3Tier Web Application
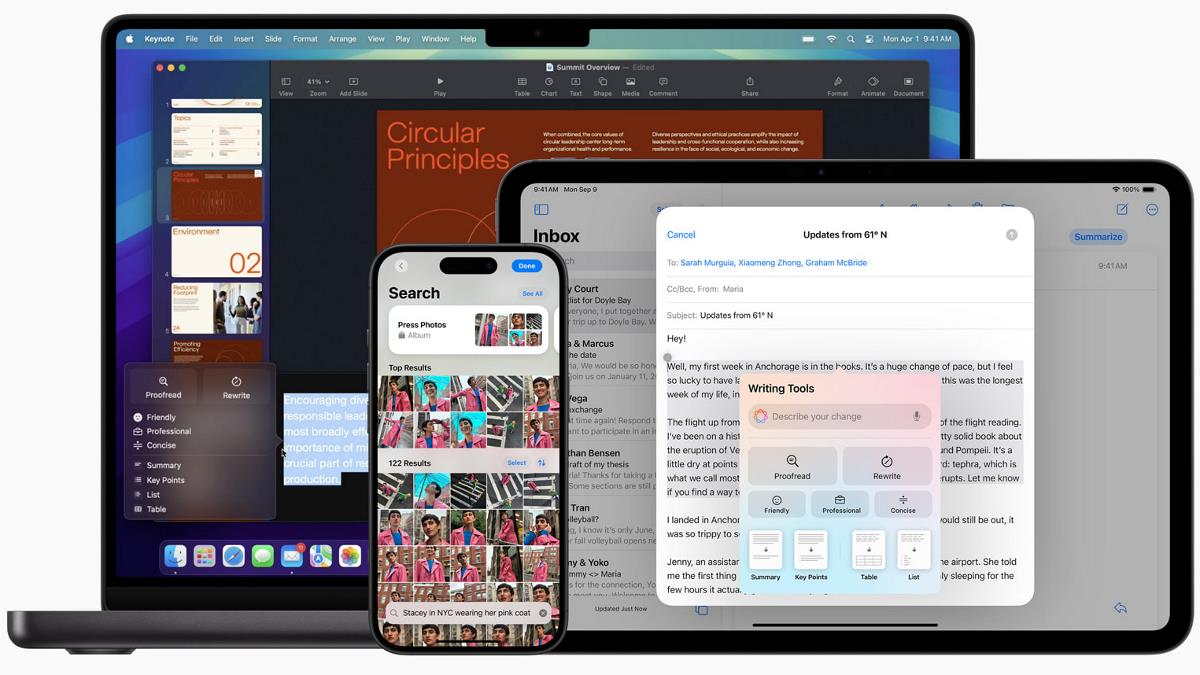
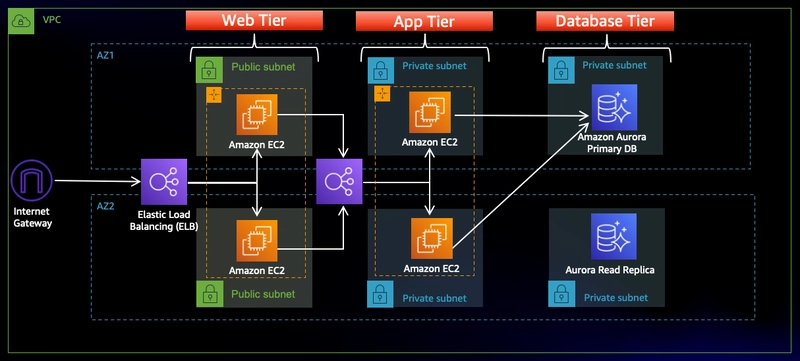
AWS Three-Tier Web Architecture: Comprehensive Setup Guide Architecture Overview ) The three-tier web architecture is a proven design pattern that separates an application into three logical tiers: Presentation Tier (Web Tier) Application Tier (App Tier) Data Tier (Database Tier) Key Components Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Subnets across multiple Availability Zones Internet Gateway NAT Gateway Security Groups Elastic Load Balancers EC2 Instances RDS Database S3 Bucket 1. Network Infrastructure Setup 1.1 VPC Configuration Create a VPC with CIDR block (e.g., 10.0.0.0/16) Enable DNS hostnames and support Use VPC Wizard or AWS Console "VPC and more" feature Subnet Strategy Public Subnets (Web Tier): For internet-facing resources Typically in different Availability Zones Associated with Internet Gateway Private Subnets (App and Database Tiers): For internal application and database resources Not directly accessible from the internet Routed through NAT Gateway 1.2 Internet and NAT Gateways Create an Internet Gateway and attach to VPC Create NAT Gateway in each public subnet Configure route tables to direct traffic appropriately 1.3 Security Groups Create distinct security groups for: Web Tier EC2 Instances Application Tier EC2 Instances Load