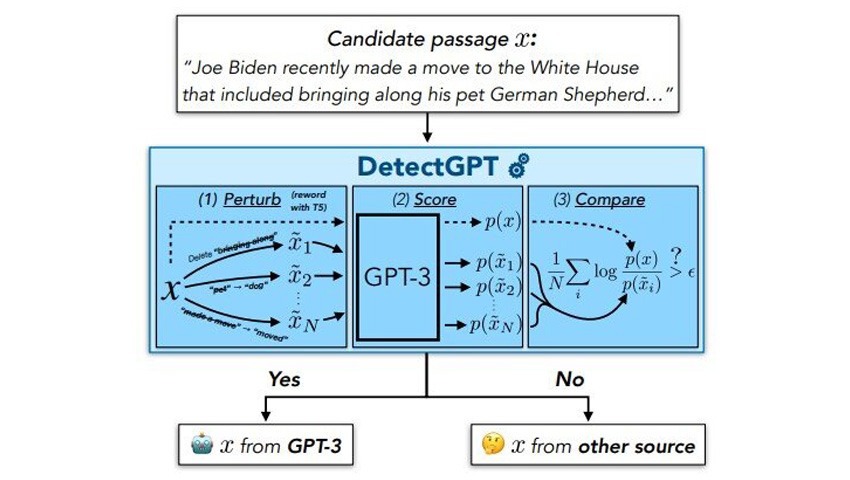
Revolutionizing Energy Markets: The Role of Blockchain in Energy Trading
Abstract: This post explores the transformative impact of blockchain technology on energy trading and renewable energy integration. By examining blockchain fundamentals, the evolution of energy markets, and real-world applications such as peer-to-peer trading and microgrids, we highlight how decentralization, transparency, and security are revolutionizing the energy sector. We also discuss challenges including scalability, regulatory hurdles, and data privacy concerns while forecasting future innovations powered by blockchain. Throughout, we reference authoritative sources and related projects, including cutting‐edge discussions on blockchain funding and open source initiatives. Introduction The global energy market is rapidly evolving, driven by the need to balance sustainability with efficiency. As renewable energy sources continue to gain traction, traditional centralized models are giving way to decentralized systems that ensure transparency, security, and lower costs. Blockchain, with its distributed ledger technology, is emerging as a powerful catalyst in this energy revolution. In this post, we delve into the role of blockchain in energy trading, explaining its core concepts, benefits, challenges, and the future outlook. For a deeper dive into this transformative technology, read the original article on revolutionizing energy markets. Background and Context Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. Its core advantage is decentralization—the removal of central authority ensures that no single party controls the data. This fosters trust among stakeholders, a critical element in high-stakes sectors like energy trading. Key Terms and Their Definitions Blockchain: A chronologically linked, decentralized ledger system that records transactions in a secure, immutable manner. Learn more about what is blockchain. Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts that automate processes like payment settlements and data verification; they help reduce transaction costs significantly. For more details, see smart contracts on blockchain. Decentralization: Eliminating a central authority in transactions, leading to a more resilient and secure infrastructure. Discover more about decentralization benefits. Historical Context Traditionally, energy markets relied on centralized infrastructures and intermediaries to manage transactions and grid operations. However, with the advent of blockchain, the industry is witnessing a paradigm shift where energy is traded in real time, using algorithms and smart contracts that ensure fairness and accuracy. Table 1. Evolution from Centralized to Decentralized Energy Systems Aspect Traditional Energy Market Blockchain-Enabled Energy Market Control Central authority (utilities) Decentralized control via peers Transaction Speed Slow and regulated Fast, real-time settlement Transparency Limited visibility Full visibility through immutable ledger Cost Efficiency High operational costs Reduced costs via smart contracts Security Vulnerable to central failures Enhanced security with cryptography Core Concepts and Features Blockchain introduces several core elements that revamp the energy trading model. Each feature contributes to more efficient, secure, and transparent energy markets. Decentralization and Trust Blockchain’s decentralized nature ensures that energy transactions do not depend on a single authority. This leads to: Trustless transactions where participants can trade without knowing or trusting one another. Increased transparency, as all transactions are recorded on a public ledger that cannot be tampered with. For further reading, check out insights on transparency and trust. Efficiency and Cost Reduction Smart contracts play a pivotal role by automating transaction processes. They help in: Reducing Transaction Costs: Automation cuts out intermediaries, lowering fees significantly. Explore more on reduced transaction costs. Enabling real-time energy pricing and settlement, which improves market responsiveness. Enhanced Security Blockchain’s robust cryptographic techniques secure data from malicious activities. Enhanced security features help protect critical energy data and trading records. More on this can be found at enhanced security. Renewable Energy Integration Blockchain facilitates the integration of renewable energy by: Simplifying the management of renewable energy certificates and carbon credits. Allowing peer-to-peer energy trading that incentivizes the use of green energy. For instance, projects like LO3 Energy and Power Ledger enable peer-to-peer energy trading. Bullet List: Key Blockchain Benefits in Energy Trading Decentralization: Eliminates the need for central authorities. Transparency: Offers clear, immutable records. Efficiency: Automates processes via s

