sent to the appropriate ports. This avoids the traditional flooding behavior and reduces unnecessary traffic on the network. 2. Makes Networks Faster By reducing bandwidth consumption, IGMP Snooping enhances overall network speed and responsiveness, particularly important for data-intensive applications like video conferencing and live streaming. 3. Optimized Bandwidth Utilization Multicast packets are sent only to devices that request them. This improves the network's efficiency and allows more bandwidth for other services. 4. Improved Security Restricting multicast traffic to relevant ports helps prevent sensitive data from being exposed to unintended recipients, reducing the risk of data leakage. 5. Prevention of Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks By controlling the spread of multicast traffic, IGMP Snooping minimizes the risk of multicast-based DoS attacks that attempt to overwhelm the network. 6. Enhanced Multicast Traffic Management Applications like IPTV and online gaming rely on real-time multicast traffic. IGMP Snooping ensures reliable, scalable delivery without overwhelming the network. IGMP Snooping Configurations 1. IGMP Snooping on VLANs In VLANs, multicast traffic is typically broadcast to all ports. IGMP Snooping allows the switch to forward traffic only to the ports with active members, optimizing VLAN efficiency. 2. Routed VLAN Interfaces (RVI) with IGMP Snooping When VLANs operate across Layer 2 and Layer 3 boundaries, RVIs help switches direct multicast traffic efficiently. The IGMP Snooping table ensures forwarding only to appropriate receivers. 3. Private VLANs (PVLANs) In complex VLAN setups involving isolated or community VLANs, IGMP Snooping still manages multicast traffic effectively, ensuring it only reaches intended recipients. IGMP Message Types Routers Send: General Queries: To discover all multicast listeners. Group-Specific Queries: To find members of a particular group. Group-and-Source-Specific Queries: (IGMPv3) To query for listeners to a group from specific sources. Hosts Respond With: Membership Reports:
In today’s interconnected world, efficient network management is a key component of delivering smooth user experiences and optimized bandwidth usage. IGMP Snooping is a network feature that helps manage multicast traffic effectively by reducing unnecessary flooding of multicast packets.
Summary
What is IGMP Snooping?
- IGMP Snooping identifies devices in multicast groups to optimize traffic delivery.
- It minimizes unnecessary multicast packet flooding by directing data to relevant devices.
How IGMP Snooping Works:
- The switch monitors IGMP messages between hosts and routers.
- A multicast forwarding table is created, mapping ports to multicast group memberships.
- Multicast traffic is sent only to the necessary ports, preventing VLAN-wide flooding.
What is IGMP Snooping?
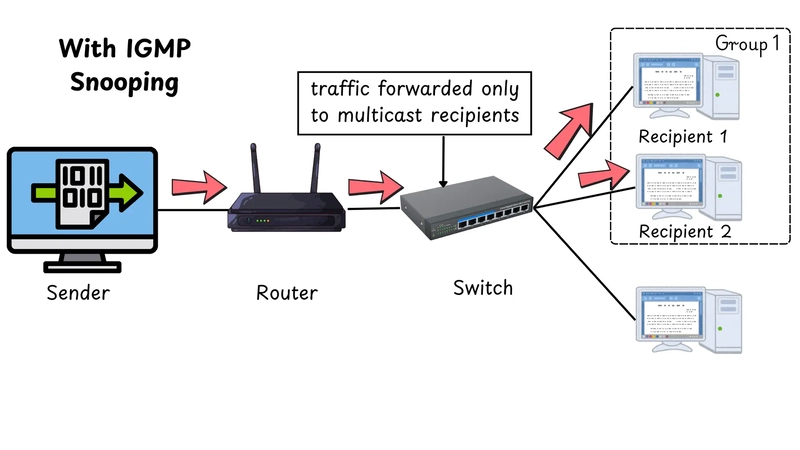
IGMP snooping (Internet Group Management Protocol Snooping) is a process used by switches to identify specific multicast groups—a set of devices that receive the same network traffic. By doing so, switches are able to forward packets to the right devices within a network in the most effective manner.
IGMP is a network layer protocol that allows multiple devices to be configured with the same multicast IP address so that they all can receive the same data transmission. Devices use IGMP to join or leave multicast groups, which are identified by a single multicast IP address.
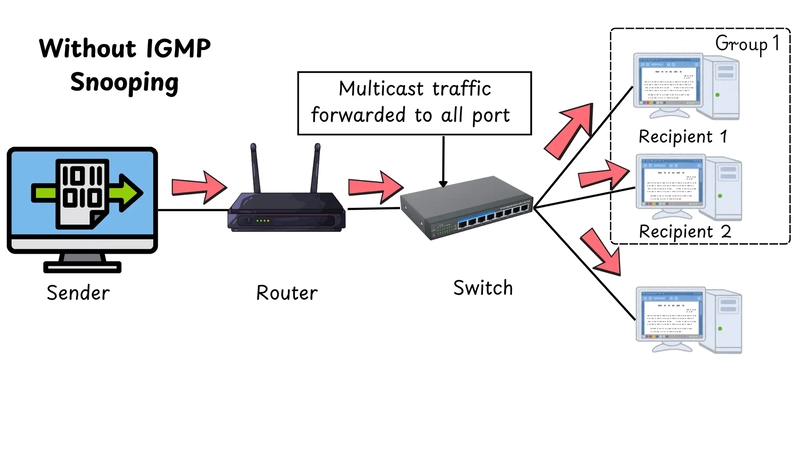
Typically, network switches operate at Layer 2 and do not interpret Layer 3 protocols like IGMP. As such, they cannot naturally determine which devices belong to which multicast group. IGMP Snooping solves this issue by enabling switches to "listen in" on IGMP messages and dynamically update their internal multicast forwarding tables. Although not part of the IGMP protocol itself, IGMP Snooping is a widely supported feature on managed network switches.