Balancers RDS Database Best Practices Implement least privilege principle Only open necessary ports Restrict inbound and outbound traffic Sample Web Security Group 1.4 Route Table 2. Compute Resources 2.1 EC2 Instances and Roles Launch instances in private subnets Use Amazon Linux 2 or Amazon Linux 2023 Create IAM roles for SSM and S3 access Web Tier EC2 Hosts web server and frontend Placed in public subnet behind load balancer Application Tier EC2 Hosts backend application logic Placed in private subnet Communicates with database tier 3. Database Tier 3.1 RDS Configuration Use Amazon Aurora MySQL Multi-AZ deployment for high availability Create subnet group across multiple AZs Database Setup Steps Create subnet group Choose Dev/Test template Configure database insights Set up monitoring (optional) 3.2 Database Configuration -- Create database CREATE DATABASE webappdb; -- Create transactions table CREATE TABLE transactions ( id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, amount DECIMAL(10,2), description VARCHAR(100), PRIMARY KEY(id) ); -- Insert sample data INSERT INTO transactions (amount, description) VALUES (400, 'groceries'), (100, 'class'), (200, 'other groceries'), (10, 'brownies'); 4. Storage and Code Deployment 4.1 S3 Bucket Create S3 bucket for application code Use versioning and encryption Configure appropriate IAM policies 4.2 Code Deployment # Clone repository git clone https://github.com/Naveen3251/AWS_3Tier.git # Update database configuration # Edit app-tier/DbConfig.js with: # - RDS endpoint # - Database credentials # - Database name (webappdb) 5. Application Setup 5.1 Node.js Configuration # Install Node Version Manager (NVM) curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.38.0/install.sh | bash # Install Node.js nvm install 16 nvm use 16 # Install PM2 process manager npm install -g pm2 # Install application dependencies npm install # Start application pm2 start index.js pm2 startup pm2 save 5.2 Verification Endpoints Health Check: GET /health Transactions: GET /transaction 6. Internal Load Balancing and Auto Scaling Create Target Group: Create Load Balancer: Review Launch Template: Load Balancer: Update Config File Web Instance Deployment Configure Web Instance 7. Monitoring and Maintenance Enable AWS CloudWatch metrics Set up alarms for resource utilization Regularly update and patch instances Implement backup strategies Estimated Costs Monitor resources using AWS Cost Explorer Consider using AWS Budgets Leverage AWS Free Tier for learning
AWS Three-Tier Web Architecture: Comprehensive Setup Guide
Architecture Overview
The three-tier web architecture is a proven design pattern that separates an application into three logical tiers:
- Presentation Tier (Web Tier)
- Application Tier (App Tier)