Abstract:
This post explores the transformative impact of blockchain technology on energy trading and renewable energy integration. By examining blockchain fundamentals, the evolution of energy markets, and real-world applications such as peer-to-peer trading and microgrids, we highlight how decentralization, transparency, and security are revolutionizing the energy sector. We also discuss challenges including scalability, regulatory hurdles, and data privacy concerns while forecasting future innovations powered by blockchain. Throughout, we reference authoritative sources and related projects, including cutting‐edge discussions on blockchain funding and open source initiatives.
Introduction
The global energy market is rapidly evolving, driven by the need to balance sustainability with efficiency. As renewable energy sources continue to gain traction, traditional centralized models are giving way to decentralized systems that ensure transparency, security, and lower costs. Blockchain, with its distributed ledger technology, is emerging as a powerful catalyst in this energy revolution. In this post, we delve into the role of blockchain in energy trading, explaining its core concepts, benefits, challenges, and the future outlook. For a deeper dive into this transformative technology, read the original article on revolutionizing energy markets.
Background and Context
Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. Its core advantage is decentralization—the removal of central authority ensures that no single party controls the data. This fosters trust among stakeholders, a critical element in high-stakes sectors like energy trading.
Key Terms and Their Definitions
- Blockchain: A chronologically linked, decentralized ledger system that records transactions in a secure, immutable manner. Learn more about what is blockchain.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts that automate processes like payment settlements and data verification; they help reduce transaction costs significantly. For more details, see smart contracts on blockchain.
- Decentralization: Eliminating a central authority in transactions, leading to a more resilient and secure infrastructure. Discover more about decentralization benefits.
Historical Context
Traditionally, energy markets relied on centralized infrastructures and intermediaries to manage transactions and grid operations. However, with the advent of blockchain, the industry is witnessing a paradigm shift where energy is traded in real time, using algorithms and smart contracts that ensure fairness and accuracy.
Table 1. Evolution from Centralized to Decentralized Energy Systems
| Aspect | Traditional Energy Market | Blockchain-Enabled Energy Market |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Central authority (utilities) | Decentralized control via peers |
| Transaction Speed | Slow and regulated | Fast, real-time settlement |
| Transparency | Limited visibility | Full visibility through immutable ledger |
| Cost Efficiency | High operational costs | Reduced costs via smart contracts |
| Security | Vulnerable to central failures | Enhanced security with cryptography |
Core Concepts and Features
Blockchain introduces several core elements that revamp the energy trading model. Each feature contributes to more efficient, secure, and transparent energy markets.
Decentralization and Trust
Blockchain’s decentralized nature ensures that energy transactions do not depend on a single authority. This leads to:
- Trustless transactions where participants can trade without knowing or trusting one another.
- Increased transparency, as all transactions are recorded on a public ledger that cannot be tampered with.
For further reading, check out insights on transparency and trust.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Smart contracts play a pivotal role by automating transaction processes. They help in:
- Reducing Transaction Costs: Automation cuts out intermediaries, lowering fees significantly. Explore more on reduced transaction costs.
- Enabling real-time energy pricing and settlement, which improves market responsiveness.