How IGMP Snooping Works
When a multicast router sends multicast traffic, traditional switches would flood it across all ports within the VLAN. IGMP Snooping changes this behavior by allowing the switch to listen for IGMP messages exchanged between hosts and multicast routers. It then uses this information to construct a multicast forwarding table.
Example Workflow:
- A host sends an IGMP membership report to join a multicast group.
- The switch records this report and updates its multicast table with the port for that group.
- When the multicast stream is sent, the switch forwards the traffic only to the port(s) with active members of that group.
This targeted delivery minimizes bandwidth usage and eliminates unnecessary traffic across the network.
Benefits of IGMP Snooping
1. Prevents Traffic Floods
IGMP Snooping ensures that multicast traffic is only sent to the appropriate ports. This avoids the traditional flooding behavior and reduces unnecessary traffic on the network.
2. Makes Networks Faster
By reducing bandwidth consumption, IGMP Snooping enhances overall network speed and responsiveness, particularly important for data-intensive applications like video conferencing and live streaming.
3. Optimized Bandwidth Utilization
Multicast packets are sent only to devices that request them. This improves the network's efficiency and allows more bandwidth for other services.
4. Improved Security
Restricting multicast traffic to relevant ports helps prevent sensitive data from being exposed to unintended recipients, reducing the risk of data leakage.
5. Prevention of Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
By controlling the spread of multicast traffic, IGMP Snooping minimizes the risk of multicast-based DoS attacks that attempt to overwhelm the network.
6. Enhanced Multicast Traffic Management
Applications like IPTV and online gaming rely on real-time multicast traffic. IGMP Snooping ensures reliable, scalable delivery without overwhelming the network.
IGMP Snooping Configurations
1. IGMP Snooping on VLANs
In VLANs, multicast traffic is typically broadcast to all ports. IGMP Snooping allows the switch to forward traffic only to the ports with active members, optimizing VLAN efficiency.
2. Routed VLAN Interfaces (RVI) with IGMP Snooping
When VLANs operate across Layer 2 and Layer 3 boundaries, RVIs help switches direct multicast traffic efficiently. The IGMP Snooping table ensures forwarding only to appropriate receivers.
3. Private VLANs (PVLANs)
In complex VLAN setups involving isolated or community VLANs, IGMP Snooping still manages multicast traffic effectively, ensuring it only reaches intended recipients.
IGMP Message Types
Routers Send:
- General Queries: To discover all multicast listeners.
- Group-Specific Queries: To find members of a particular group.
- Group-and-Source-Specific Queries: (IGMPv3) To query for listeners to a group from specific sources.
Hosts Respond With:
- Membership Reports: To join a multicast group.
- Leave Reports: To exit a group (used in IGMPv2 and IGMPv3).
How Hosts Join and Leave Multicast Groups
- Joining: Hosts either respond to general queries or send unsolicited membership reports.
- Leaving: Hosts send leave messages (in IGMPv2 and v3) or simply stop responding to queries (silent leave).
Using IGMP Querier for Layer 2 Networks
In environments lacking a multicast router, switches can elect an IGMP querier. This device sends out general queries to maintain updated membership information, ensuring multicast data is forwarded appropriately and doesn’t go undelivered.
Support for IGMP Versions
- IGMPv1: Basic membership reporting, no leave messages.
- IGMPv2: Adds explicit leave messages and group-specific queries.
- IGMPv3: Introduces source-specific multicast, allowing more granular control over which sources are accepted.
General Forwarding Rules with IGMP Snooping
- Forward IGMP general queries to all interfaces.
- Forward group-specific queries to only interested ports.