- Data Tier (Database Tier)
Key Components
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
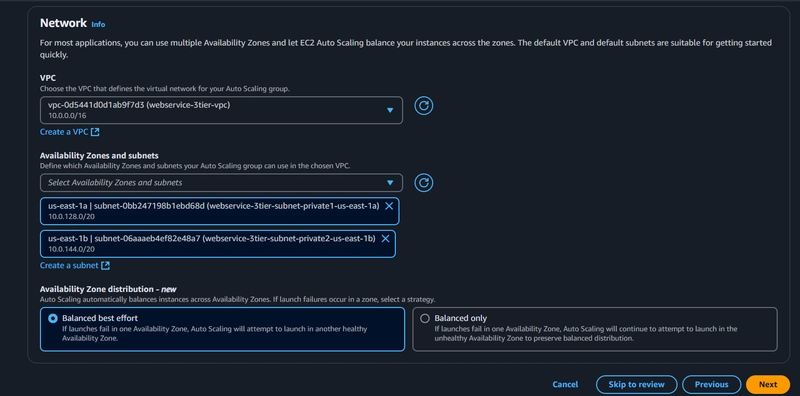
- Subnets across multiple Availability Zones
- Internet Gateway
- NAT Gateway
- Security Groups
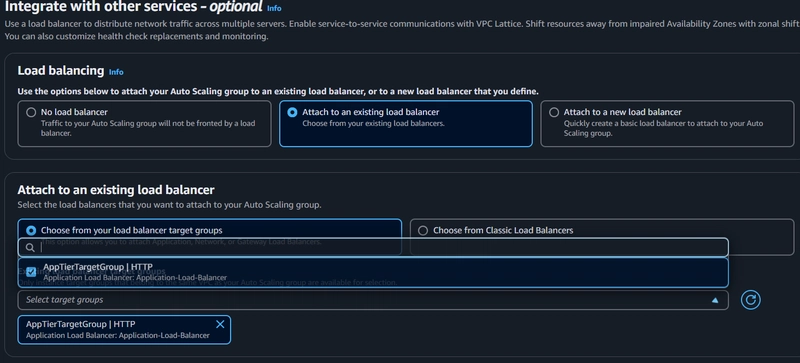
- Elastic Load Balancers
- EC2 Instances
- RDS Database
- S3 Bucket
1. Network Infrastructure Setup
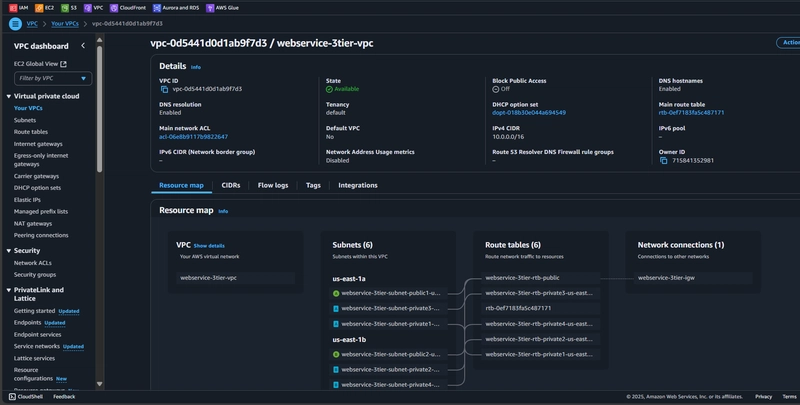
1.1 VPC Configuration
- Create a VPC with CIDR block (e.g., 10.0.0.0/16)
- Enable DNS hostnames and support
- Use VPC Wizard or AWS Console "VPC and more" feature
Subnet Strategy
-
Public Subnets (Web Tier):
- For internet-facing resources
- Typically in different Availability Zones
- Associated with Internet Gateway
-
Private Subnets (App and Database Tiers):
- For internal application and database resources
- Not directly accessible from the internet
- Routed through NAT Gateway
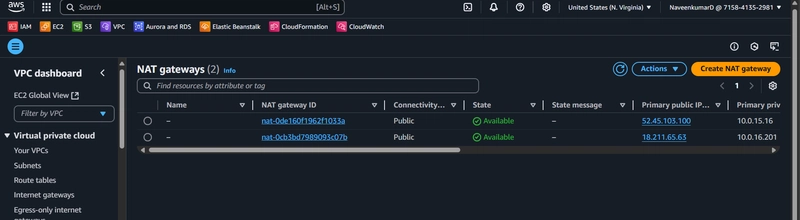
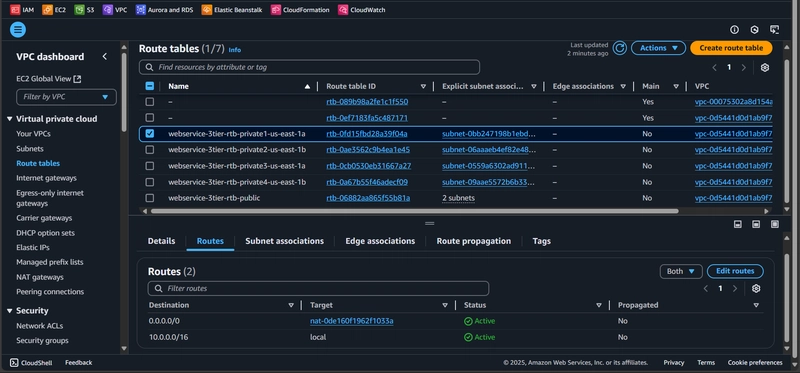
1.2 Internet and NAT Gateways
- Create an Internet Gateway and attach to VPC
- Create NAT Gateway in each public subnet
- Configure route tables to direct traffic appropriately
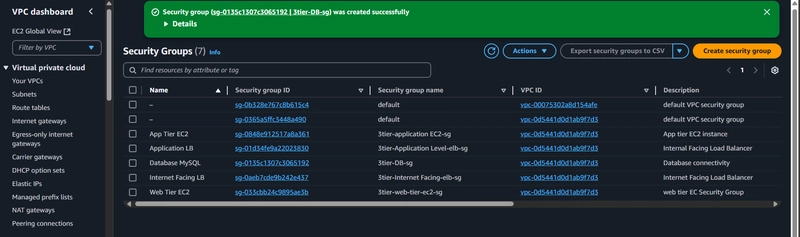
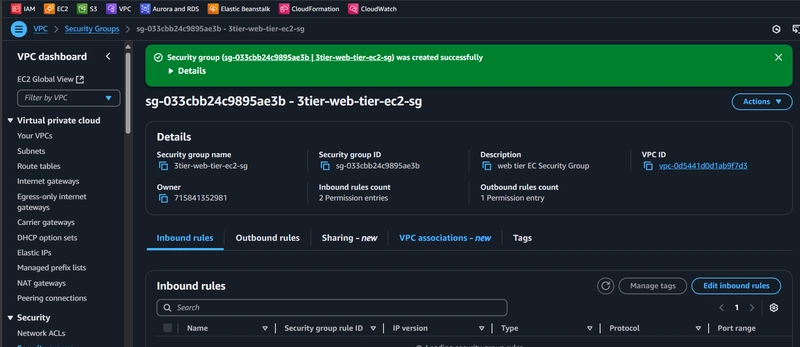
1.3 Security Groups
Create distinct security groups for:
- Web Tier EC2 Instances
- Application Tier EC2 Instances
- Load Balancers