Enhanced Security
Blockchain’s robust cryptographic techniques secure data from malicious activities. Enhanced security features help protect critical energy data and trading records. More on this can be found at enhanced security.
Renewable Energy Integration
Blockchain facilitates the integration of renewable energy by:
- Simplifying the management of renewable energy certificates and carbon credits.
- Allowing peer-to-peer energy trading that incentivizes the use of green energy. For instance, projects like LO3 Energy and Power Ledger enable peer-to-peer energy trading.
Bullet List: Key Blockchain Benefits in Energy Trading
- Decentralization: Eliminates the need for central authorities.
- Transparency: Offers clear, immutable records.
- Efficiency: Automates processes via smart contracts.
- Cost Reduction: Cuts out intermediaries, reducing fees.
- Enhanced Security: Utilizes cryptography to secure data.
- Renewable Energy Support: Enables better management of green energy resources.
Applications and Use Cases
Blockchain finds various practical applications in energy trading. Some notable examples include:
1. Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading
Platforms such as LO3 Energy and Power Ledger allow consumers and producers to trade surplus energy directly, bypassing traditional intermediaries. This model:
- Lowers costs by cutting middlemen.
- Empowers consumers with more control over their energy sources.
- Increases market efficiency and demand response.
2. Microgrids and Distributed Energy Resources
Blockchain technology enables the efficient management of microgrids—local energy systems that operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. Benefits include:
- Real-time balancing of supply and demand.
- Improved grid stability and reduced blackout risks.
- Better integration of renewable energy sources.
Learn more about microgrids at blockchain and microgrids.
3. Real-time Energy Pricing and Grid Management
Blockchain can also support the implementation of dynamic pricing models. By enabling real-time energy pricing, blockchain helps:
- Reflect immediate changes in energy supply and demand.
- Enhance grid management and load balancing.
- Incentivize energy saving during peak hours.
Read more about real-time pricing and improved grid management.
Table 2. Comparative Overview of Use Cases
| Use Case | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Peer-to-Peer Trading | Direct energy exchange without intermediaries | Cost reduction, Consumer empowerment, Increased efficiency |
| Microgrids | Localized energy management | Real-time load balancing, Enhanced grid stability |
| Real-time Pricing | Dynamic pricing using smart contracts | Market responsiveness, Incentivized energy saving |
Challenges and Limitations
While blockchain offers significant benefits, several challenges need addressing:
Scalability and Interoperability
- Scalability: As energy trading volumes increase, blockchain networks may face scalability issues that hinder performance. This challenge is addressed in discussions on scalability challenges.
- Interoperability: Integrating blockchain with existing legacy systems and diverse energy infrastructures can prove complex. Compatibility with current systems requires standardization.
Regulatory and Market Acceptance Hurdles
- Regulatory Constraints: Regulatory frameworks often lag behind technological advancements. Navigating legal and compliance issues is critical, as analyzed in regulatory challenges.
- Market Acceptance: The energy sector’s traditionally conservative nature may slow adoption. Educating stakeholders and demonstrating cost-benefit advantages are necessary to foster market uptake.
Data Privacy
Energy transactions involve sensitive data. Safeguarding privacy without compromising transparency poses a significant challenge. Detailed discussions on these concerns can be found here and blockchain privacy.
Additional Insights from the Dev Community:
The open source and developer community actively discuss related issues, including funding models and licensing innovations. For instance:
- Blockchain for Open Source Funding: A New Paradigm explores how blockchain is reshaping funding.
- Scaling Ethereum with Arbitrum offers insights on scalability solutions that are applicable to energy markets.
- Understanding GitHub Sponsors Fueling Open Source Development further elucidates community-driven funding mechanisms that can be paralleled in blockchain deployments.
Future Outlook and Innovations
The future of blockchain in energy trading is highly promising. Several technological and regulatory trends are expected to shape this landscape:
Technological Advancements
- Layer-2 Scaling Solutions: Emerging technologies are working to overcome blockchain’s scalability issues, ensuring faster transactions and higher throughput.
- Advanced Smart Contract Functionality: Future smart contracts could offer even more robust automation, handling complex trading and settlement scenarios.