- Flood unregistered multicast packets to all router ports.
- Forward registered multicast traffic to member and router interfaces.
Best Practices for IGMP Snooping Configuration
- Enable IGMP Snooping: Use CLI or GUI on managed switches.
- Set IGMP Querier: Especially useful in Layer 2 networks.
- Tune Timers: Adjust query intervals and timeouts as needed.
- Monitor Activity: Regularly review the multicast table and traffic flows.
How Pinggy Can Assist in IGMP Snooping Testing and Validation
While IGMP Snooping improves multicast efficiency on internal networks, testing, validating, or demonstrating its behavior can be challenging—especially in isolated lab environments or networks without access to external multicast sources. This is where tools like Pinggy become functionally useful.
Pinggy enables developers and network engineers to expose local services or interfaces to the public internet using secure tunnels. In the context of multicast and IGMP Snooping, this capability provides several benefits:
1. Remote Monitoring of Multicast Tools
Multicast traffic analyzers and IGMP loggers can be exposed via Pinggy, allowing remote access to real-time multicast group data, switch behavior, and network performance without complex VPN setups.
2. Simulating External Multicast Clients
By routing traffic from external sources into the testbed, Pinggy enables simulations of remote clients joining or leaving multicast groups, providing valuable test scenarios for multicast routing behavior.
3. Facilitating Debugging in Hybrid Networks
For networks with a mix of physical and virtual components, Pinggy helps bridge the access gap, allowing developers to view packet flows and test IGMP behavior across different layers and devices.
4. Sharing Live Lab Results or Configurations
During collaborative troubleshooting or training, Pinggy allows engineers to share dashboards, CLI outputs, or logs securely and temporarily—improving cross-team productivity.
⚠ Note: Always ensure sensitive data is protected when exposing services. Pinggy is best used in controlled environments or with restricted access.
Conclusion
IGMP Snooping plays a crucial role in optimizing multicast traffic within modern networks. By ensuring multicast packets are only forwarded to relevant recipients, it enhances performance, conserves bandwidth, and improves network security. Whether configuring basic VLANs or deploying advanced multicast architectures involving PVLANs and queriers, IGMP Snooping helps ensure smooth, scalable, and efficient network operations.
Moreover, with tools like Pinggy, network professionals can gain deeper insight into multicast behavior, test configurations remotely, and validate system responses—making it an invaluable ally in developing robust and intelligent networking solutions.









































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)





























































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Learn to Code Certification Bundle (97% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)
![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)







































































































.png?#)




(1).jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)





























_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)
.webp?#)
.webp?#)










































































































![Apple Considers Delaying Smart Home Hub Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96946/96946/96946-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Pro Won't Feature Two-Toned Back [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96944/96944/96944-640.jpg)
![Tariffs Threaten Apple's $999 iPhone Price Point in the U.S. [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96943/96943/96943-640.jpg)