- RDS Database
Best Practices
- Implement least privilege principle
- Only open necessary ports
- Restrict inbound and outbound traffic
Sample Web Security Group
1.4 Route Table
2. Compute Resources
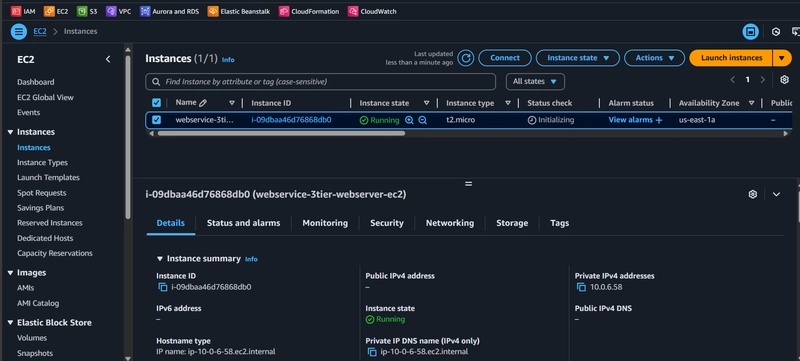
2.1 EC2 Instances and Roles
- Launch instances in private subnets
- Use Amazon Linux 2 or Amazon Linux 2023
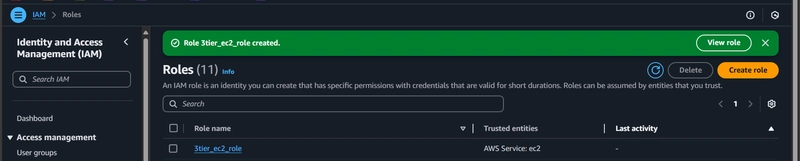
- Create IAM roles for SSM and S3 access
Web Tier EC2
- Hosts web server and frontend
- Placed in public subnet behind load balancer
Application Tier EC2
- Hosts backend application logic
- Placed in private subnet
- Communicates with database tier
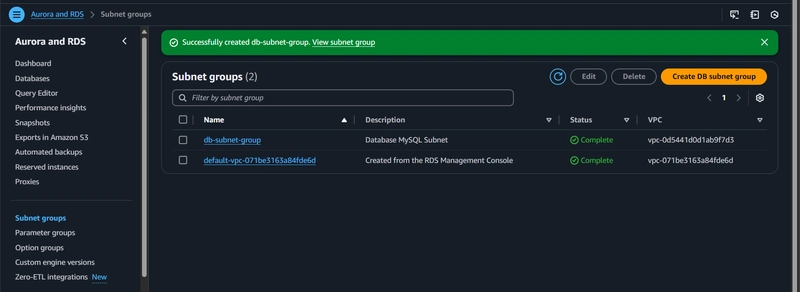
3. Database Tier
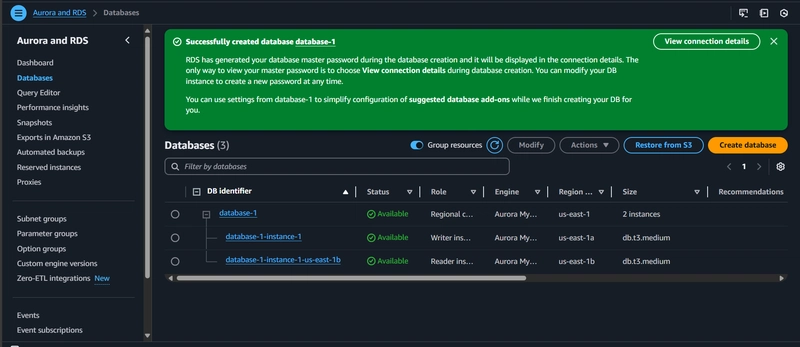
3.1 RDS Configuration
- Use Amazon Aurora MySQL
- Multi-AZ deployment for high availability
- Create subnet group across multiple AZs
Database Setup Steps
- Create subnet group
- Choose Dev/Test template
- Configure database insights
- Set up monitoring (optional)
3.2 Database Configuration
-- Create database
CREATE DATABASE webappdb;
-- Create transactions table
CREATE TABLE transactions (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
amount DECIMAL(10,2),
description VARCHAR(100),
PRIMARY KEY(id)
);
-- Insert sample data
INSERT INTO transactions (amount, description)
VALUES
(400, 'groceries'),
(100, 'class'),
(200, 'other groceries'),