- Integration with IoT: The fusion of blockchain with Internet of Things (IoT) devices will streamline data collection and real-time monitoring of energy grids.
Policy and Regulatory Evolution
As regulators become more familiar with blockchain, policy frameworks are expected to:
- Encourage pilot projects that demonstrate blockchain’s capabilities.
- Establish standards for interoperability and data privacy.
- Provide incentives for renewable energy integration, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Environmental Impact and Sustainable Practices
Blockchain can drive sustainable energy practices by:
- Enhancing transparency in carbon credits and renewable certifications.
- Facilitating global trading in renewable energy certificates.
- Empowering communities to manage local, sustainable energy resources.
For a detailed discussion on future trends, check out future outlook and insights on the future of open source with blockchain integration.
Summary
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing energy markets through decentralization, transparency, enhanced security, and cost efficiency. The transition from centralized control to distributed networks offers compelling benefits for peer-to-peer energy trading, microgrid management, and real-time pricing models. However, challenges such as scalability, regulatory compliance, and data privacy need continuous innovation and collaborative efforts among stakeholders.
Key points include:
- Blockchain Fundamentals: Its distributed ledger provides unprecedented trust and transparency.
- Practical Applications: Peer-to-peer trading and microgrids lead the way for consumer empowerment.
- Challenges: Scalability, regulatory constraints, interoperability, and privacy concerns must be addressed.
- Future Trends: Innovations in layer-2 scaling, IoT integration, and supportive policy frameworks will further drive transformation.
For more comprehensive insights, revisit the original article on blockchain and energy trading and explore additional topics such as blockchain and renewable energy.
Embracing blockchain in the energy sector is not just a technological upgrade—it is a vital step toward a sustainable, secure, and efficient global energy future.
By integrating advanced technologies and engaging community-driven innovations, the energy markets are on a transformative path. As blockchain continues to evolve and address its challenges, its role in reshaping how energy is traded and managed will undoubtedly expand, paving the way for a greener, more decentralized future.
Feel free to explore additional resources and discussions:
- Understanding Blockchain Technology
- The Evolution of Energy Markets
- Facilitation of Renewable Energy Integration
Stay tuned for more updates on how technology continues to revolutionize our world!

































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 143]: ChatGPT Revenue Surge, New AGI Timelines, Amazon’s AI Agent, Claude for Education, Model Context Protocol & LLMs Pass the Turing Test](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20143%20cover.png)




























































































































![[DEALS] Koofr Cloud Storage: Lifetime Subscription (1TB) (80% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


















































































































-RTAガチ勢がSwitch2体験会でゼルダのラスボスを撃破して世界初のEDを流してしまう...【ゼルダの伝説ブレスオブザワイルドSwitch2-Edition】-00-06-05.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)




















_roibu_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)













































































































![M4 MacBook Air Drops to Just $849 - Act Fast! [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97140/97140/97140-640.jpg)
![Apple Smart Glasses Not Close to Being Ready as Meta Targets 2025 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97139/97139/97139-640.jpg)
![iPadOS 19 May Introduce Menu Bar, iOS 19 to Support External Displays [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97137/97137/97137-640.jpg)