(10, 'brownies');
4. Storage and Code Deployment
4.1 S3 Bucket
- Create S3 bucket for application code
- Use versioning and encryption
- Configure appropriate IAM policies
4.2 Code Deployment
# Clone repository
git clone https://github.com/Naveen3251/AWS_3Tier.git
# Update database configuration
# Edit app-tier/DbConfig.js with:
# - RDS endpoint
# - Database credentials
# - Database name (webappdb)
5. Application Setup
5.1 Node.js Configuration
# Install Node Version Manager (NVM)
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.38.0/install.sh | bash
# Install Node.js
nvm install 16
nvm use 16
# Install PM2 process manager
npm install -g pm2
# Install application dependencies
npm install
# Start application
pm2 start index.js
pm2 startup
pm2 save
5.2 Verification Endpoints
- Health Check:
GET /health - Transactions:
GET /transaction
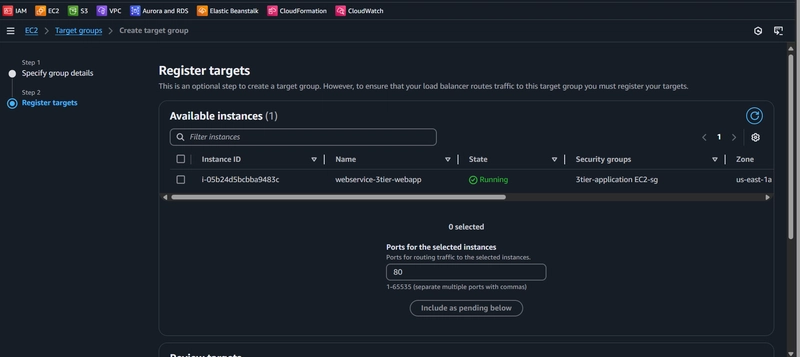
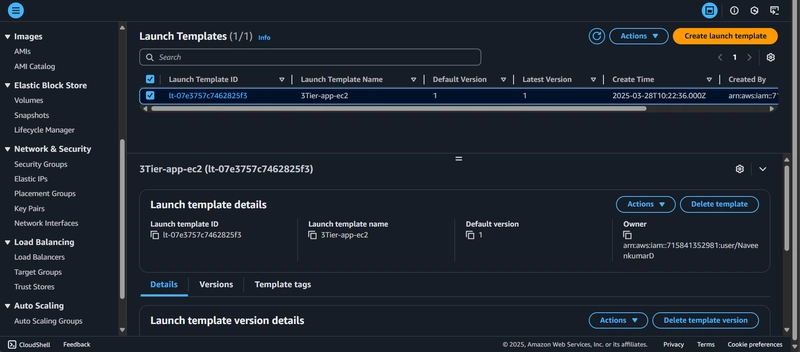
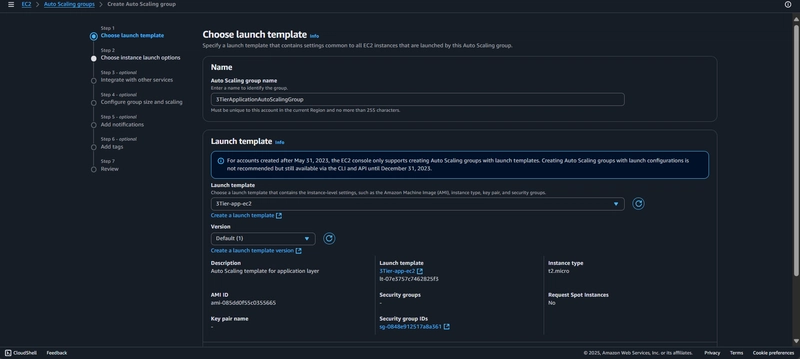
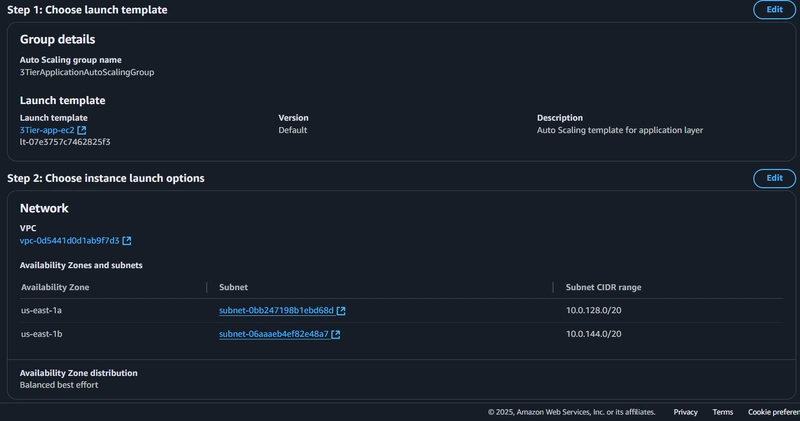
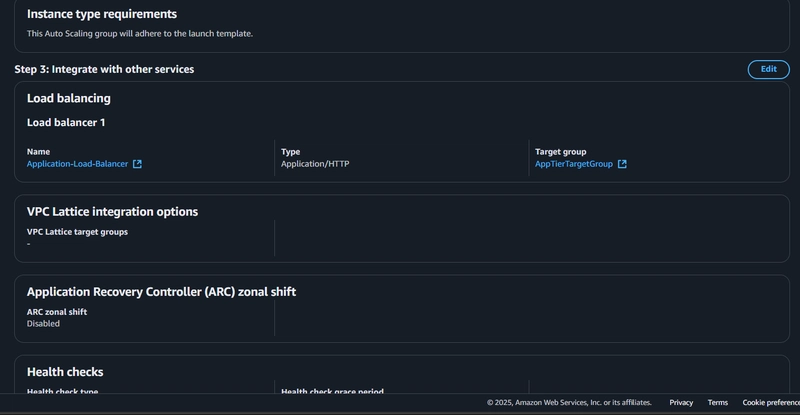
6. Internal Load Balancing and Auto Scaling
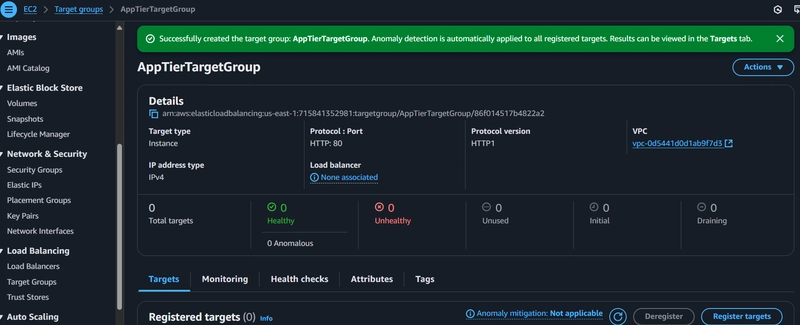
Create Target Group:
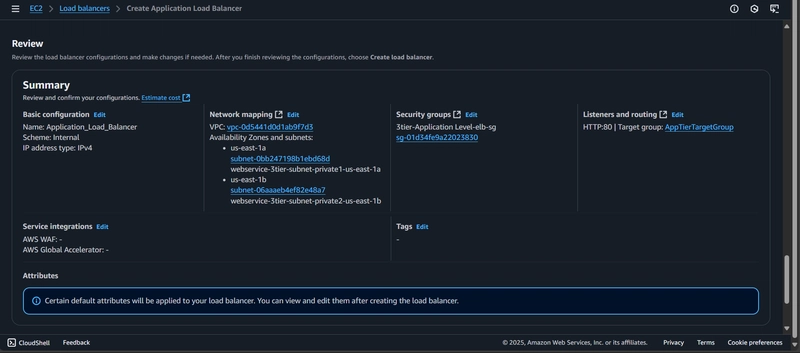
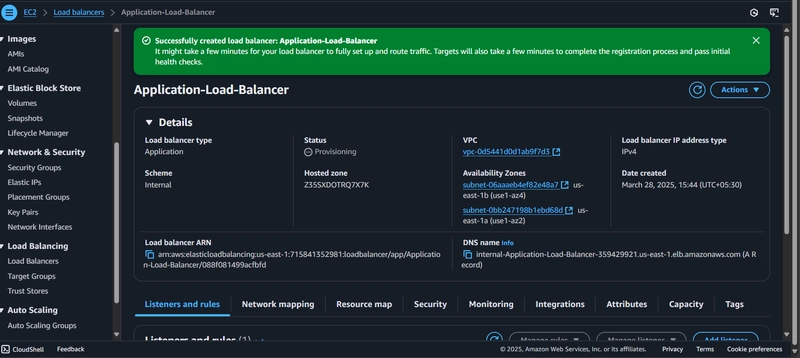
Create Load Balancer:
Review
Launch Template:
Update Config File
Web Instance Deployment
Configure Web Instance
7. Monitoring and Maintenance
- Enable AWS CloudWatch metrics
- Set up alarms for resource utilization
- Regularly update and patch instances
- Implement backup strategies
Estimated Costs
- Monitor resources using AWS Cost Explorer
- Consider using AWS Budgets
- Leverage AWS Free Tier for learning









































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)







































































































































































































![GrandChase tier list of the best characters available [April 2025]](https://media.pocketgamer.com/artwork/na-33057-1637756796/grandchase-ios-android-3rd-anniversary.jpg?#)






































































.webp?#)




























































































![Here’s everything new in Android 16 Beta 4 [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/11/Android-16-logo-top-down.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











![New Beats USB-C Charging Cables Now Available on Amazon [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97060/97060/97060-640.jpg)

![Apple M4 13-inch iPad Pro On Sale for $200 Off [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97056/97056/97056-640.jpg)